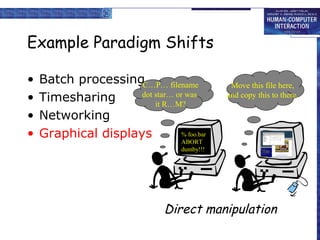
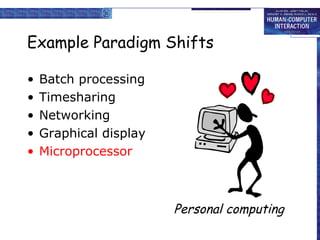
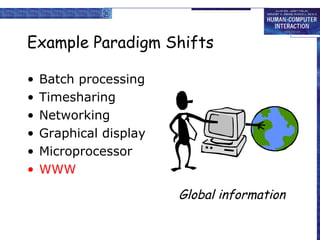
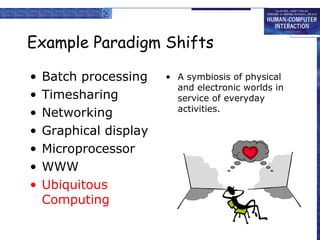
This document discusses the history of paradigms in human-computer interaction (HCI). It describes several paradigm shifts in interactive system design including: from batch processing to time-sharing and interactive computing; from networking to community computing; from graphical displays to direct manipulation; from personal computing to global information access on the World Wide Web; and from ubiquitous computing to sensor-based and context-aware interaction. Understanding these paradigm shifts is important for developing usable interactive systems and demonstrating their usability.