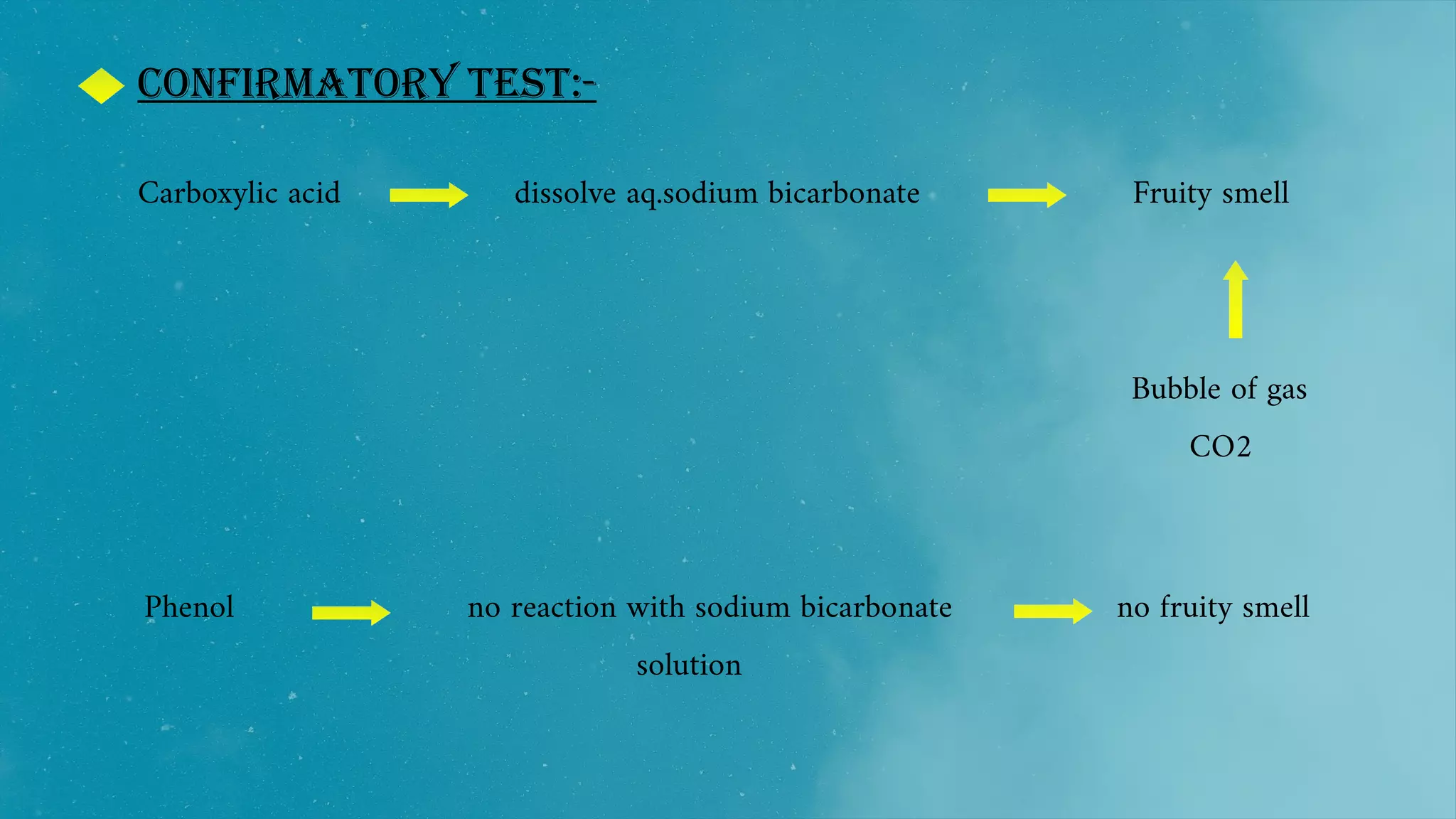
This document provides information about qualitative tests for phenols. It describes 3 common tests:
1) The ferric chloride test, where most phenols form dark colored complexes with ferric chloride.
2) Libermann's test, where phenols react to form colored compounds like indophenol which are identified.
