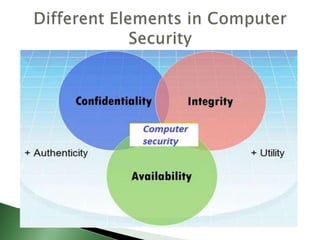
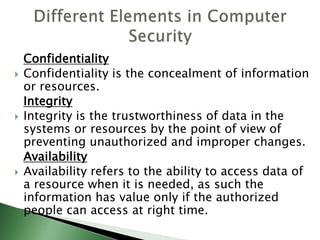
The document discusses various topics related to computer security including definitions of computer security, cyber security, and IT security. It defines key concepts like confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It also defines common security threats like unauthorized access, hackers, vulnerabilities, and attacks. It discusses security measures like antivirus software, firewalls, and provides examples of computer crimes and viruses.