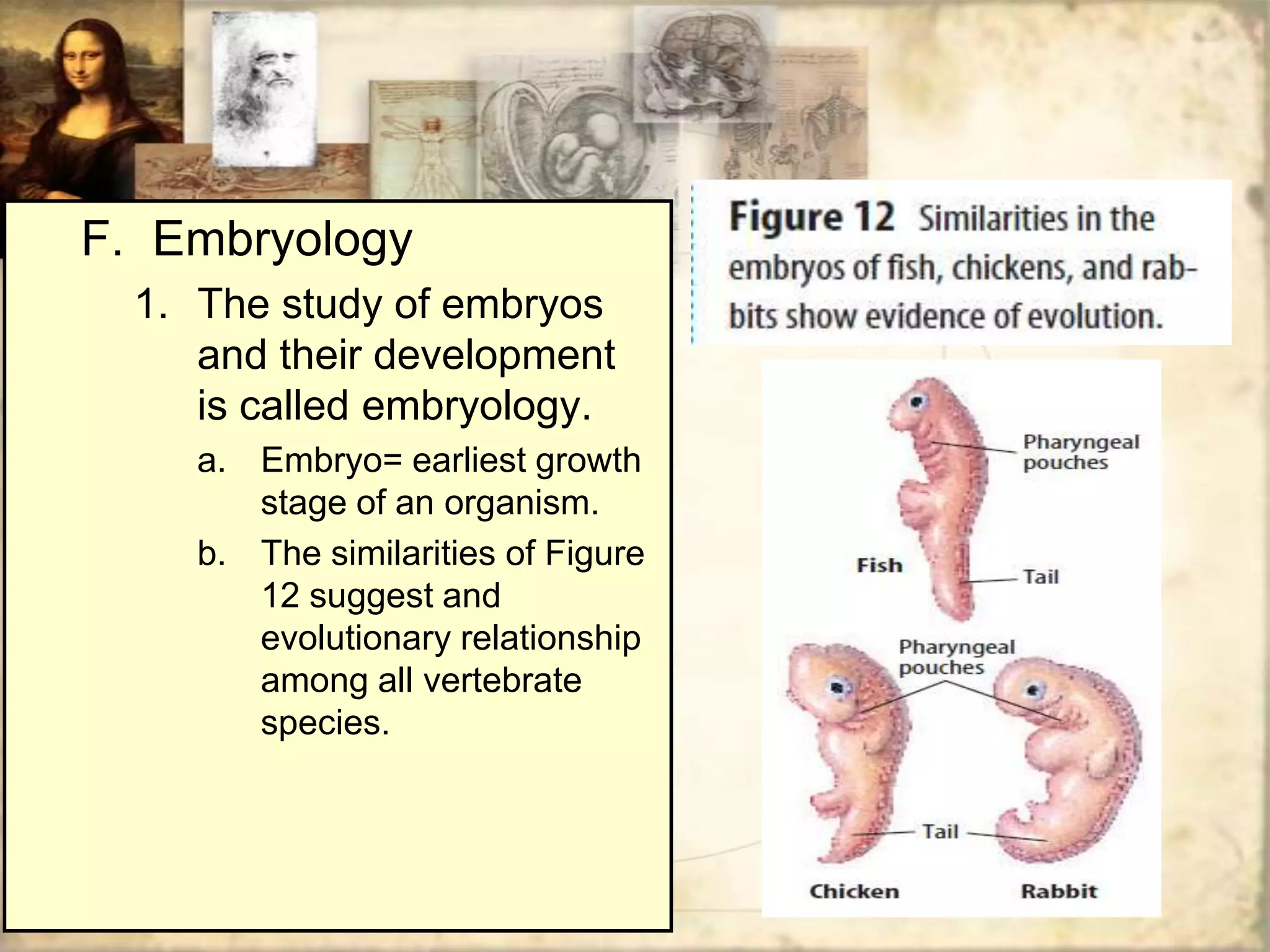
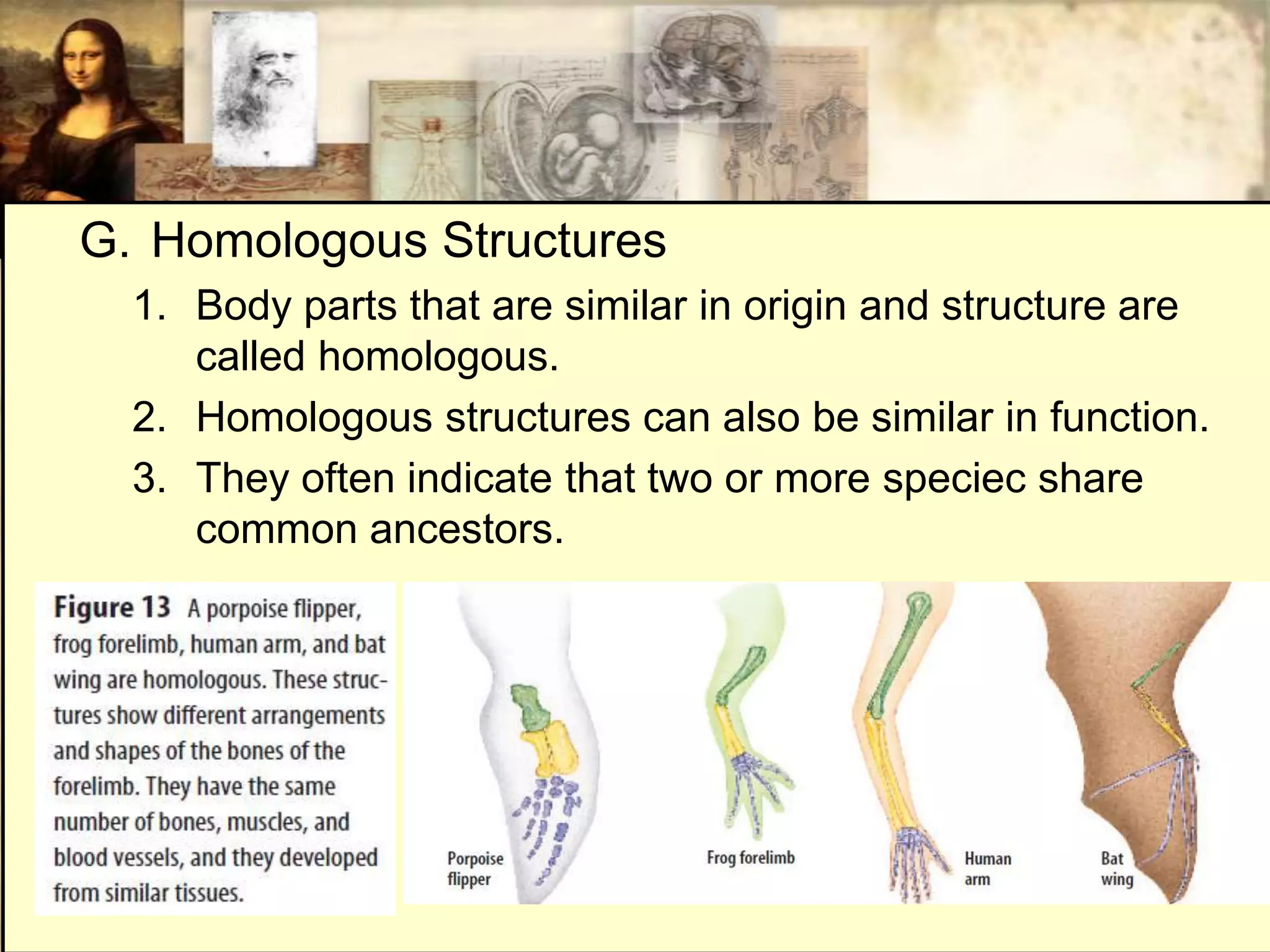
This document discusses various clues that provide evidence for evolution, including fossils, homologous structures, and vestigial structures. It explains that fossils are formed from the remains of ancient organisms and are found within sedimentary rock layers. By examining fossils found within different rock layers, paleontologists can determine organisms' approximate ages and how they changed over time. The arrangement of fossils also indicates that simpler life forms predated more complex ones. Homologous structures and vestigial structures in related species also suggest a shared evolutionary history. DNA evidence further supports how extinct species are related to modern descendants.