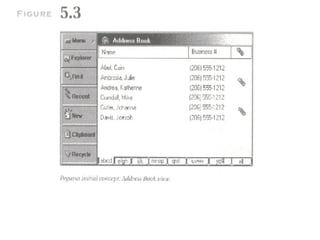
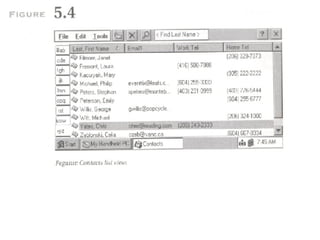
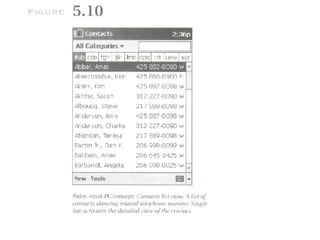
The document discusses the evolution of the user interface design for Microsoft Windows CE. It describes three iterations: the Handheld PC from 1995 which resembled a desktop PC but had usability issues; the Palm PC from 1998 which had a smaller screen and alternative inputs like handwriting but data entry was still difficult; and the Auto PC from 1998 which was designed for in-car use without a touchscreen or stylus and emphasized voice commands. While Windows CE aimed for consistency with desktop Windows, usability tests revealed issues at each stage and consistency alone did not guarantee success.






![Evolution of Windows CE Design: Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] The first H/PC prototype contained concepts of desktop PCs but did not have much affinity Screen size 480 x 240 pixels Input/Output Methods A keyboard for touch-typing A touch screen for navigation on the interface Silk-screened buttons that enabled global functionality Single-tap activation for the applications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-7-320.jpg)

![Evolution of Windows CE Design Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] Usability Testing: Controlled Experiments People found the size of certain targets too small People were not able to identify the active areas on the interface People were confused with the selection / activation model In other words, the interface design is failed!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-10-320.jpg)
![Evolution of Windows CE Design Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] New interface that strongly resembles Windows Desktop The same input/output characteristics, tasks and product goals Usability Testing Most targets are perceived as too small to hit Single-tap activation is efficient Auto-save model fails](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-11-320.jpg)
![Evolution of Windows CE Design Palm PC (P/PC) [1998] Design Goals Fit the H/PC interface into a smaller size 320 x 240 pixel screen Provide quick information look-up and entry Enable information customization Make it smaller and easy to carry Alternative Input/Output methods to H/PC Hardware buttons for scrolling up/down Handwriting recognition and voice recording](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-13-320.jpg)


![Evolution of Windows CE Design Palm PC (P/PC) [1998] Usability Testing: Controlled Experiments Data entry using a small on-screen keyboard is tedious The use of keyboard is rated as easiest to use Subjects were the fastest and most accurate with the keyboard In general, handwriting recognizer is rated low as an input method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-17-320.jpg)
![Evolution of Windows CE Design Auto PC (A/PC) [1998] First product that deviates from the Windows 95 look designed to support tasks of a mobile professional while driving Uses New forms of Input/Output Methods No stylus and no touch screen A numeric keypad for character inputs Speaker-independent voice command interface Sound feedback about the state of the system Infrared connections to H/PCs and P/PCs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-18-320.jpg)

![Evolution of Windows CE Design Auto PC (A/PC) [1998] Usability Testing: Field Studies Interoperability of in-car equipment was compelling People usually plan their tasks before getting into the car They need to be kept informed about schedule changes The data is then synchronized at the office/home](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-151833-18777/85/Chapter5-21-320.jpg)