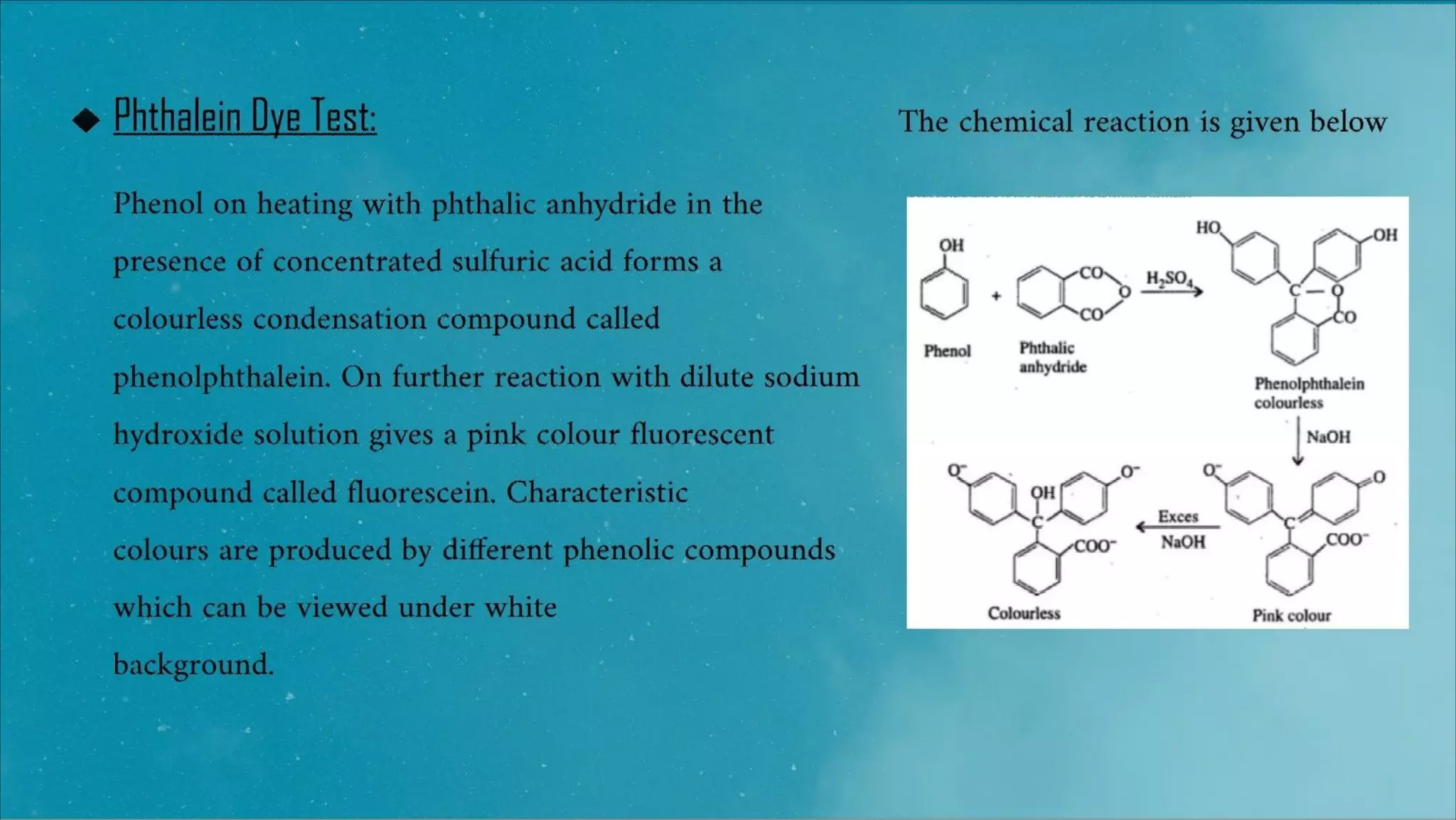
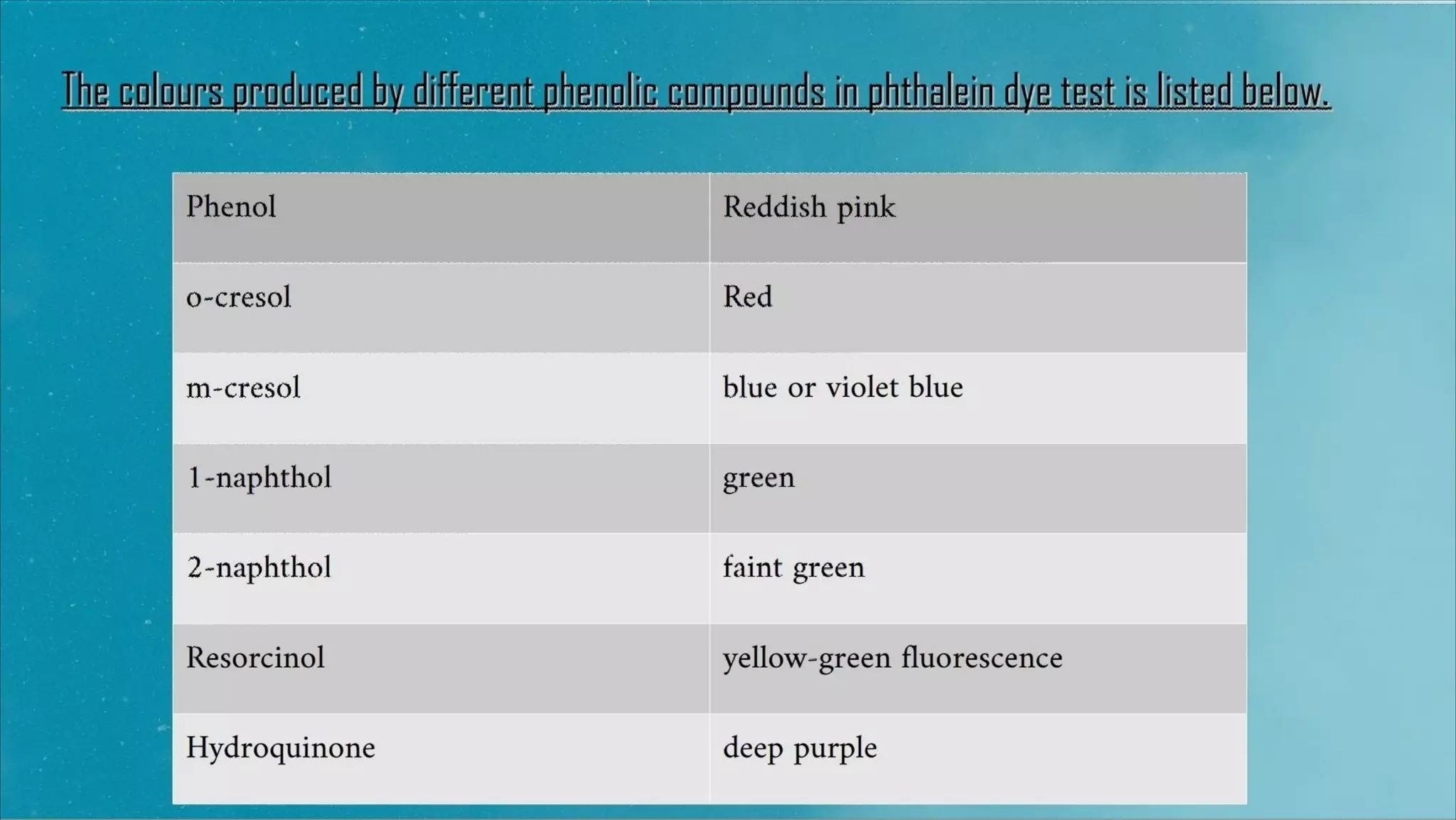
3) The phthalein dye test, where phenols condense to form phenolphthalein which produces a pink color in sodium hydroxide.
