This document provides information on vocal cord paralysis, including:
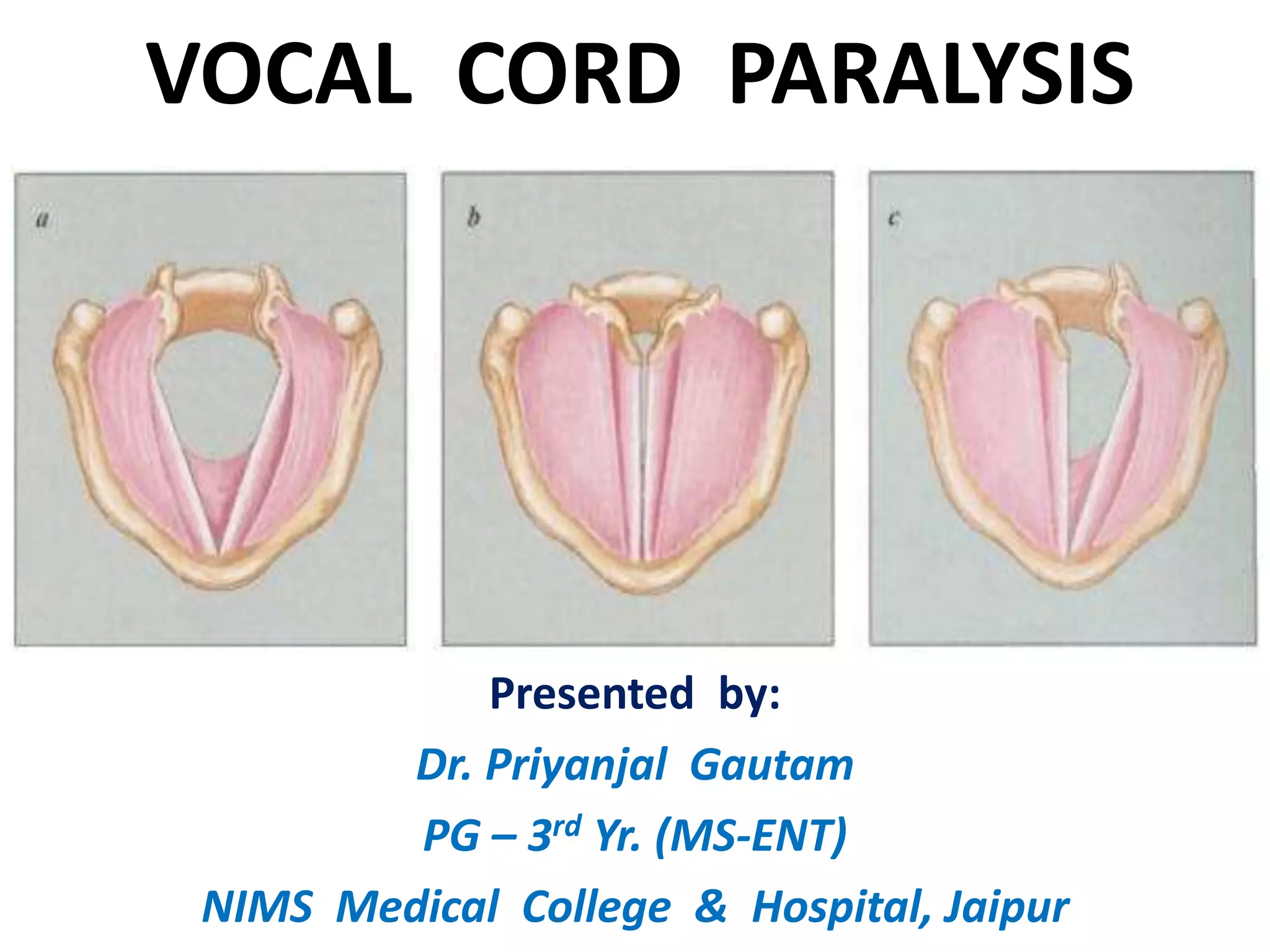
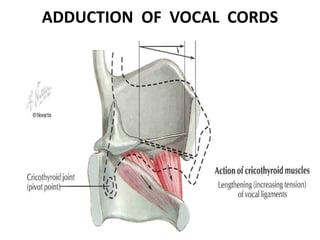
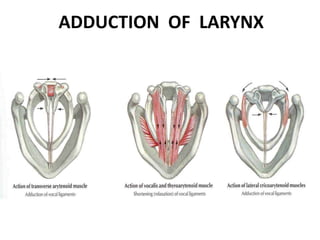
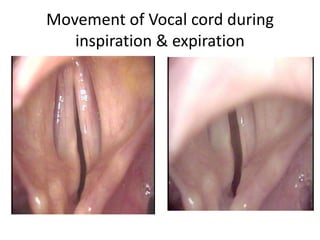
1. Vocal cord paralysis is defined as total interruption of nerve impulses resulting in no movement of laryngeal muscles, while paresis is partial interruption causing weak movement.
