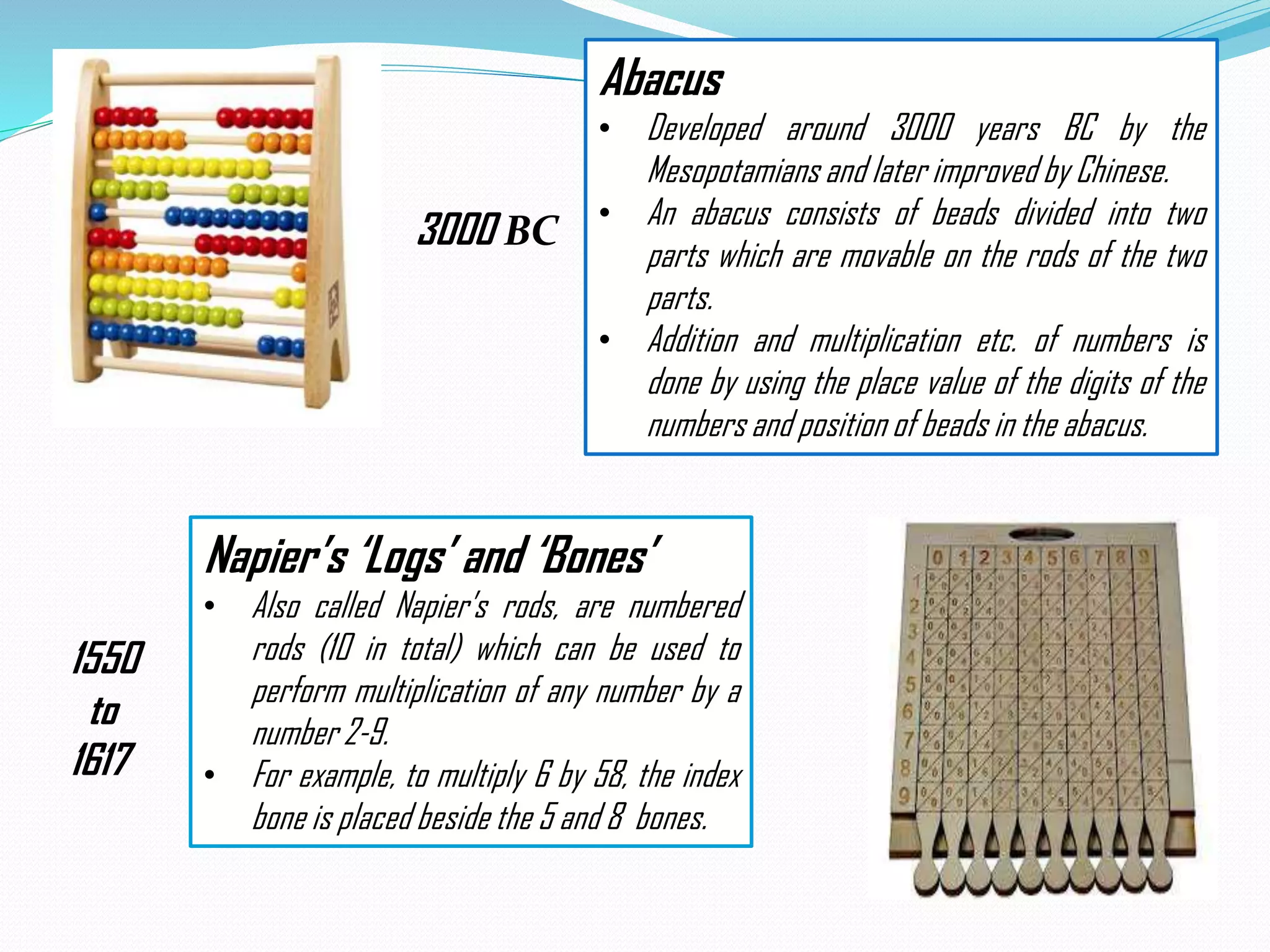
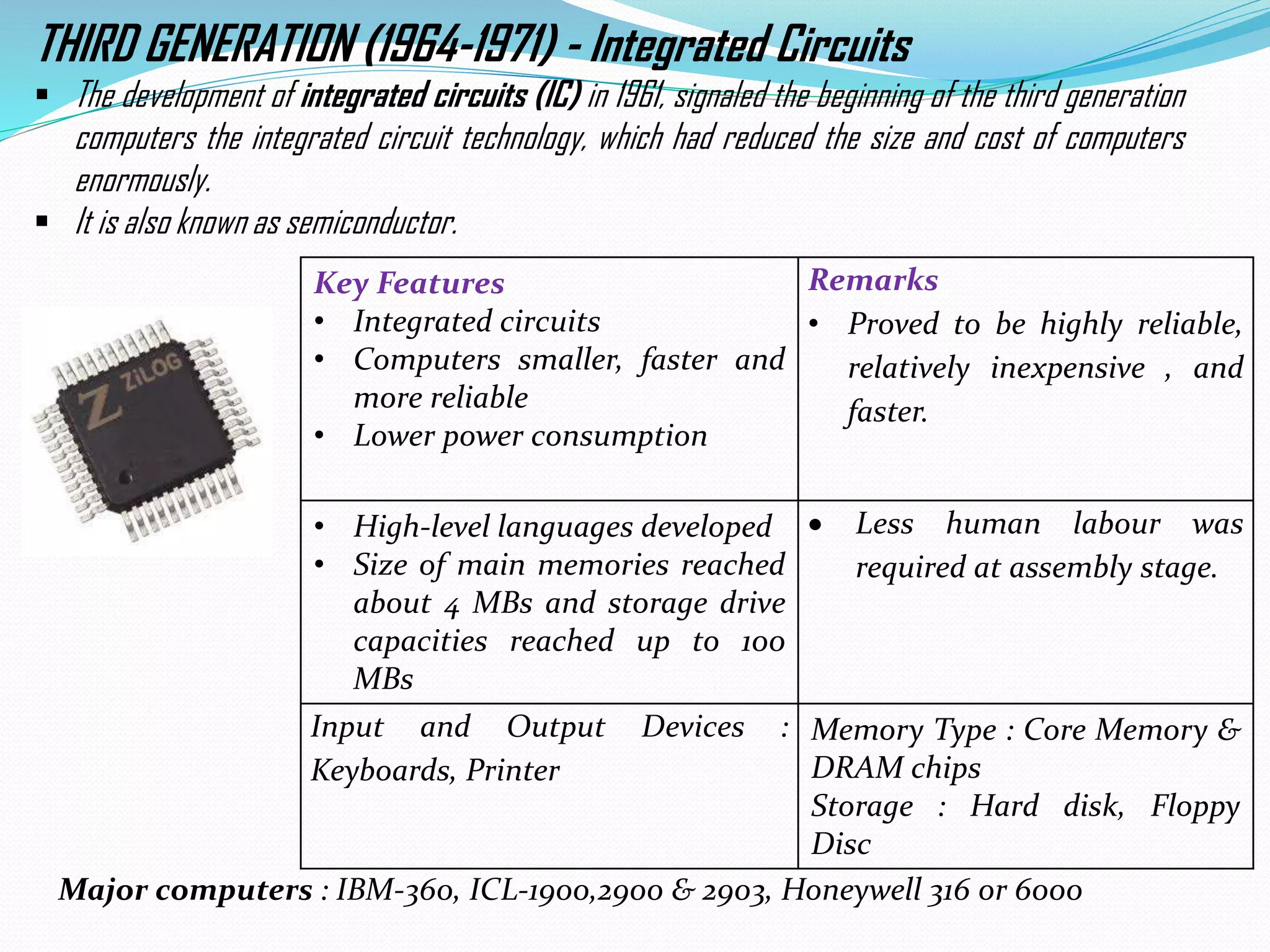
The document summarizes the evolution of information technology (IT) from the 1970s to present day. It covers the evolution of computers from early mechanical devices like the abacus to modern integrated circuits. It also discusses the evolution of storage technologies from punched cards to cloud storage. Finally, it outlines the evolution of software, including operating systems from UNIX to Windows, programming languages from machine code to artificial intelligence languages, and general software applications.