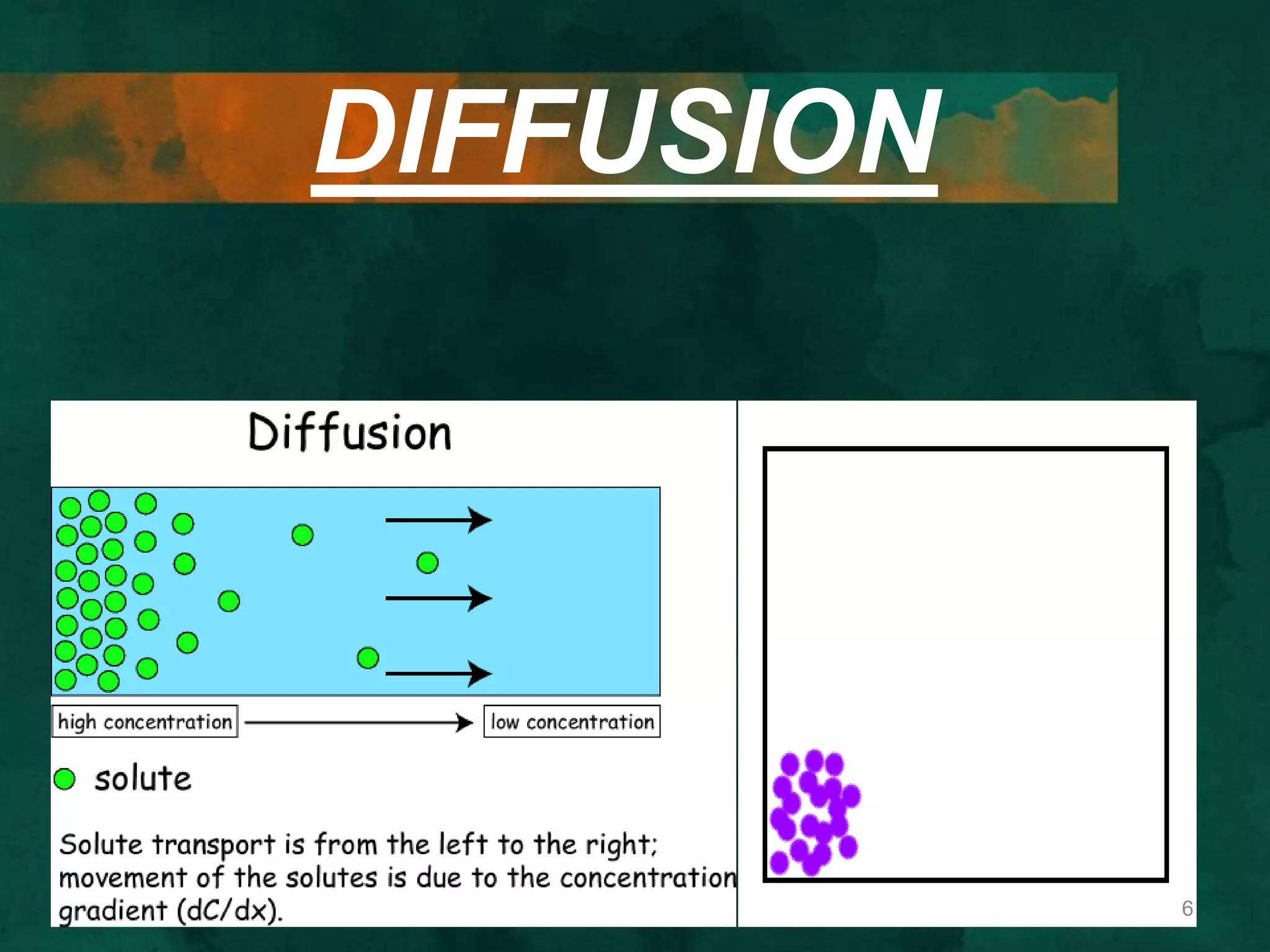