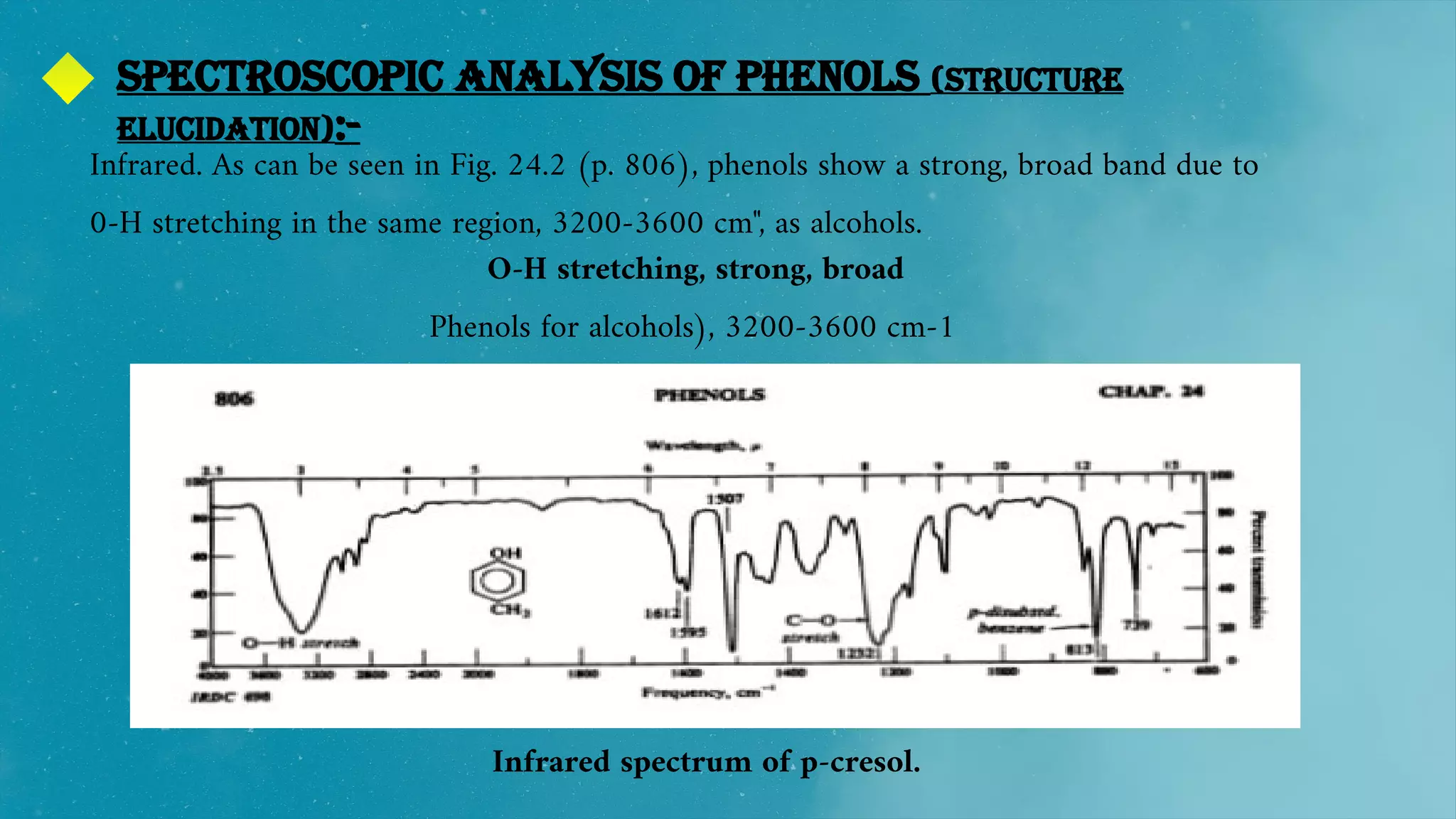
The document also discusses the solubility, structure, and spectroscopic analysis of phenols.




![Ferric Chloride Test:
complex. Most phenols give dark coloured solution.
