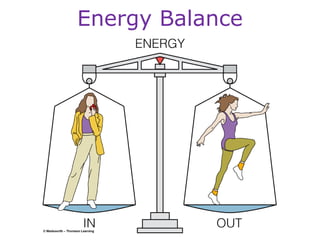
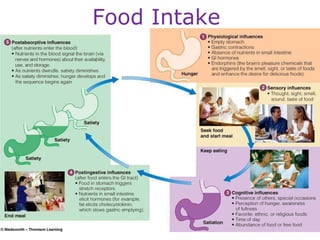
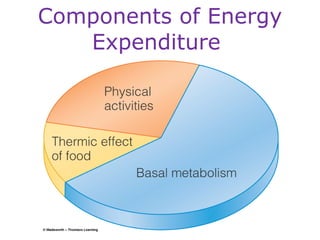
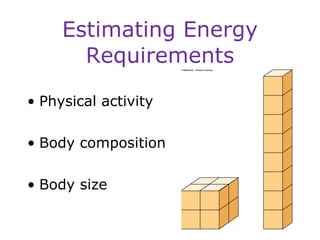
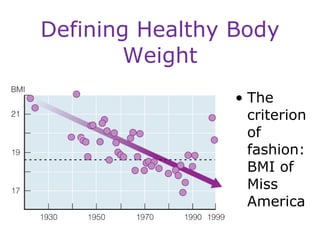
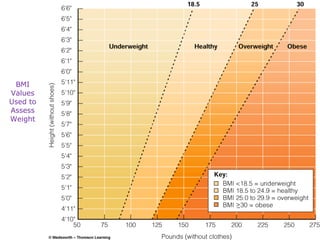
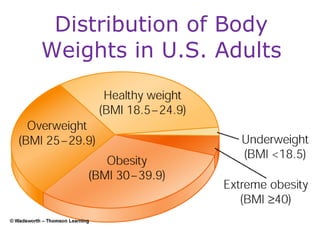
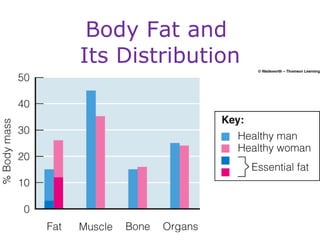
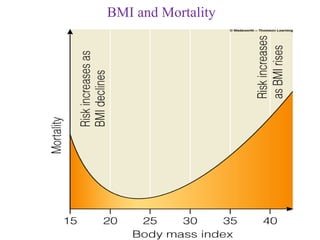
This document discusses various topics related to energy balance, body composition, estimating energy requirements, defining healthy body weight, measuring body fat, and weight loss diets. It covers direct and indirect calorimetry, factors that influence food intake and energy expenditure, methods for assessing body weight and composition, health risks associated with being underweight or overweight, and claims made by popular high-protein low-carbohydrate diets.