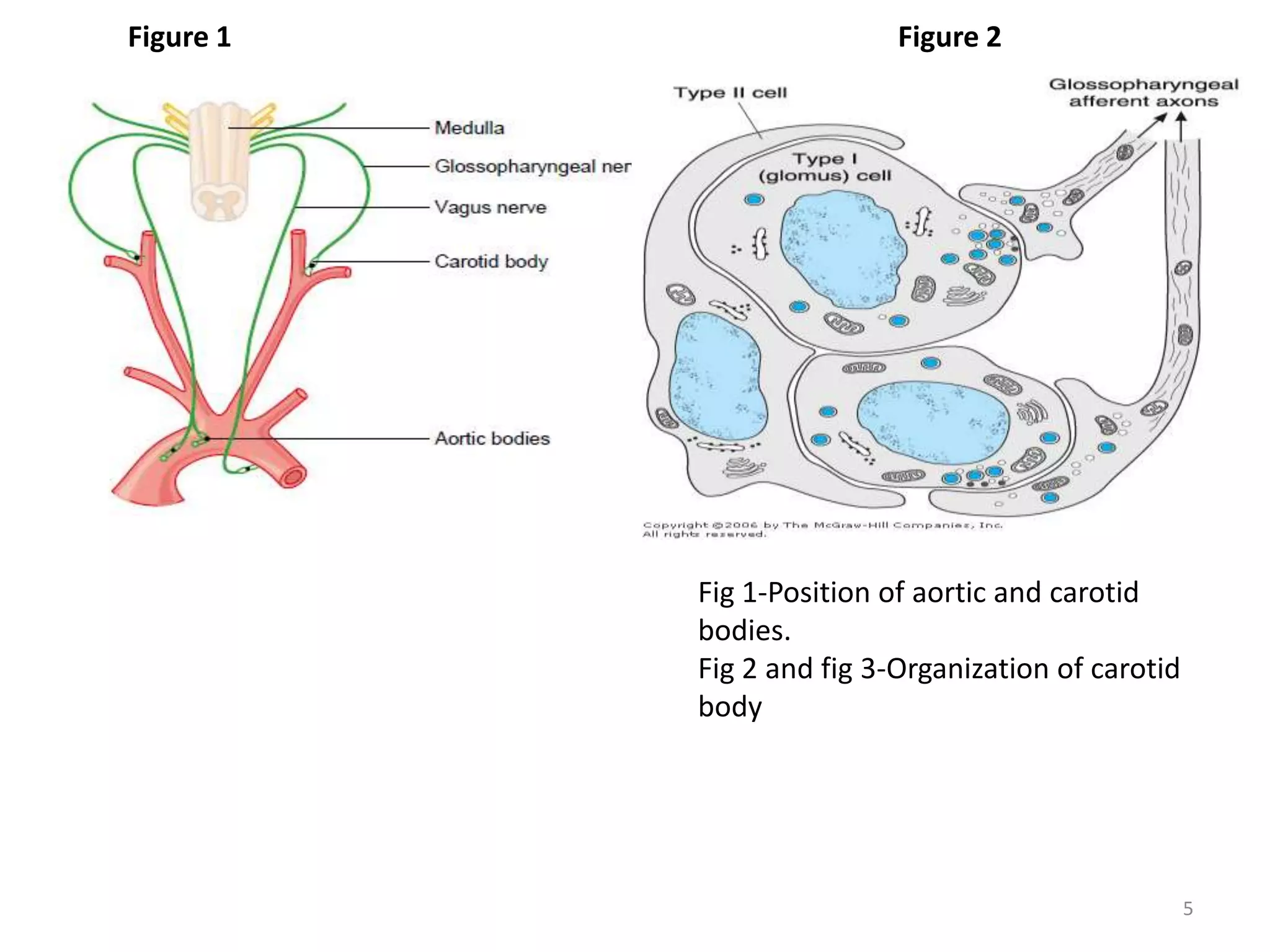
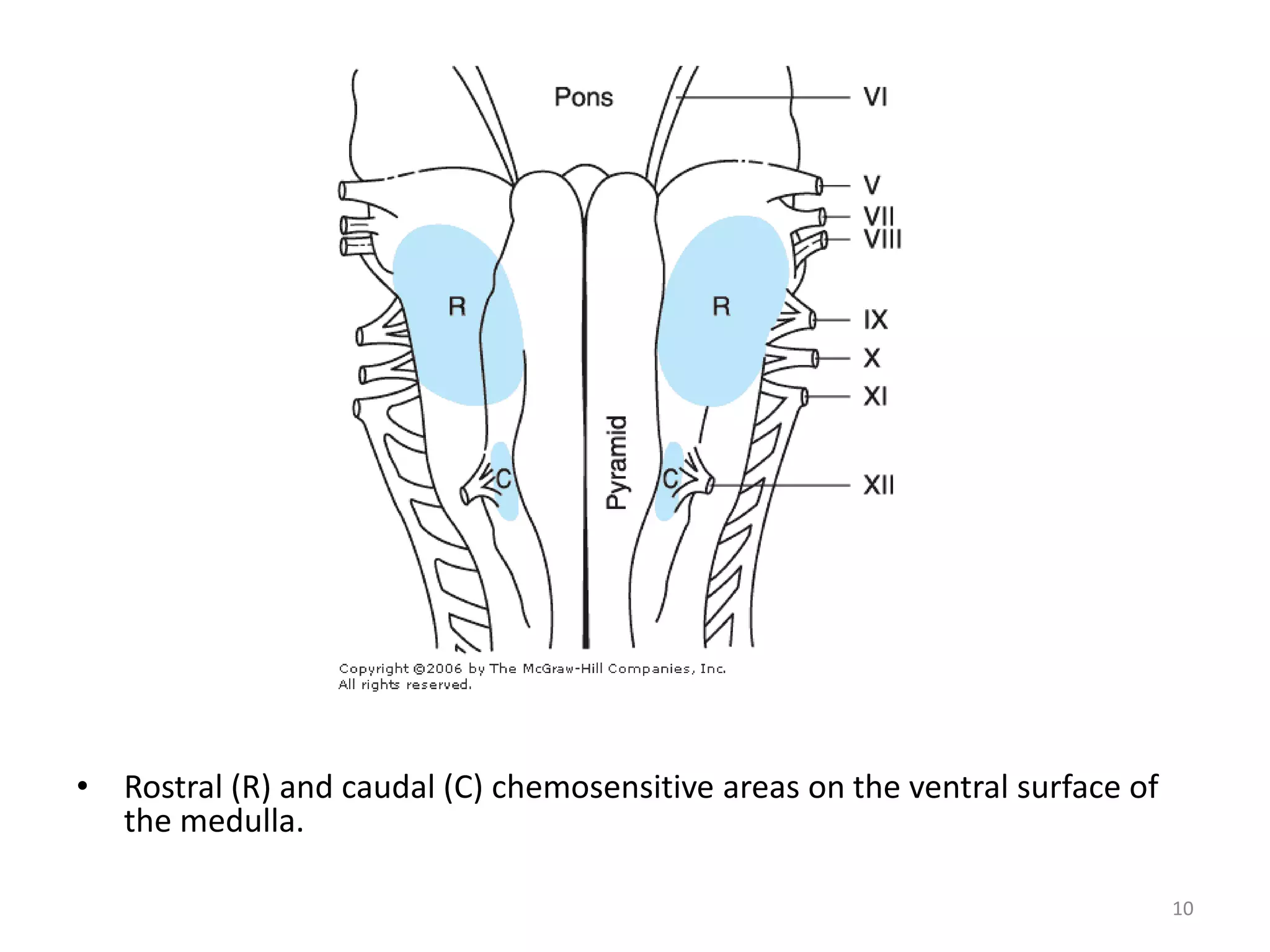
The document summarizes the chemical control of respiration through respiratory chemoreceptors. There are three types of chemoreceptors: peripheral chemoreceptors located in the carotid bodies and aortic bodies that detect changes in arterial pCO2, pO2, and pH; central or medullary chemoreceptors located in the brainstem that are stimulated by increased hydrogen ion concentration in cerebrospinal fluid; and both peripheral and central chemoreceptors work together to maintain homeostasis and stimulate respiration in response to changes in oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ion levels in order to regulate respiration.