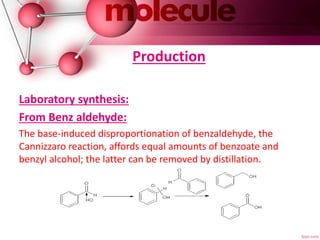
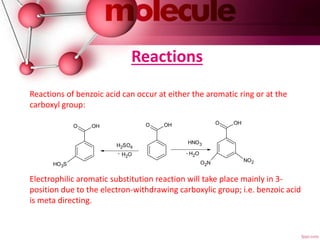
Benzoic acid is a colorless crystalline solid that occurs naturally in many plants. It can be produced commercially through the partial oxidation of toluene or synthesized in the laboratory through various methods like the hydrolysis of benzonitrile. Its main use is in the production of phenol, and it is also used to make plasticizers and in some medicinal ointments. Benzoic acid is metabolized in the body and excreted as hippuric acid in urine. Reactions can occur on the aromatic ring or carboxyl group, with electrophilic aromatic substitutions favoring the meta position.






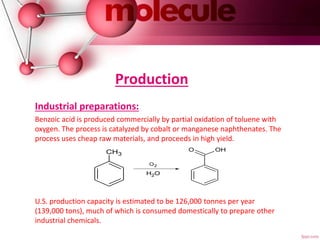

![Production
Laboratory synthesis:
1. By hydrolysis:
Like other nitriles and amides, benzonitrile and benzamide
can be hydrolyzed to benzoic acid or its conjugate base in
acid or basic conditions.
2 From benzyl chloride:
Benzoic acid can be prepared by oxidation of benzyl
chloride in the presence of alkaline KMnO4:
C6H5CH2Cl + 2 KOH + 2 [O] → C6H5COOH + KCl + H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bnzoicacidppt-170220085453/85/Bnzoic-acid-ppt-9-320.jpg)