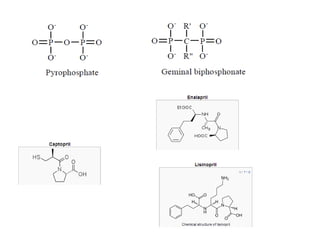
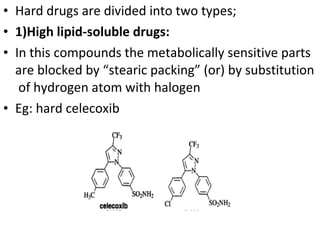
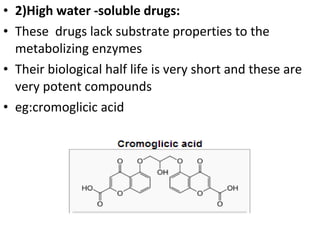
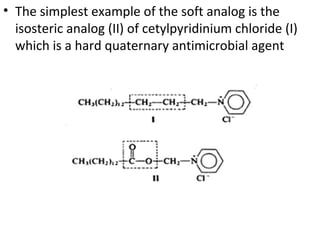
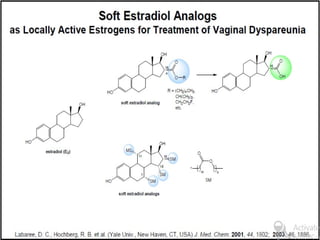
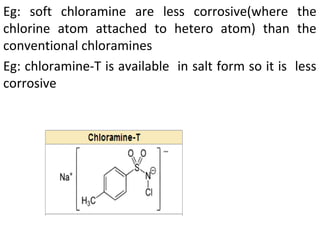
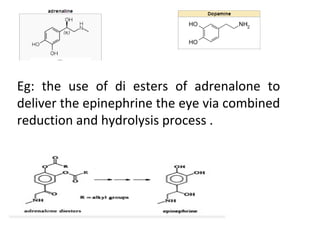
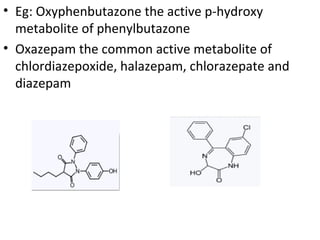
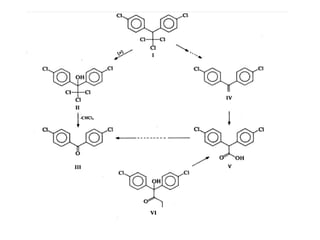
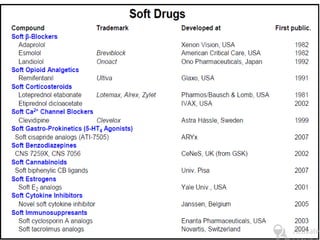
This document discusses hard and soft drugs. Hard drugs are biologically active and non-metabolizable, while soft drugs are designed to have predictable and controllable metabolism into nontoxic products after their therapeutic effect. Soft drugs have advantages like avoiding toxic metabolites and increasing the therapeutic index. They are divided into categories like soft analogs, activated soft compounds, natural soft drugs, and those based on active or inactive metabolite approaches. The document provides examples to illustrate differences between hard drugs, soft drugs, and prodrugs.