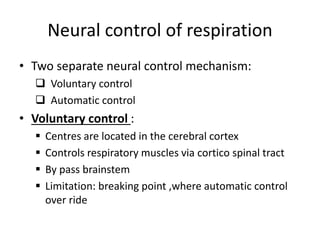
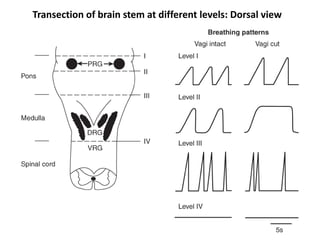
The document outlines the neural control of respiration, detailing both voluntary and automatic mechanisms, which involve various centers in the brain including the medullary and pontine respiratory centers. It highlights the roles of the central pattern generator and the Hering-Breuer reflex in regulating respiratory rhythm and safety. Additionally, it discusses factors affecting respiratory control, emphasizing the implications of impairments such as Ondine's curse and stroke.