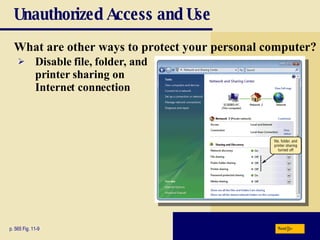
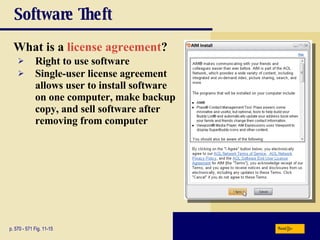
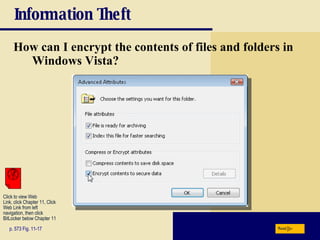
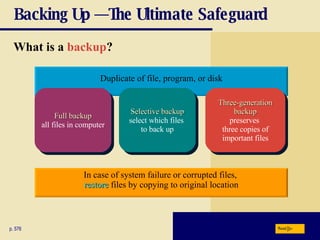
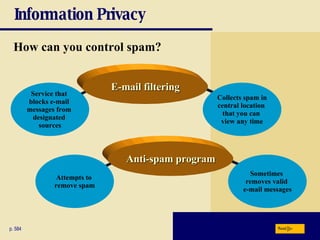
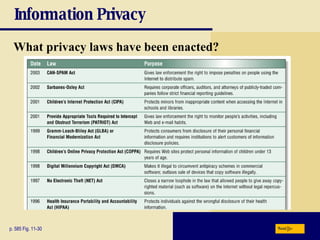
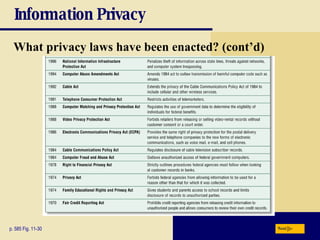
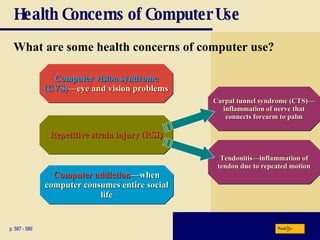
This chapter discusses computer security risks like viruses, worms and Trojan horses. It describes safeguards like antivirus software, firewalls and passwords. The chapter also covers ethics issues around information privacy, software piracy and computer use. Potential health issues from overuse like repetitive strain injuries are explained, along with ergonomic precautions and green computing practices.