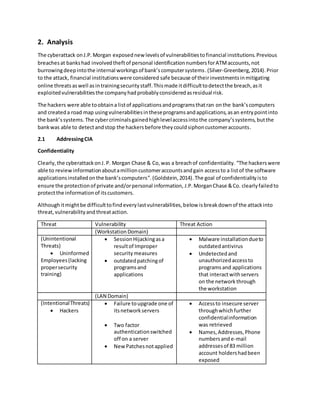
The case study analyzes the significant cyberattack on J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. in July 2014 that compromised over 76 million customer accounts due to vulnerabilities in the bank's IT infrastructure, including the failure to implement two-factor authentication. The attack exposed the bank's weaknesses and resulted in unauthorized access to sensitive information, highlighting the need for improved employee training and network security measures. Proposed countermeasures include security freezes for customers and enhanced awareness to prevent future incidents.