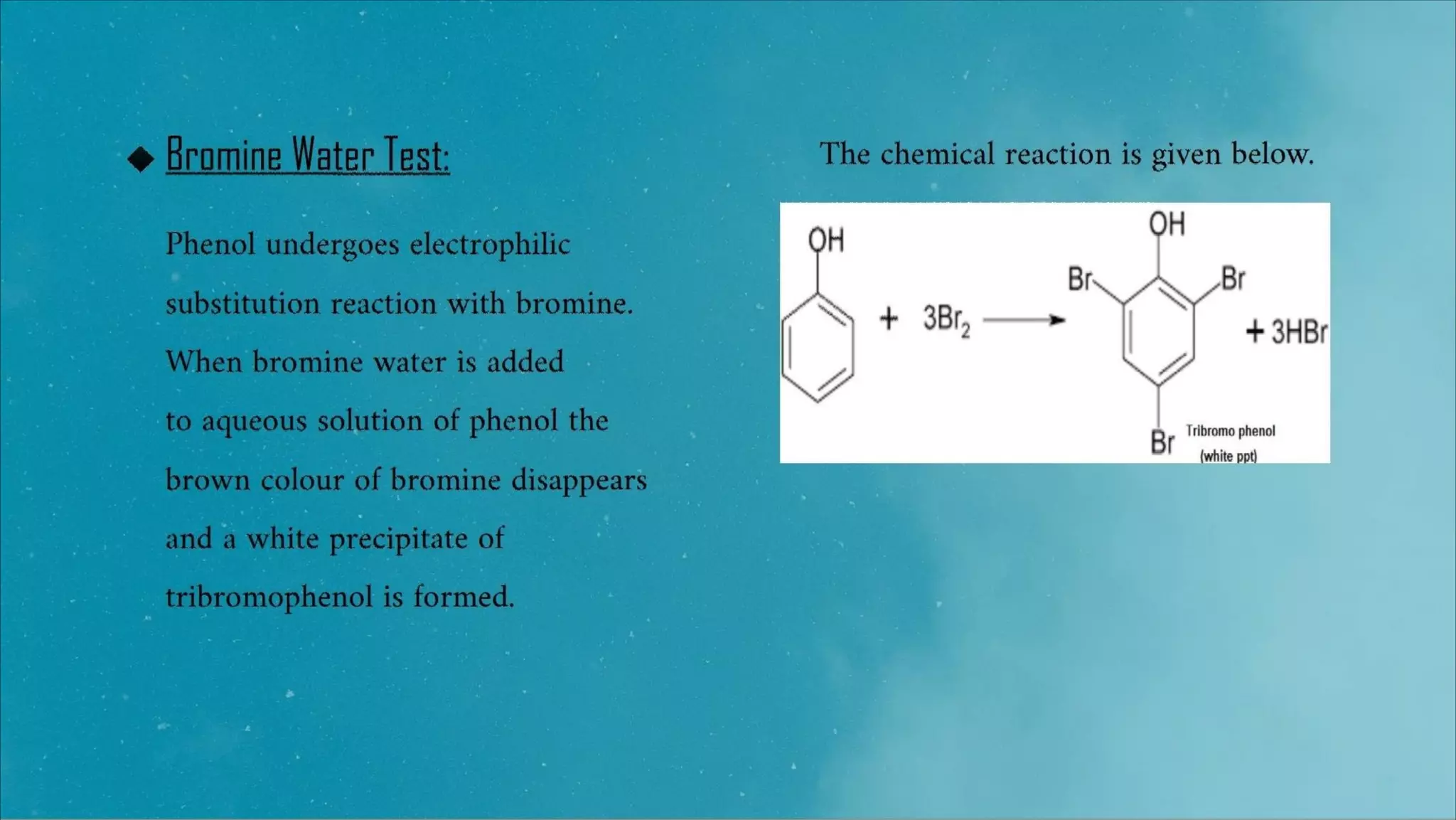
The chemical reaction is given below.
6C H OH + F
eC→l [Fe(C H O) ] (violet colour complex)+ 3HCl + 3H
esol
Phenol, resorcinol, Ortho cresol, Para cr Violet or blue colouration
Catechol Green colouration
Hydroquinone Violet or transient blue color
Pyrogallol Blue rapidly changing to red](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysisofphenolsandqualitativetestsforphenols-211220151204/75/Analysis-of-phenols-and-qualitative-tests-for-phenols-5-2048.jpg)