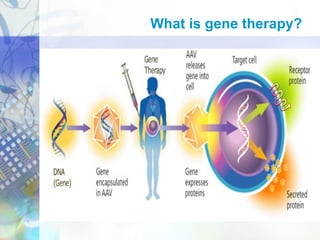
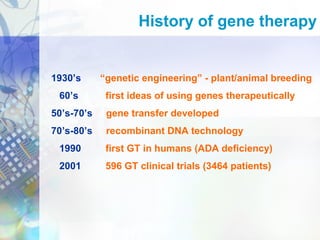
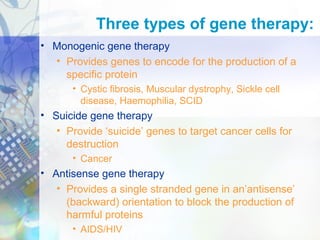
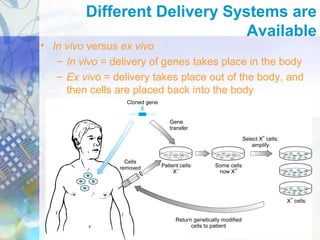
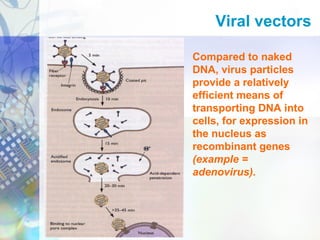
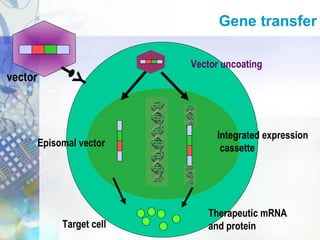
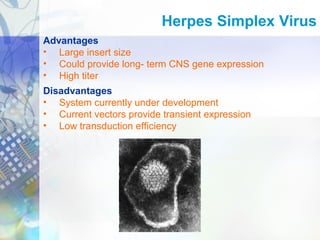
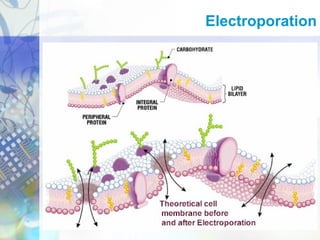
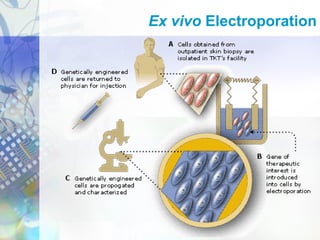
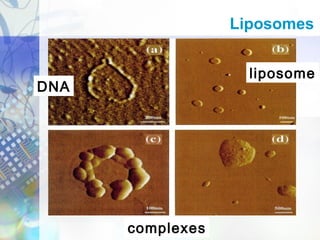
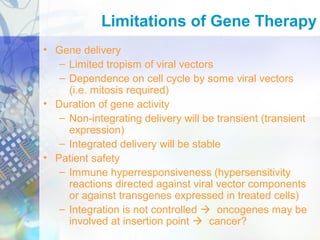
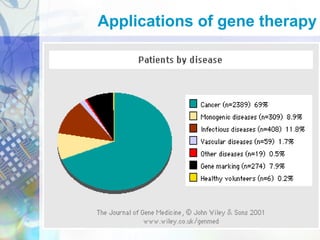
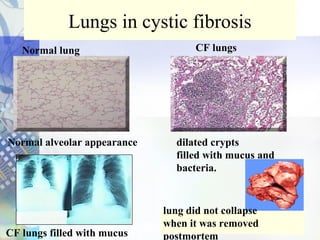
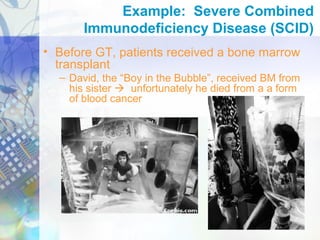
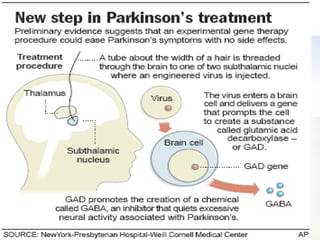
Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to treat disease. It is used for inherited disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases. Viruses are commonly used as vectors to deliver therapeutic genes, though safety issues exist. Some early successes included treating severe combined immunodeficiency using retroviruses to deliver the ADA gene ex vivo. However, the first death in gene therapy occurred treating ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency using an adenovirus vector, highlighting the risks. Improved delivery methods like liposomes may help overcome current limitations and advance this promising approach.