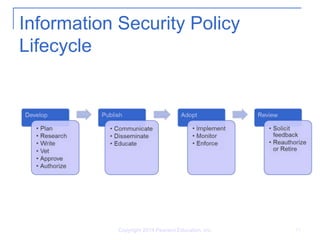
This document discusses the role and importance of policies in organizations and governments. It describes how policies provide guidance for corporate culture and civil society. The document also outlines the key phases of an information security policy lifecycle - develop, publish, adopt, and review - and lists the characteristics of a successful policy, including being endorsed, relevant, realistic, attainable, adaptable, enforceable, and inclusive.