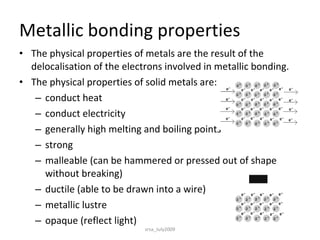
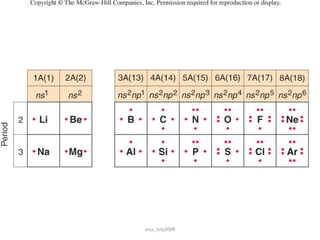
There are three main types of chemical bonds:
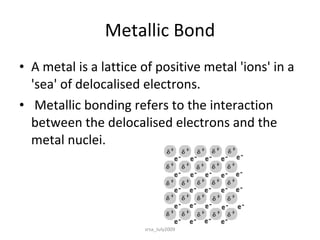
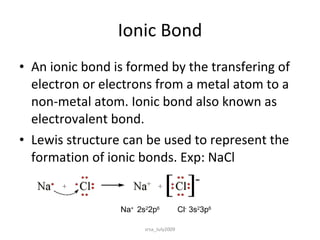
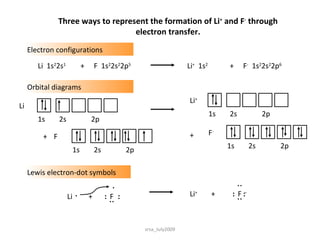
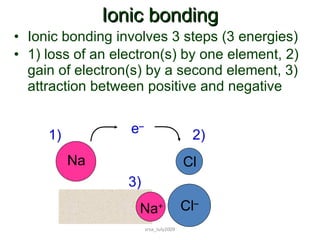
1) Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred from a metal to a non-metal atom. They result in charged ions that are attracted to each other.
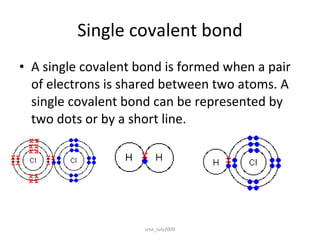
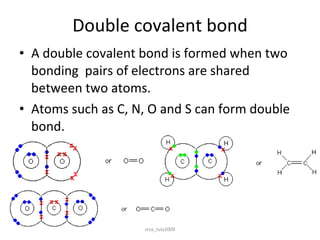
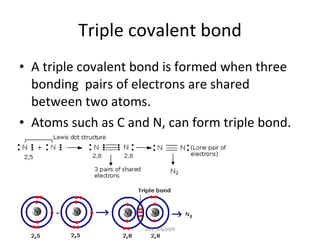
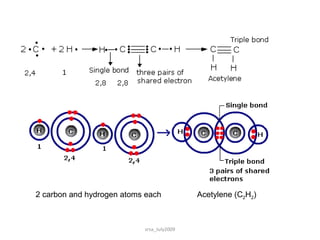
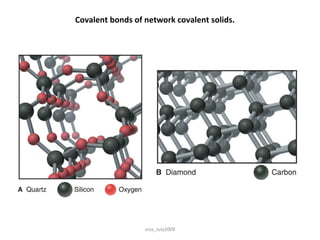
2) Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons through single, double or triple bonds. Covalent compounds have low melting points and are electrical insulators.
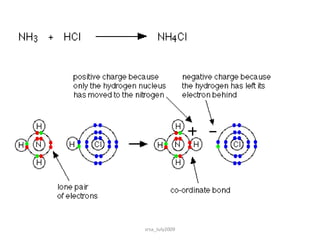
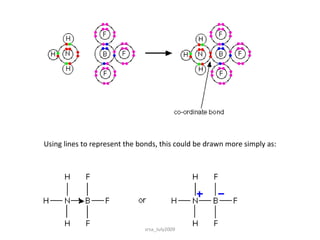
3) Dative bonds form when one atom donates a lone pair of electrons to an atom with an incomplete octet.



![Exercise: aluminium fluoride AlF 3 magnesium chloride MgCl 2 srsa_July2009 [ O ] 2– [Mg] 2+ O Mg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbonding-111027204940-phpapp02/85/Chemical-bonding-8-320.jpg)