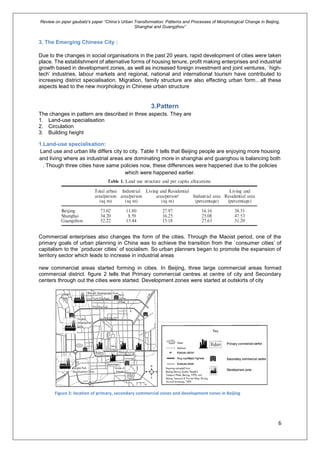
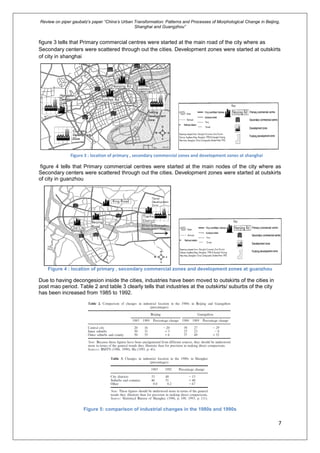
Piper Gaubatz's paper examines the urban transformation in China, focusing on the morphological changes in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou since the economic reforms of 1979. It analyzes the evolution of urban forms, land-use specialization, circulation, and the impact of rapid urbanization on city planning and social structures. The research highlights the differences in urban experiences across regions and addresses key historical contexts from pre-Mao to contemporary urban developments.