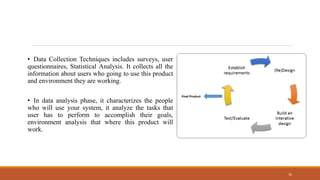
This document discusses human-computer interaction and user interface design. It covers interaction design principles like understanding users and iteration. It also describes common interaction styles like command line interfaces, menus, forms, and the WIMP (windows, icons, menus, pointer) style. User-centered design techniques are outlined, including data collection, analysis, modeling, prototyping and evaluation to create effective, efficient and satisfying user experiences.