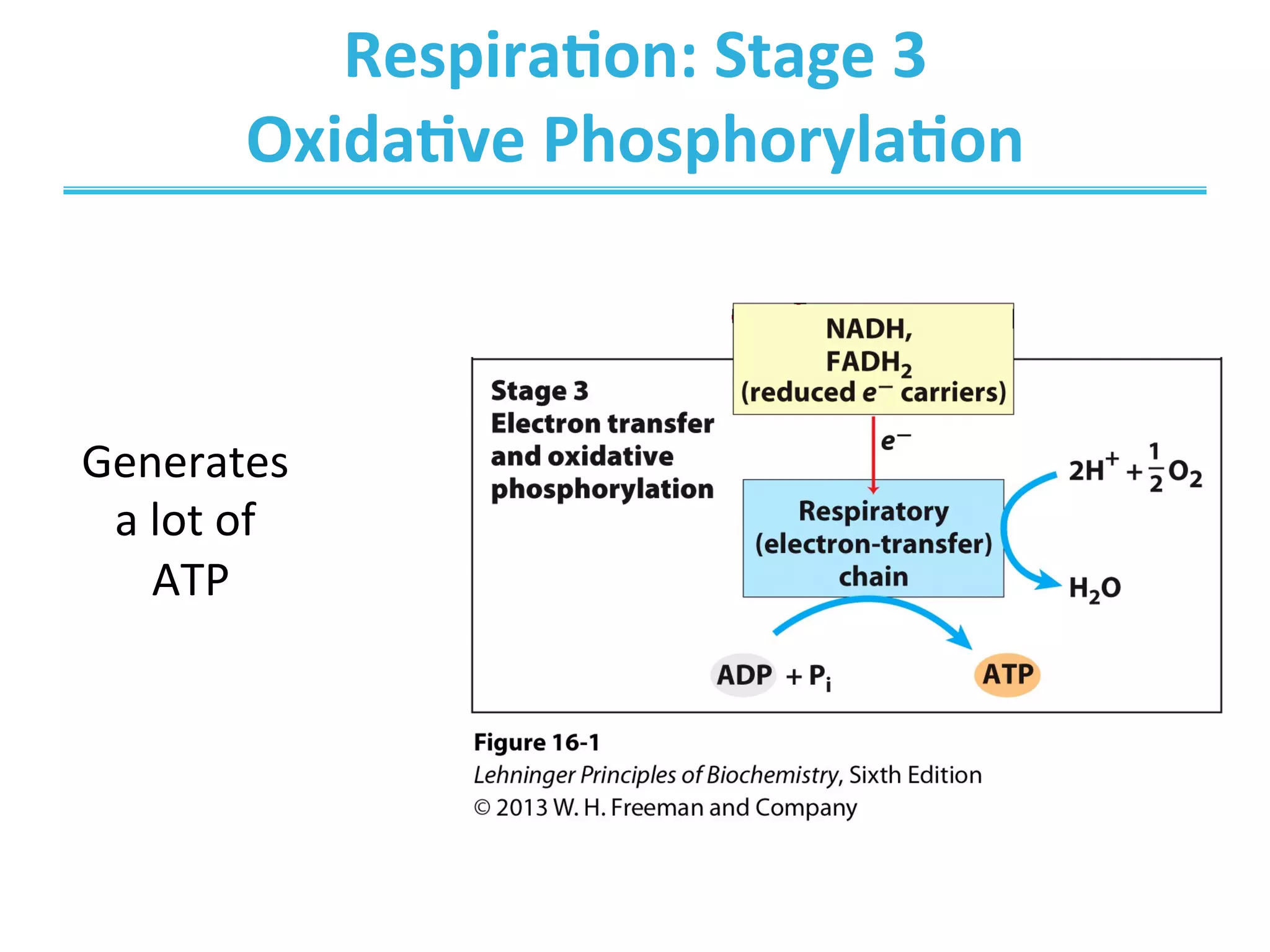
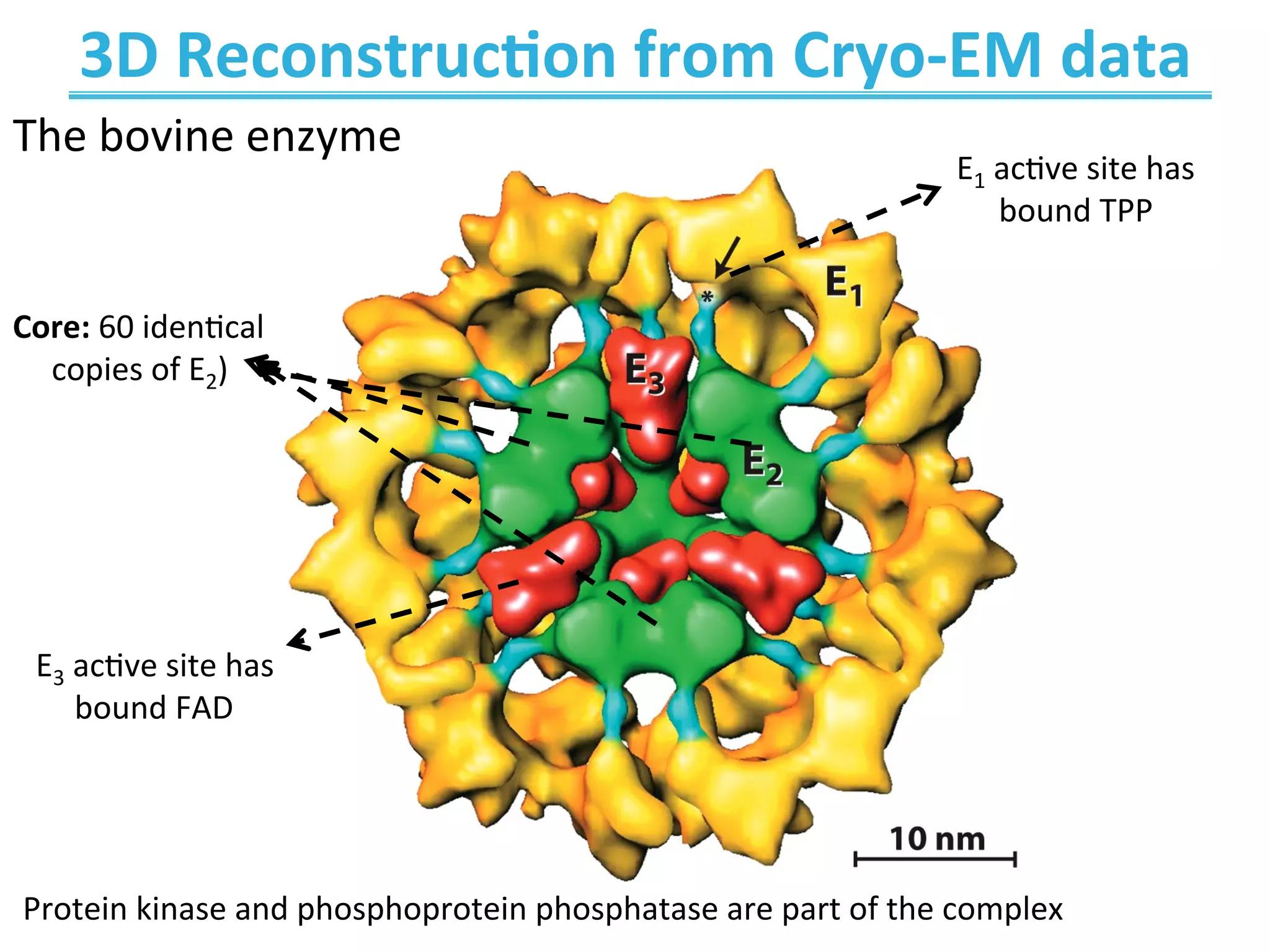
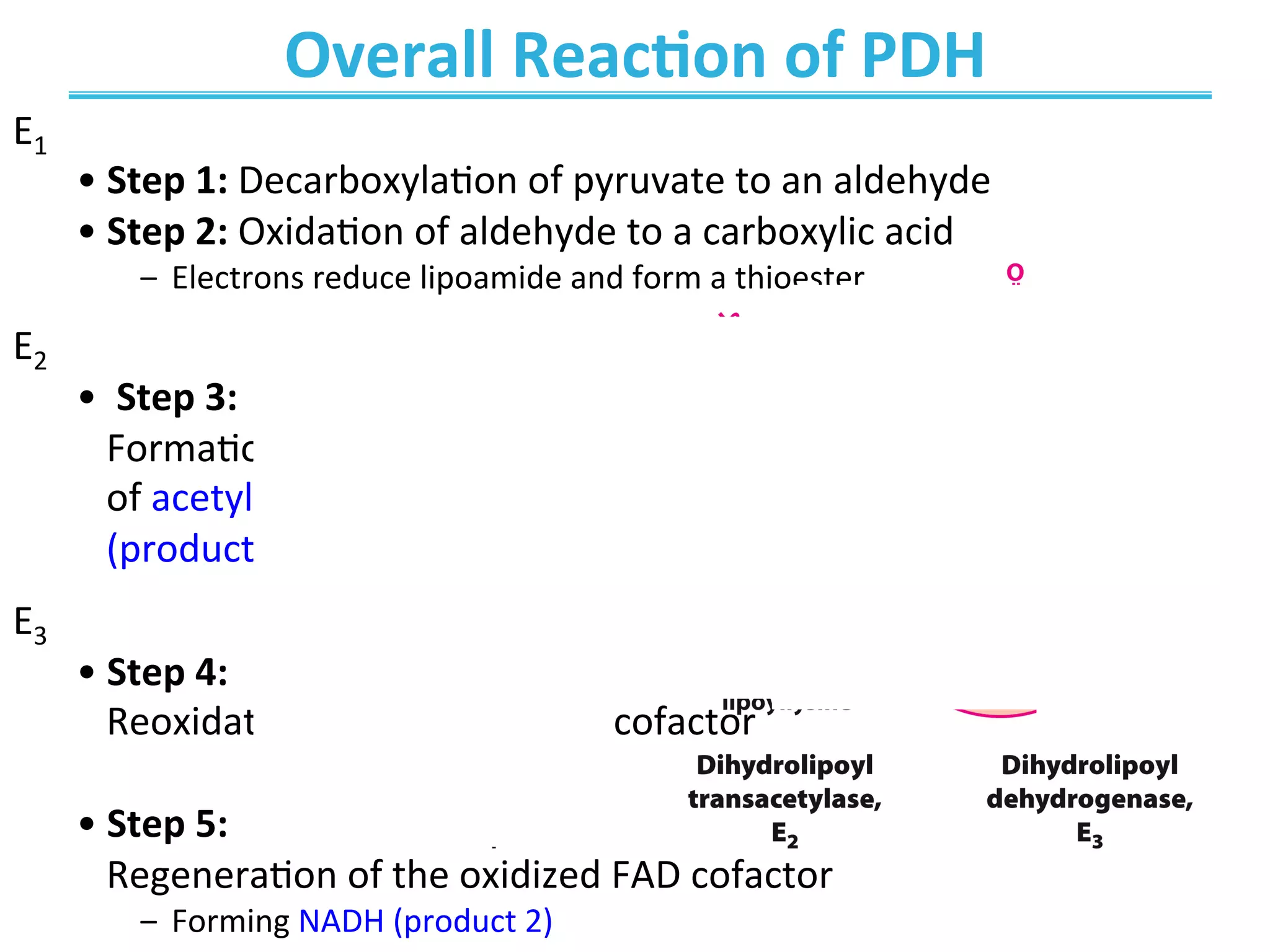
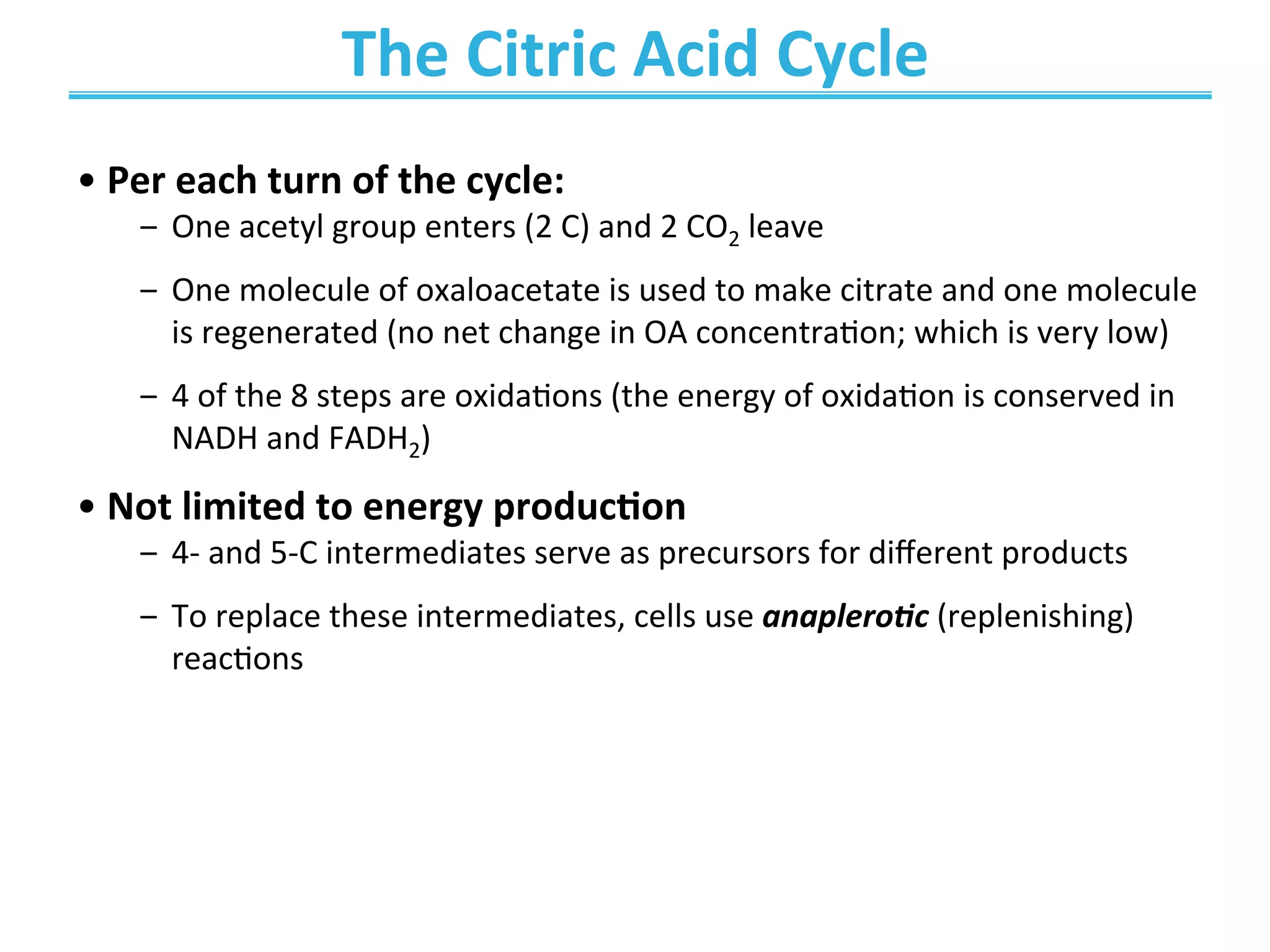
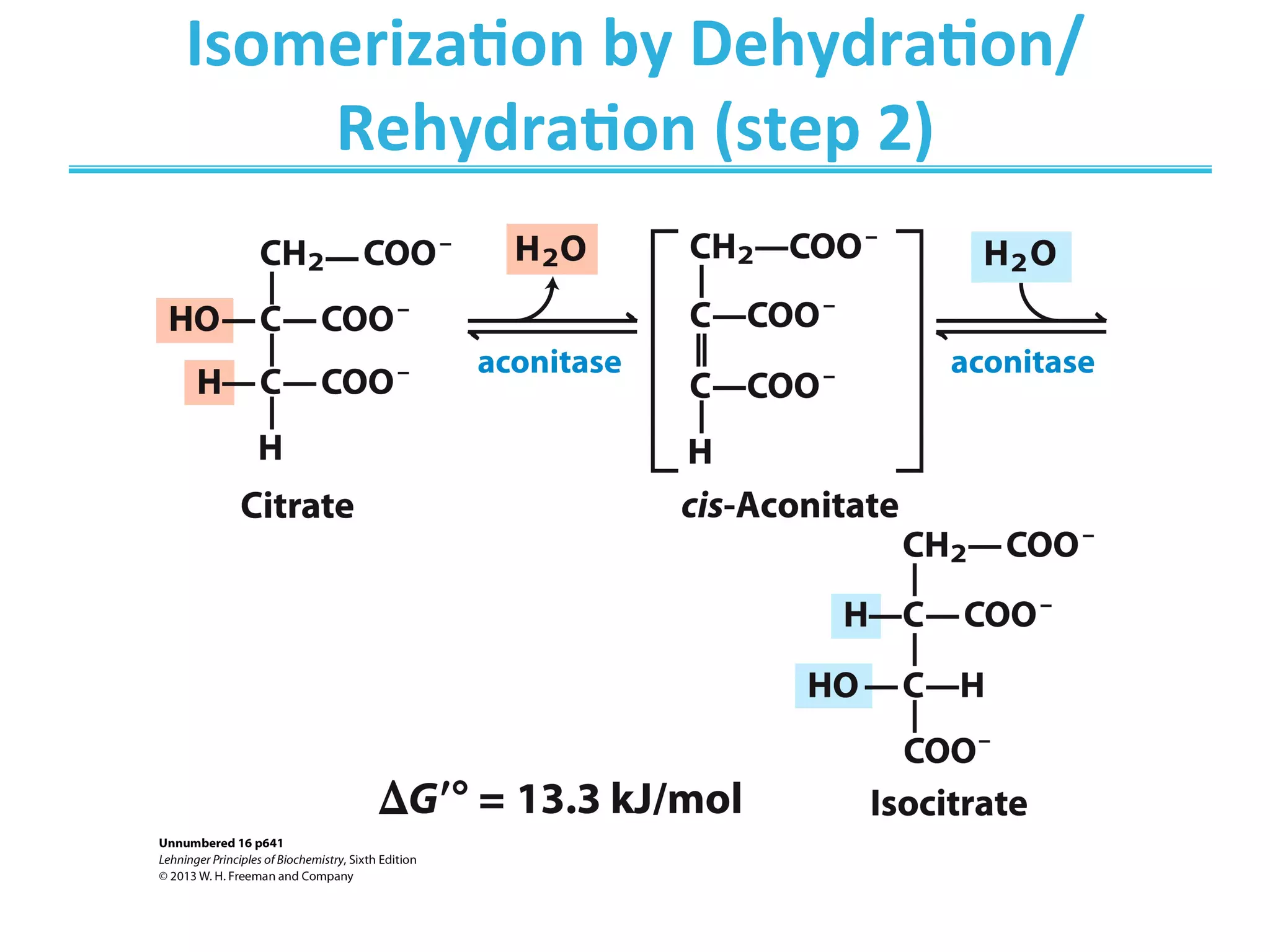
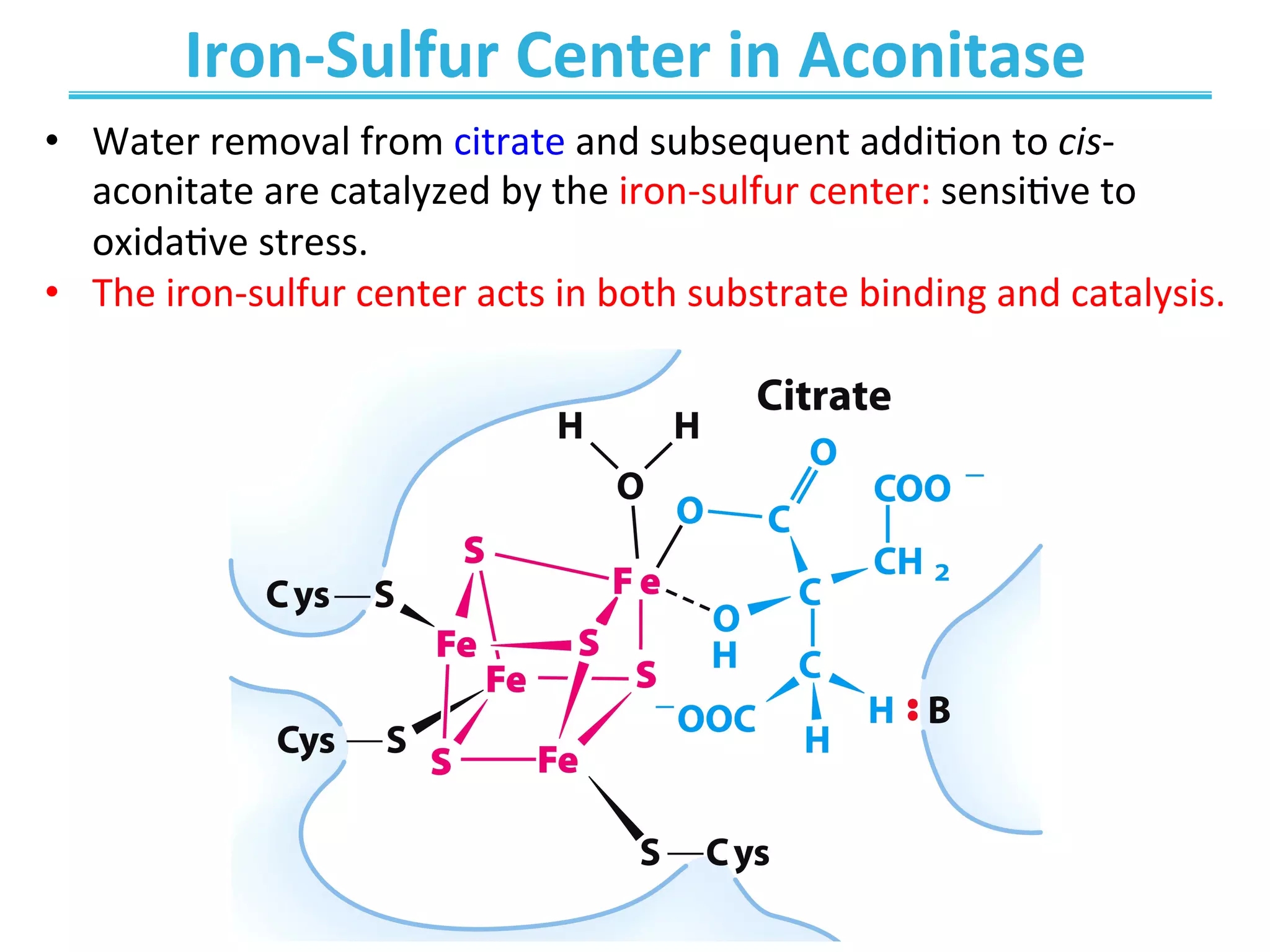
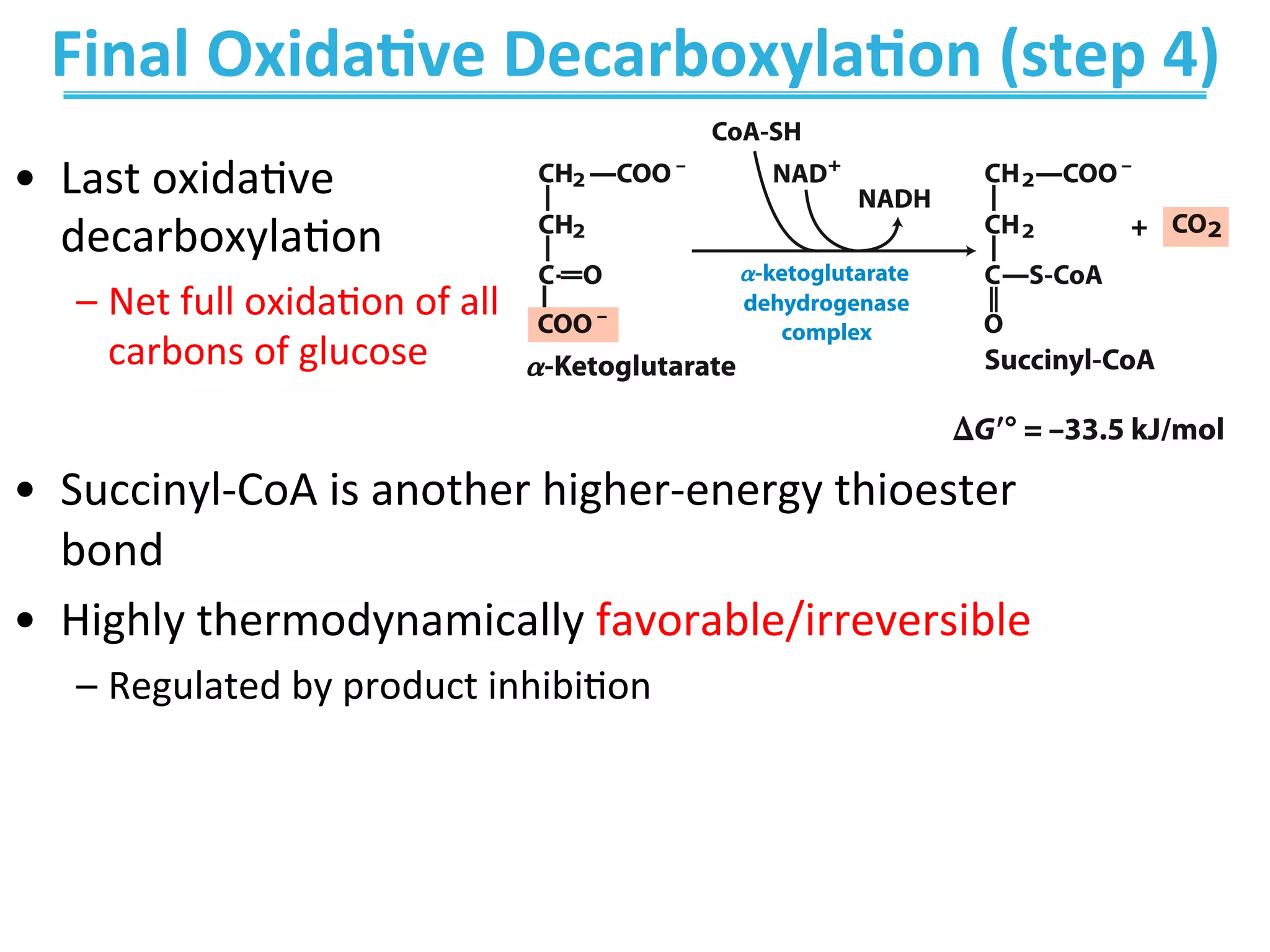
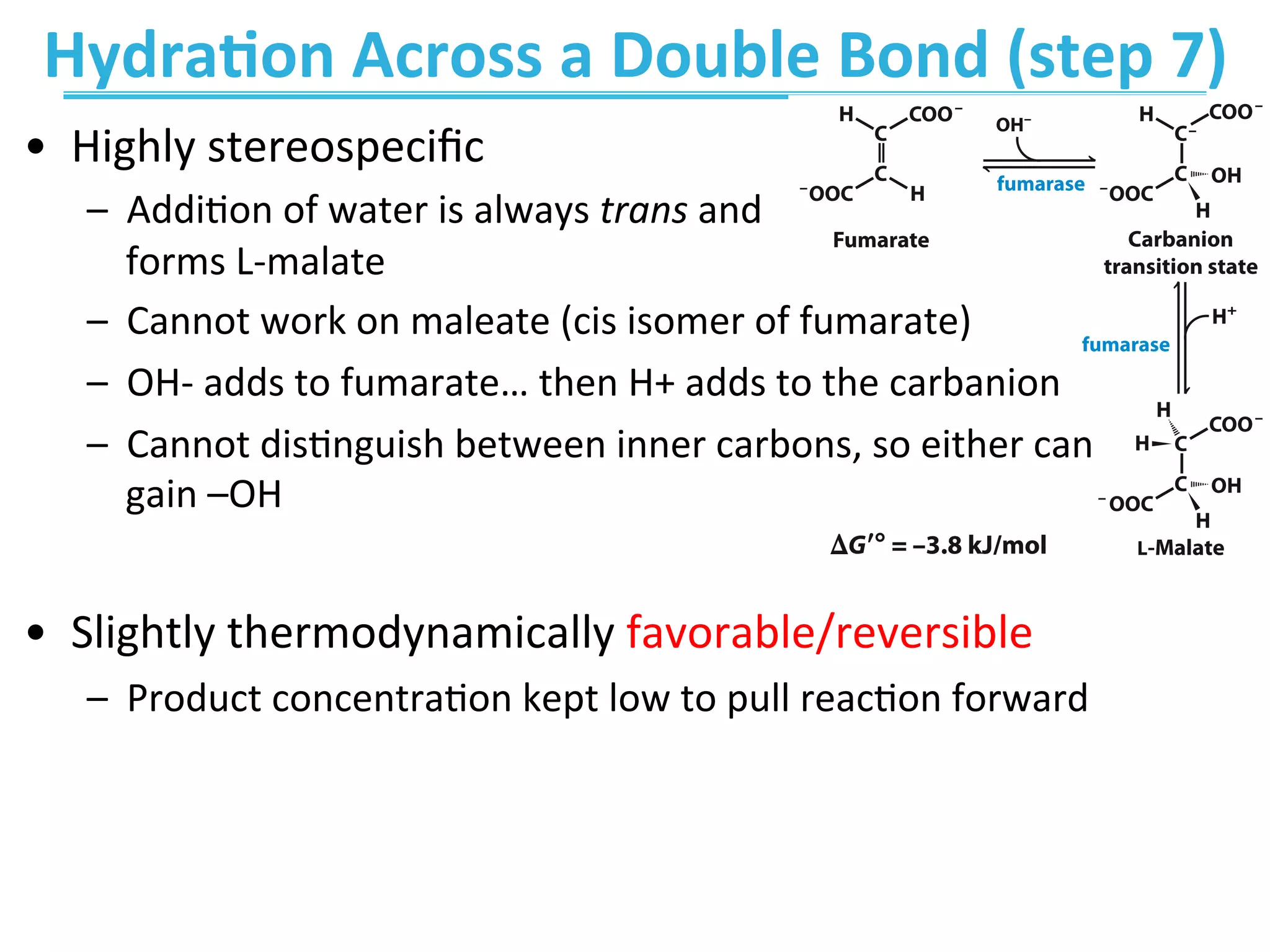
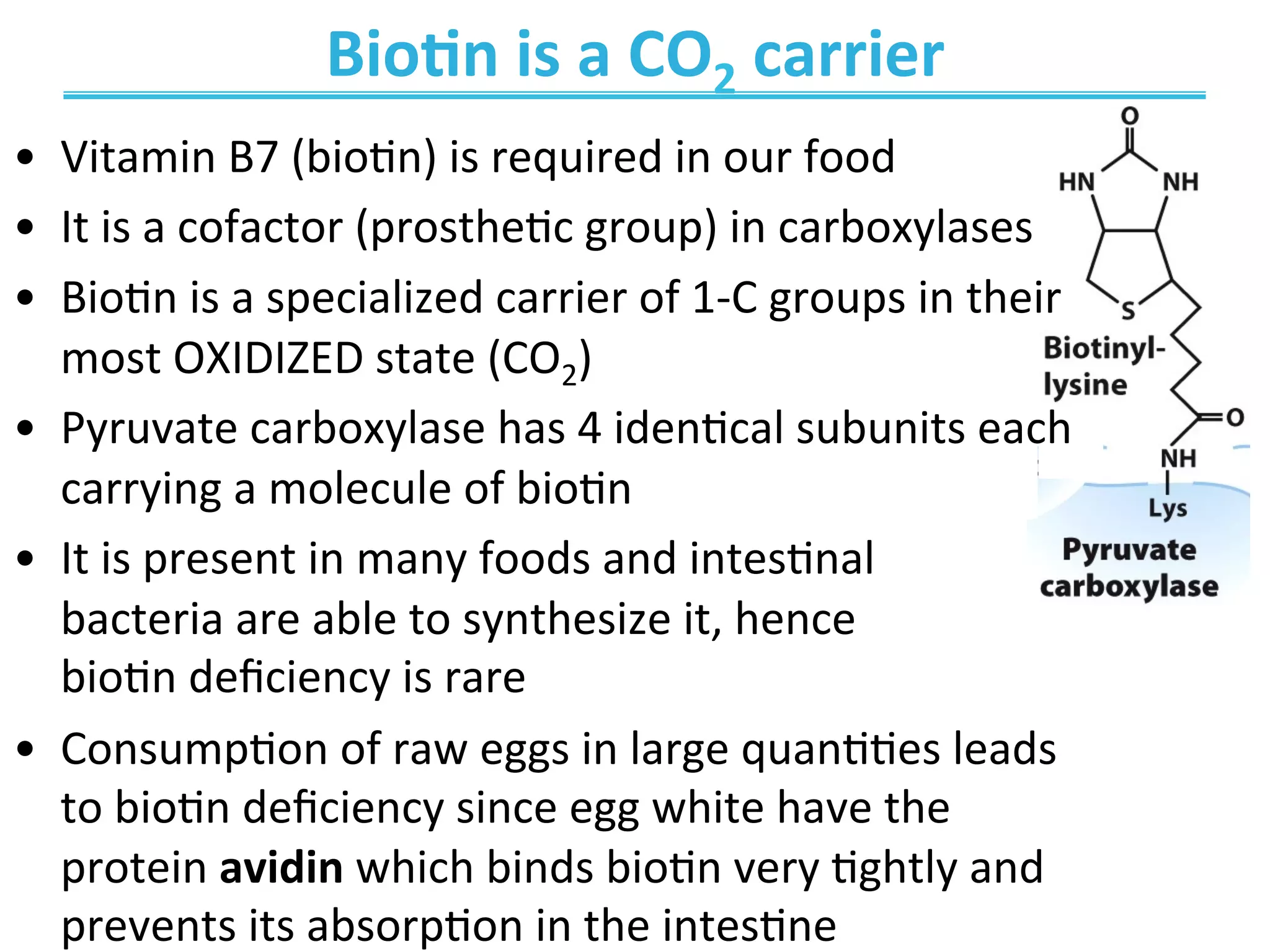
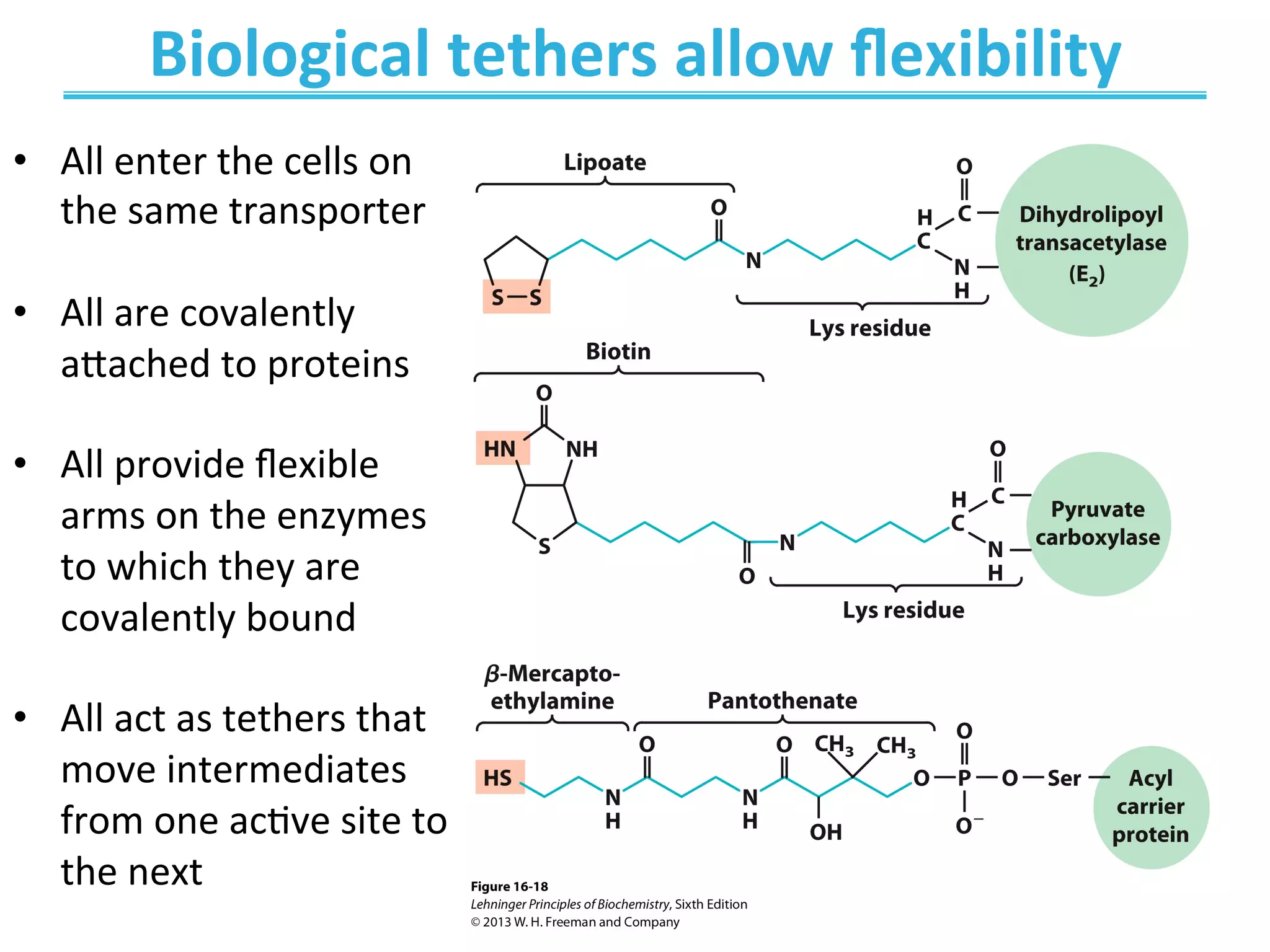
