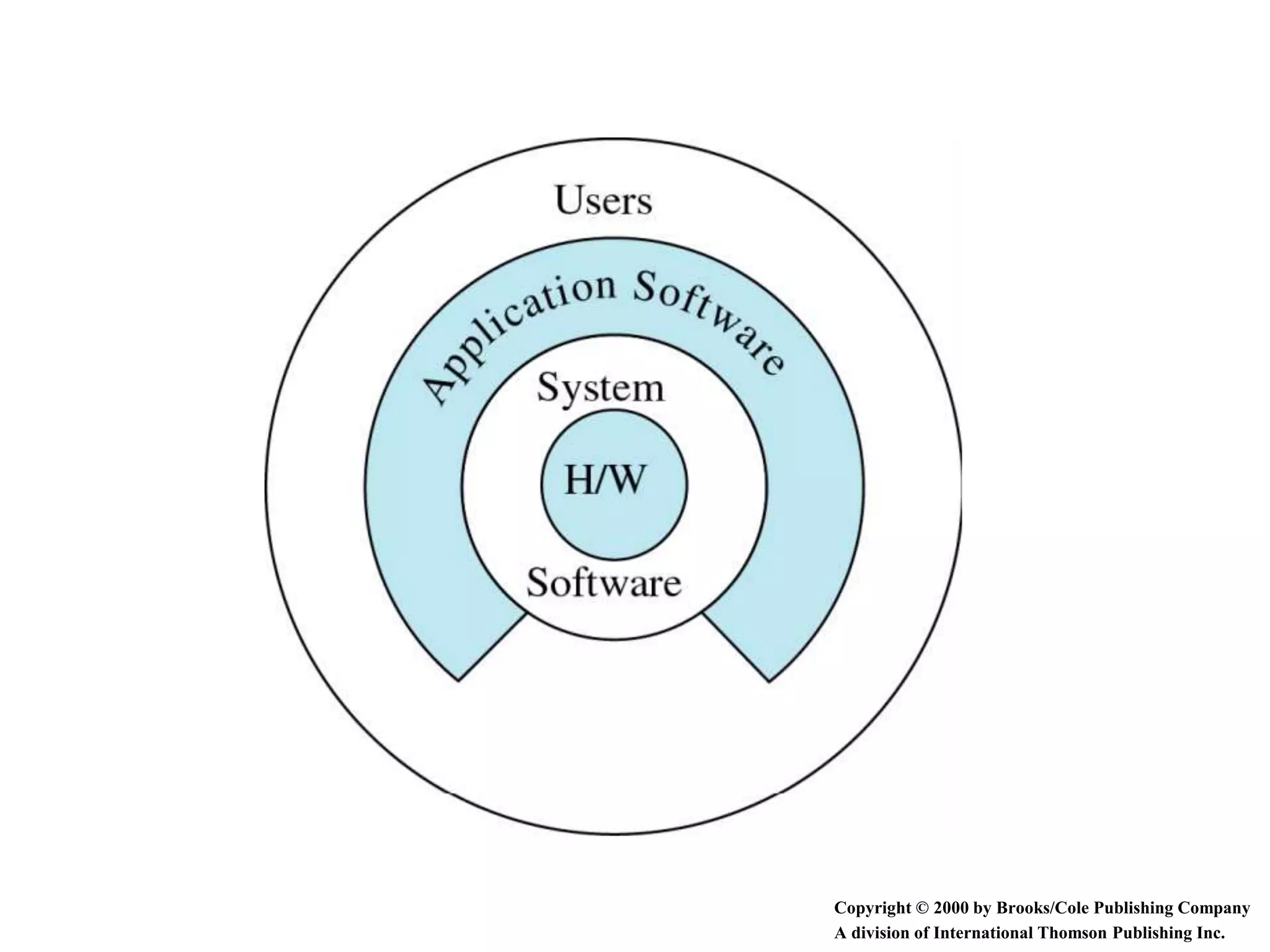
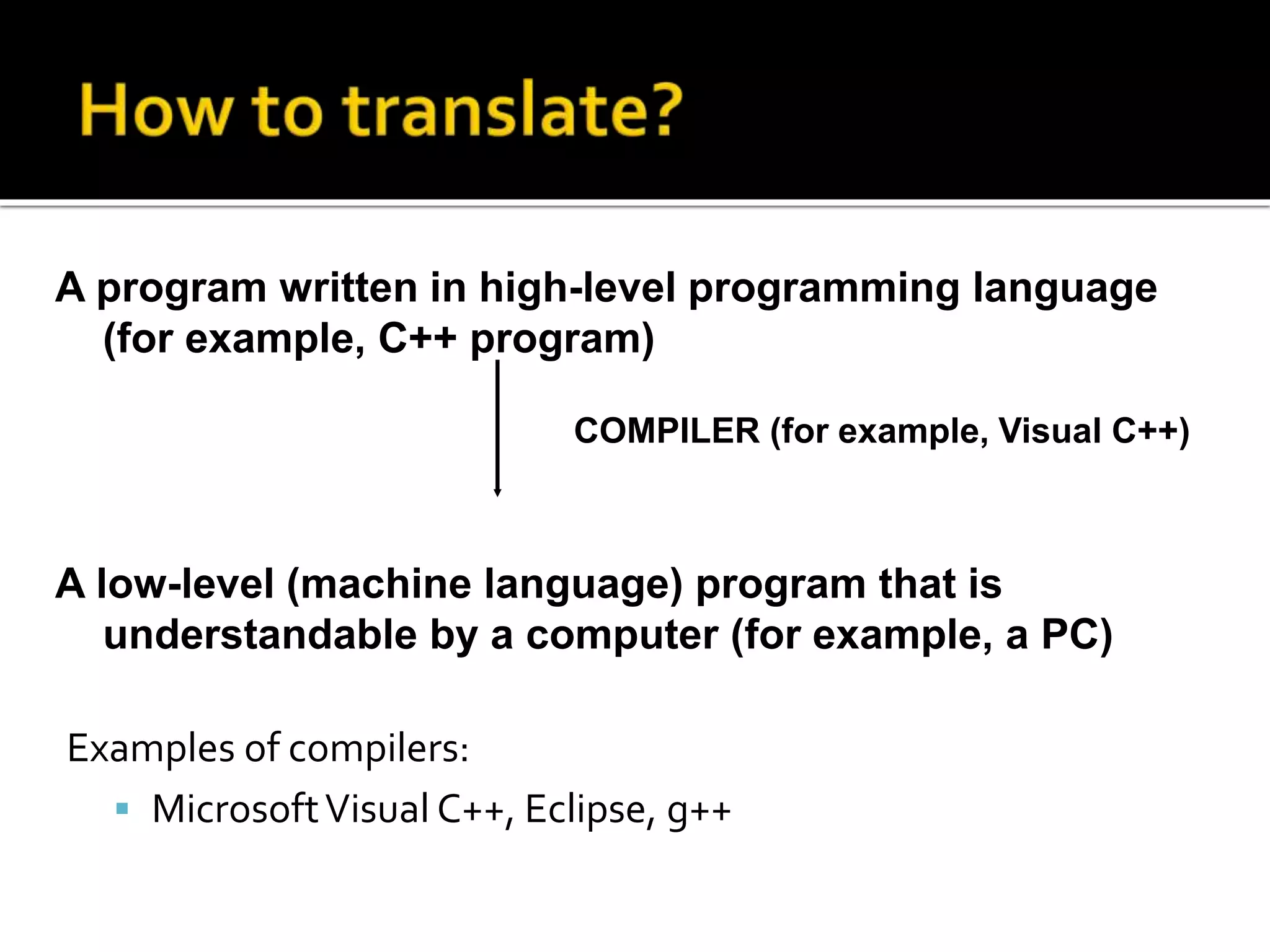
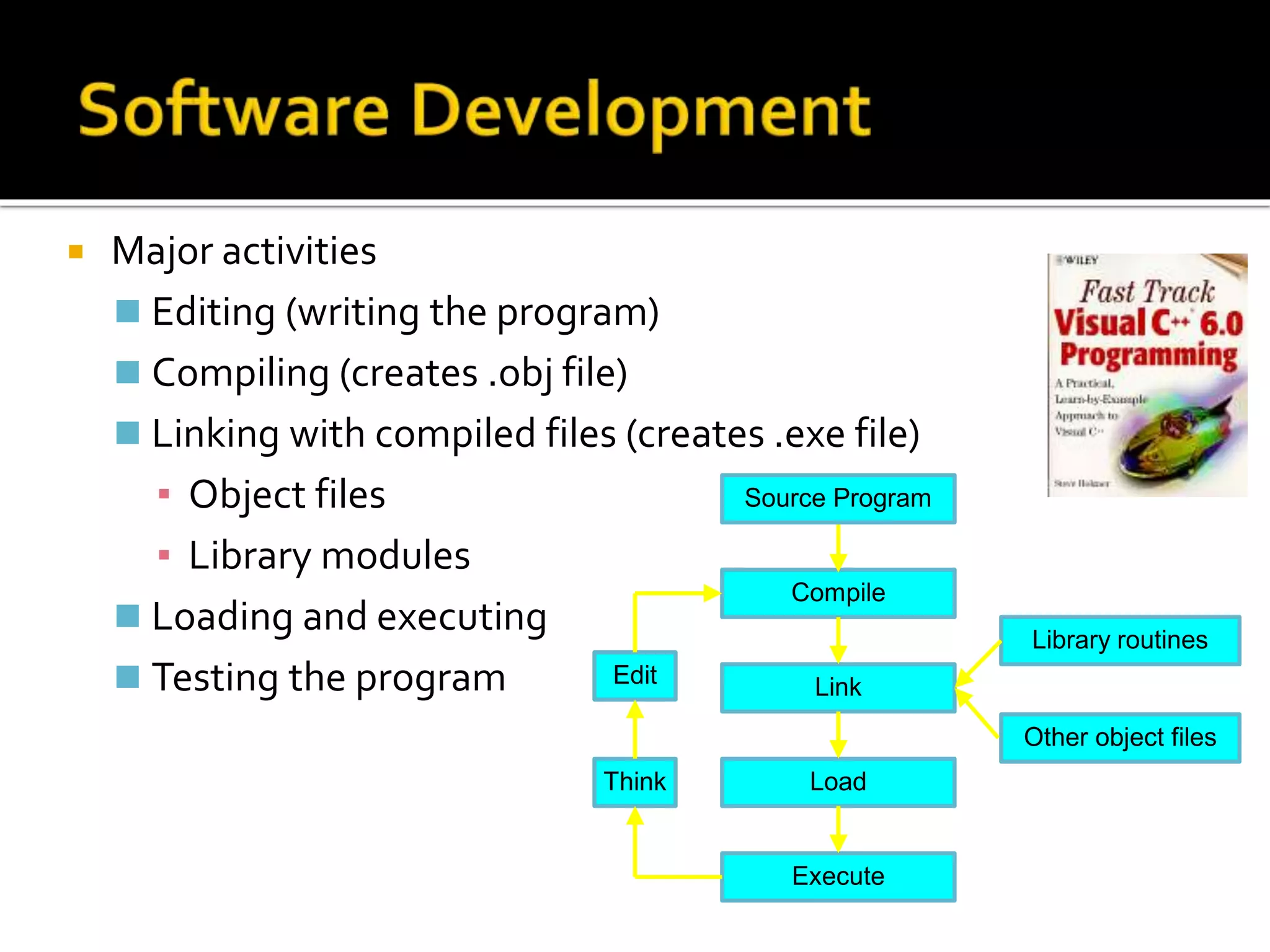
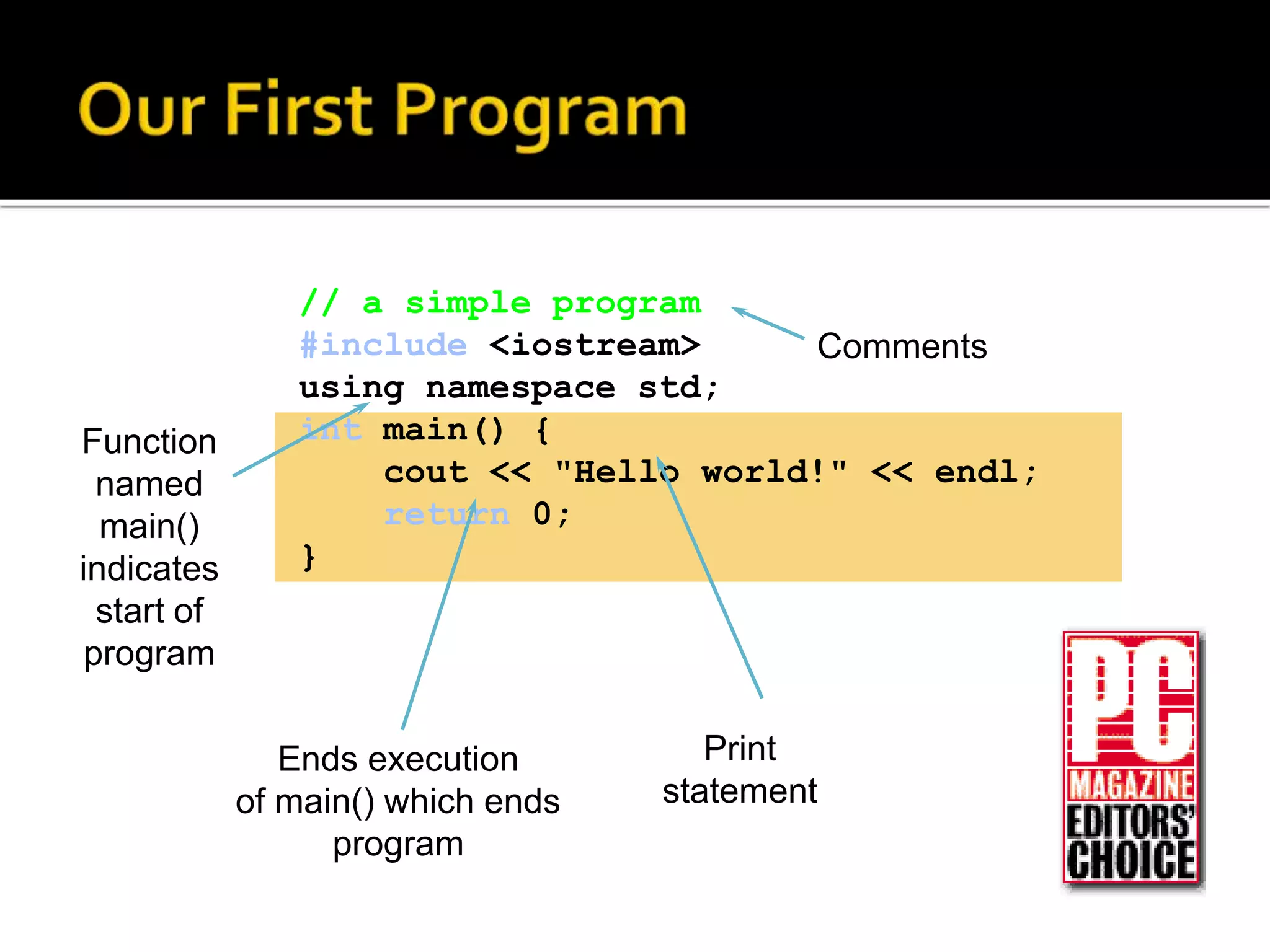
This document discusses different types of software, including operating systems and applications software. It explains that computer hardware requires software to provide instructions. There are two main types of software: system software like operating systems, and application software which performs specific tasks. When choosing software, it's important to check system requirements to ensure the hardware can run it. Requirements include memory, storage, and operating system compatibility. The document also outlines programming languages from low-level binary to high-level languages, and the translation process from source code to executable programs using compilers and linkers.