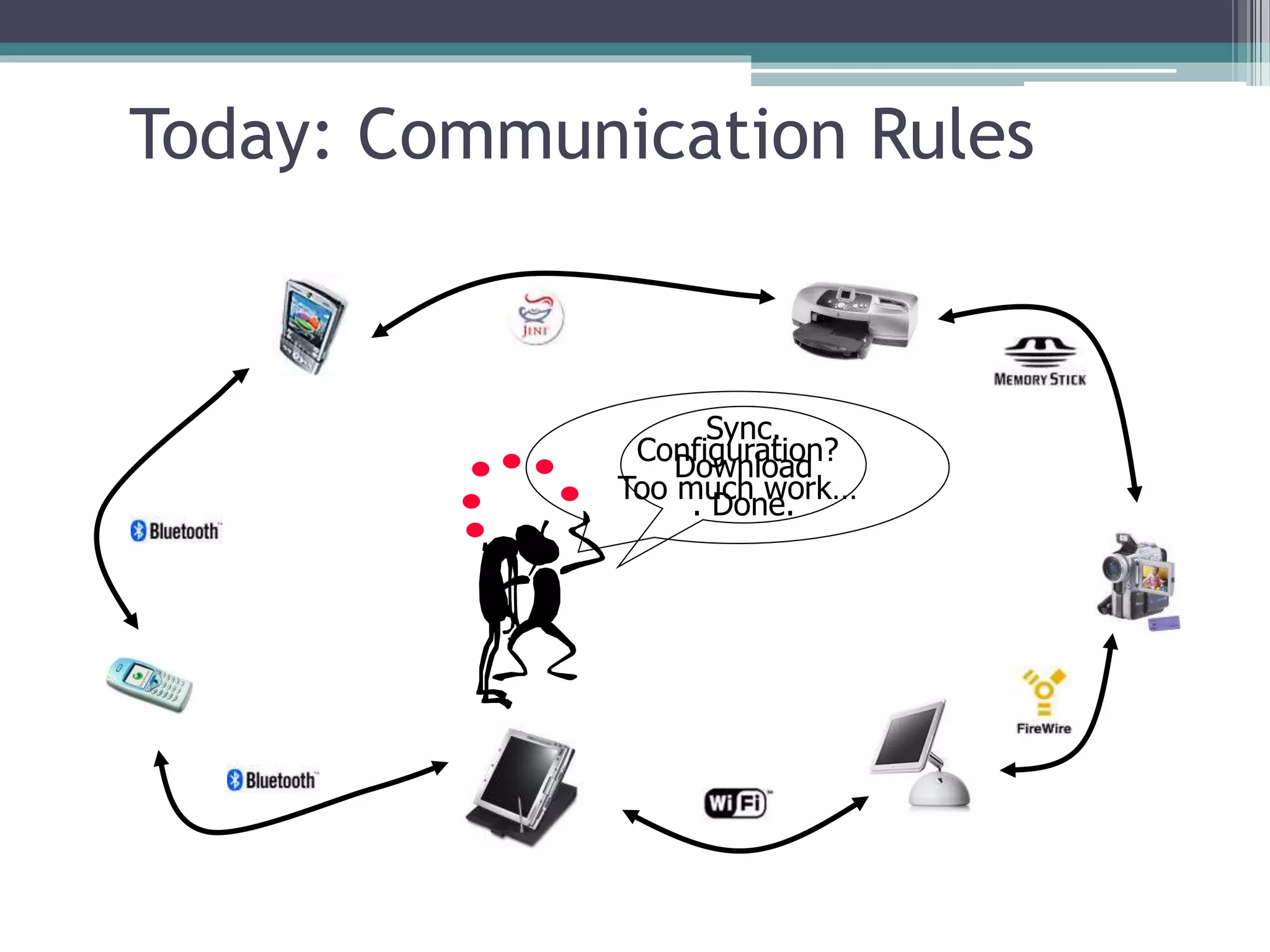
Ubiquitous computing refers to technology that is integrated into everyday life to the extent that it is indistinguishable from it. The vision is for computing services to be available anytime and anywhere through devices that are increasingly more powerful, smaller, and cheaper. Ubiquitous computing is changing daily activities by allowing people to communicate and interact with hundreds of computing devices in new ways. However, it also presents challenges in systems design, security and privacy, and how teaching and learning can take advantage of ubiquitous access to resources and tools.