The document discusses cellular respiration, which occurs in three stages: 1) acetyl-CoA production from organic fuels like glucose and fatty acids, 2) acetyl-CoA oxidation in the citric acid cycle (CAC) to produce NADH, FADH2, and GTP, and 3) oxidative phosphorylation to generate large amounts of ATP. The citric acid cycle involves a series of chemical reactions that generate energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. These stages capture energy from nutrients and facilitate the production of ATP to fuel cellular work.












![C-‐C
Bond
Forma>on
by
Condensa>on
of
Acetyl-‐CoA
and
Oxaloacetate
(step
1)
• CondensaEon
of
acetyl-‐CoA
and
oxaloacetate
• The
only
reacEon
with
C-‐C
bond
formaEon
• Uses
Acid/Base
Catalysis
– Carbonyl of oxaloacetate
is a good electrophile (stabilization of carbanions)
– Methyl group has been converted to methylene
• Rate-‐limi*ng
step
of
CAC
• AcEvity
largely
depends
on
[oxaloacetate]
• Highly
thermodynamically
favorable/irreversible
– Regulated
by
substrate
availability
and
product
inhibiEon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-160419082018-160427181734/75/Chapter16-160419082018-17-2048.jpg)


![Aconitase
is
a
“moonligh>ng”
enzyme
• When
Fe
is
deficient,
aconitase
loses
its
Fe-‐S
center
and
acquires
a
new
role
in
Fe
homeostasis
• Cytosolic
Aconitase
is
an
enzyme
(with
Fe-‐S)
and
a
regulator
of
protein
synthesis
(
–
Fe)