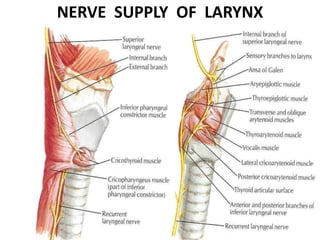
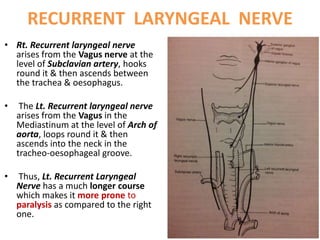
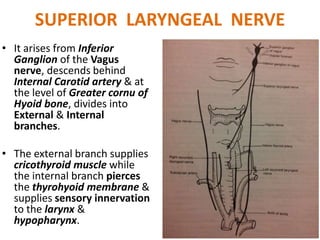
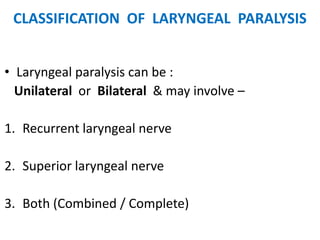
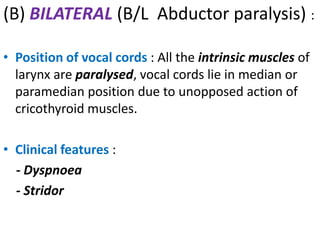
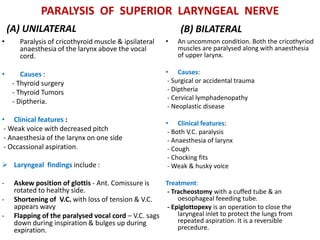
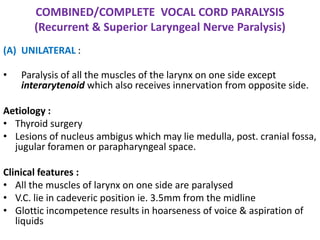
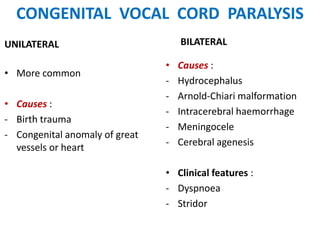
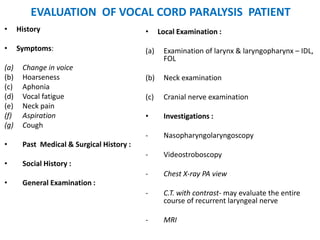
2. Causes of laryngeal paralysis can be supranuclear, nuclear, related to high or low vagal lesions, or systemic. Paralysis may be unilateral, bilateral, or involve the recurrent laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal nerve, or both.
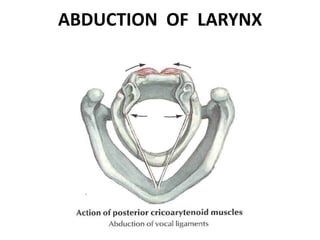
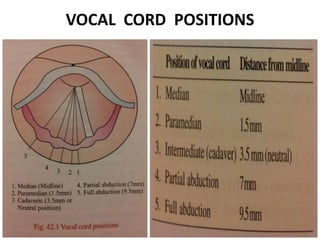
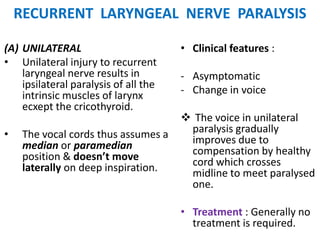
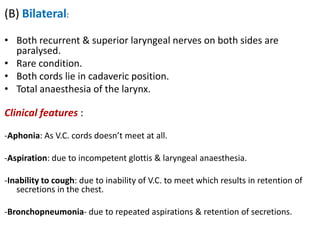
3. In unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis, the vocal cord assumes a median position and does not move laterally on inspiration. Bilateral paralysis causes stridor and dyspnea due to