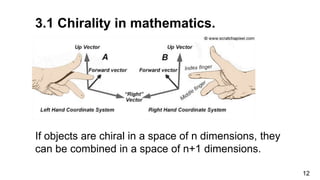
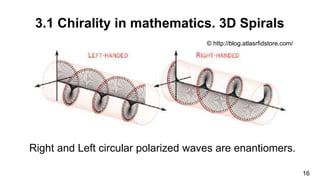
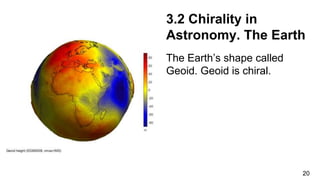
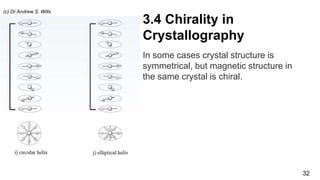
1. The document discusses chirality, or handedness, and how it appears in various areas of science including mathematics, astronomy, chemistry, biology, and crystallography.
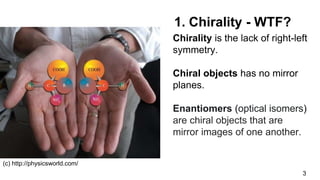
2. Chirality is the lack of mirror symmetry and occurs when objects are non-superimposable on their mirror image. Enantiomers, which are mirror images of each other, are examples of chiral objects.
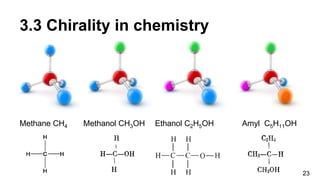
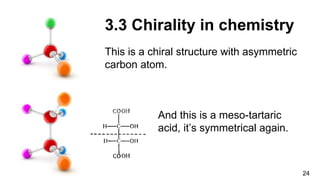
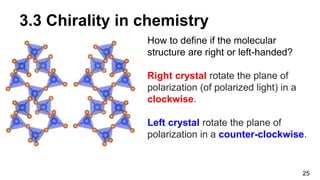
3. Chirality is present in many everyday objects like hands and shoes, as well as phenomena like spiral galaxies and hurricanes. In science, chirality appears in areas like amino acids, sugars, crystals, and molecular structures with asymmetric carbon atoms.