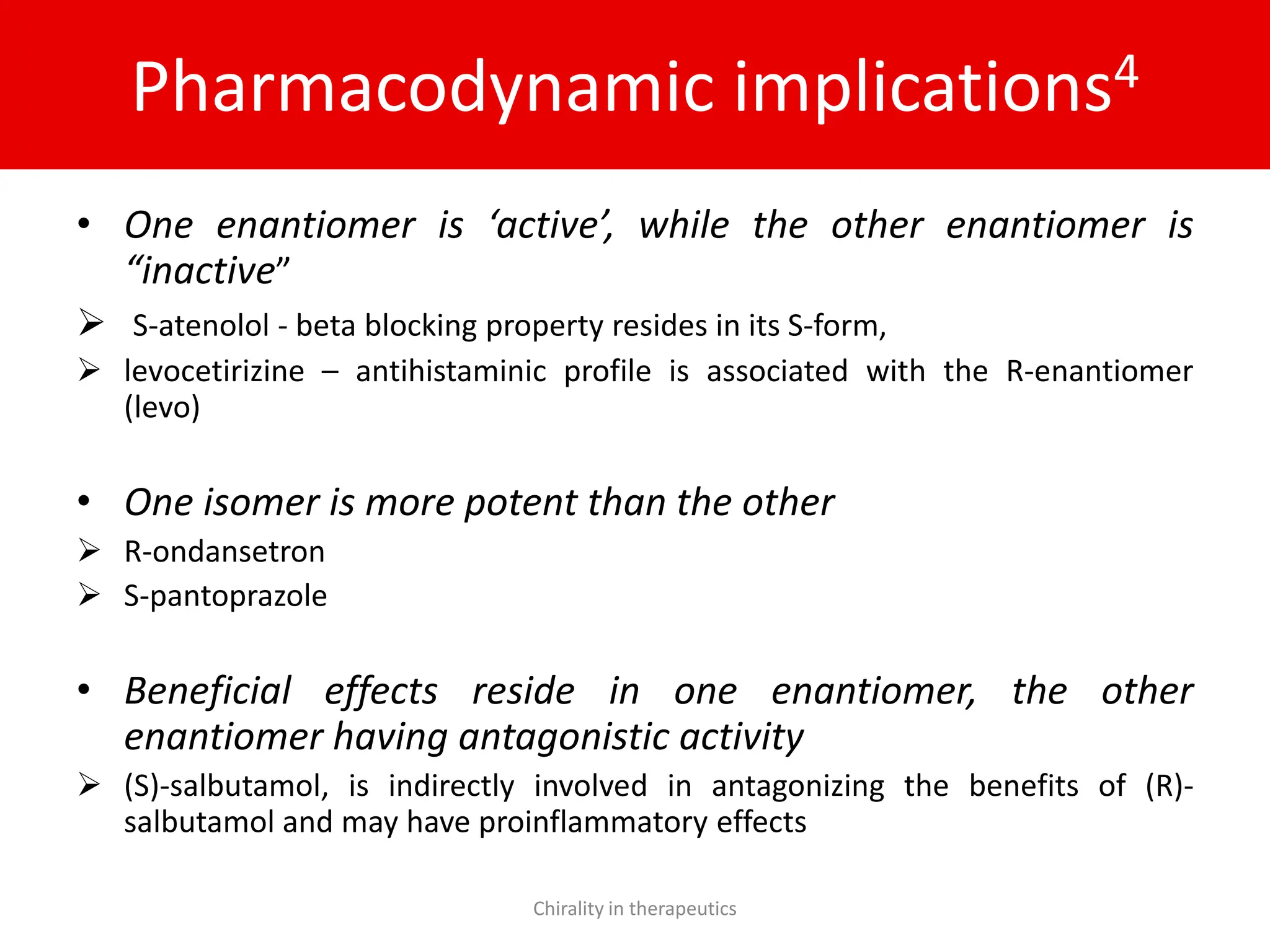
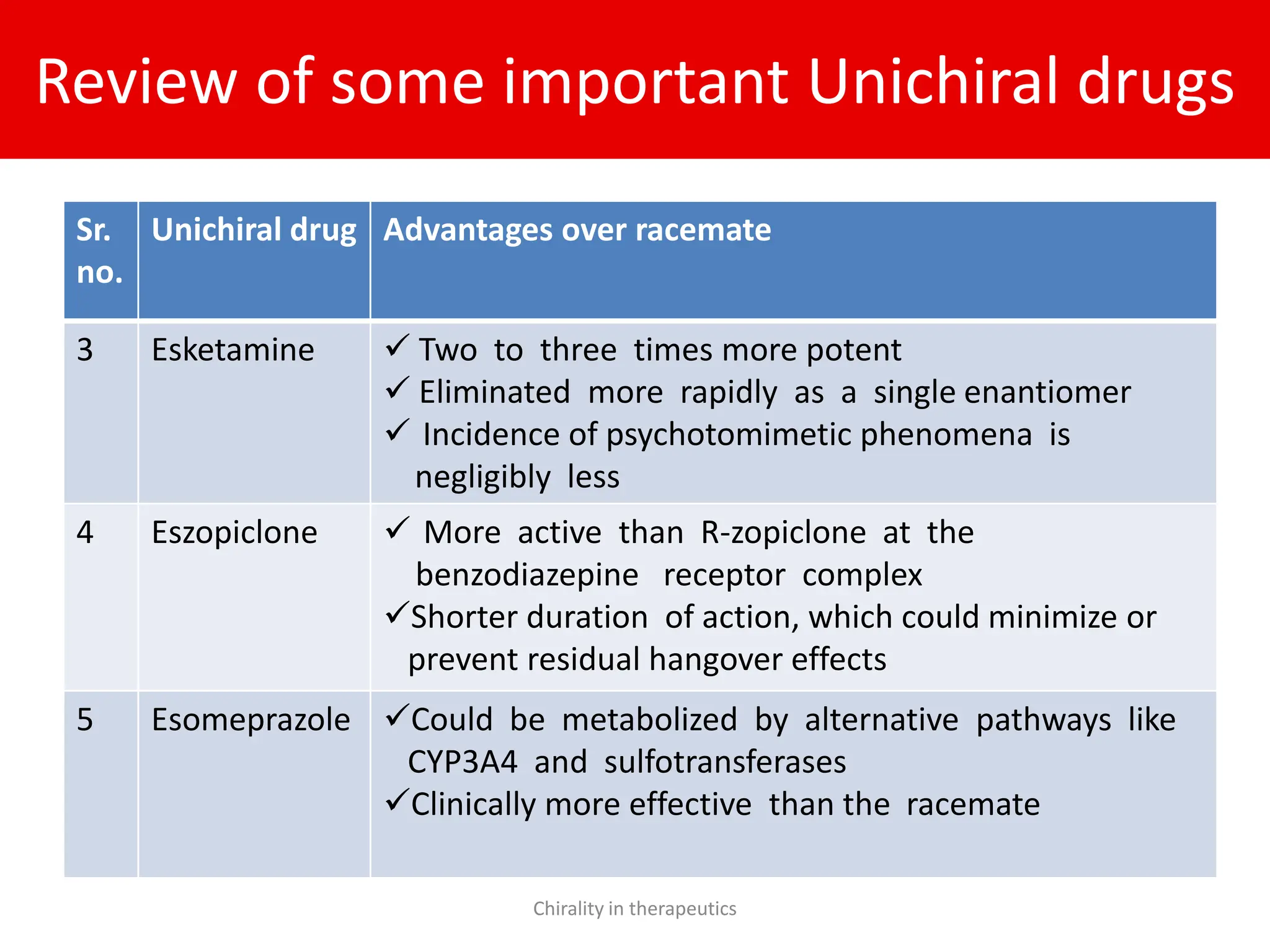
Chirality plays a crucial role in pharmaceuticals, with 56% of currently used drugs being chiral and significant differences in biological activities observed between enantiomers. The document outlines the chemical properties of chiral molecules, their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic implications, and the advantages of using single enantiomers over racemates. It emphasizes the trend towards developing chiral drugs to enhance therapeutic outcomes while minimizing side effects and drug interactions.