• In
humans
Fe
levels
must
be
regulated:
too
liKle
à
anemia;
too
much
à
liver
damage
• Transferrin:
carries
Fe
in
the
blood
• Transferrin
receptor:
receives
and
endocytoses
Fe
• Ferri*n:
stores
excess
Fe
inside
the
cells
• Apoaconitase
(
–
Fe)
regulates
protein
levels
by
stabilizing
or
destabilizing
the
mRNA
of
transferrin
receptor
or
ferriEn
• Apoaconitase
à
êferriEn
and
é
TfR
synthesis
(the
results
would
be
an
increase
in
cellular
[Fe])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-160419082018-160427181734/75/Chapter16-160419082018-22-2048.jpg)











![Anaplero>c
Reac>ons
• Must
replenish
the
intermediates
in
order
for
the
cycle
and
central
metabolic
pathway
to
conEnue
• 4-‐carbon
intermediates
are
formed
by
carboxylaEon
of
3-‐carbon
precursors
• The
replenishing
and
consuming
reacEons
are
in
dynamic
balance
([CAC
intermediates]
is
~
constant)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-160419082018-160427181734/75/Chapter16-160419082018-36-2048.jpg)
![Anaplero>c
Reac>ons
• Must
replenish
the
intermediates
in
order
for
the
cycle
and
central
metabolic
pathway
to
conEnue
• 4-‐carbon
intermediates
are
formed
by
carboxylaEon
of
3-‐carbon
precursors
• The
replenishing
and
consuming
reacEons
are
in
dynamic
balance
([CAC
intermediates]
is
~
constant)
• Regulatory
enzyme
–
inac*ve
in
the
absence
of
acetyl-‐CoA
• More
acetyl-‐CoA,
more
acEvity
è
more
OAA
to
react
with
acetyl-‐CoA
to
start
the
cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-160419082018-160427181734/75/Chapter16-160419082018-37-2048.jpg)
![Regula>on
of
the
Citric
Acid
Cycle
Cell
has
high
energy
demands!
Cell
is
supplied
with
enough
energy
[NADH]/[NAD+]
and
[ATP]/[ADP]
are
high](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter16-160419082018-160427181734/75/Chapter16-160419082018-40-2048.jpg)