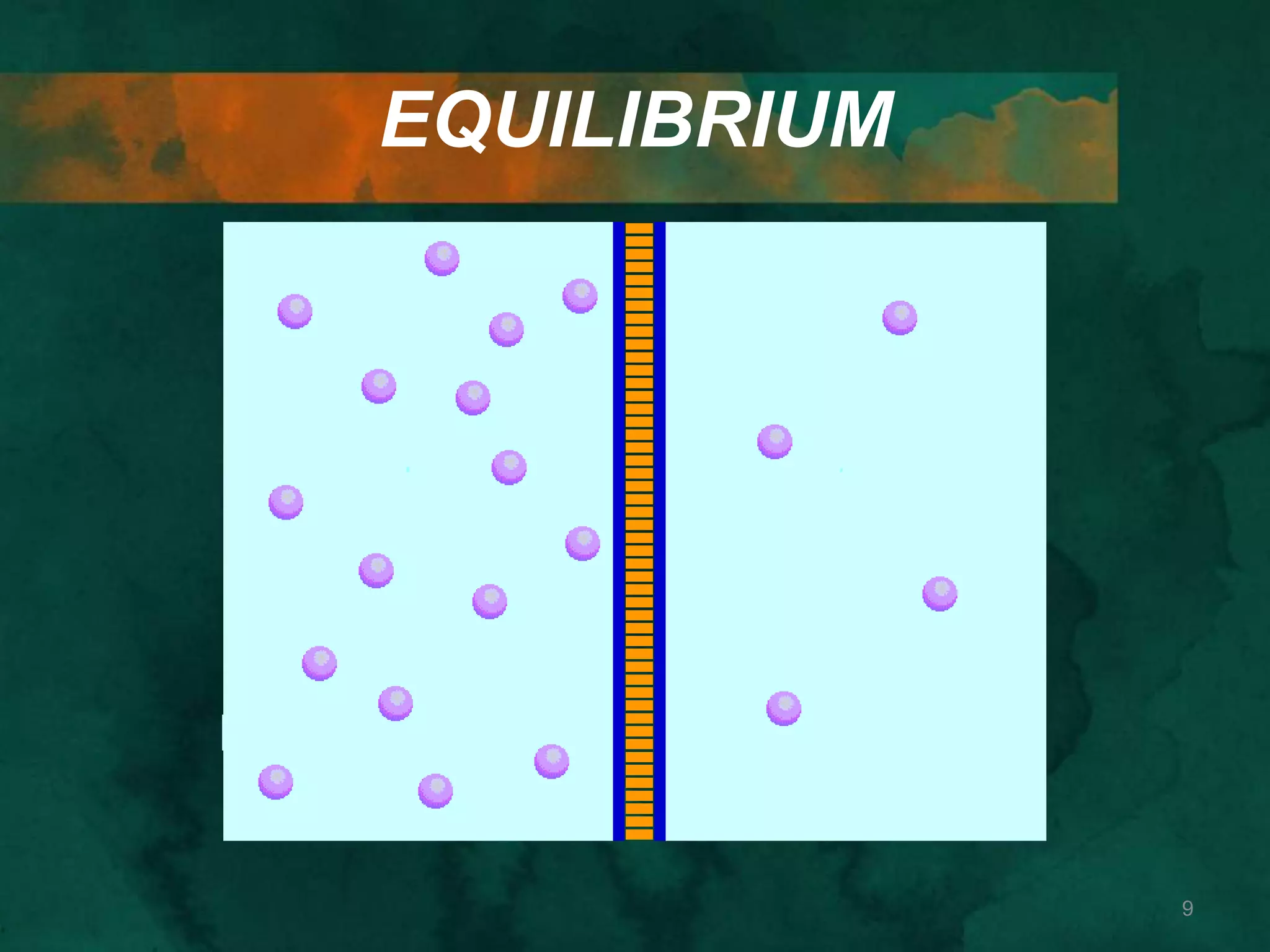
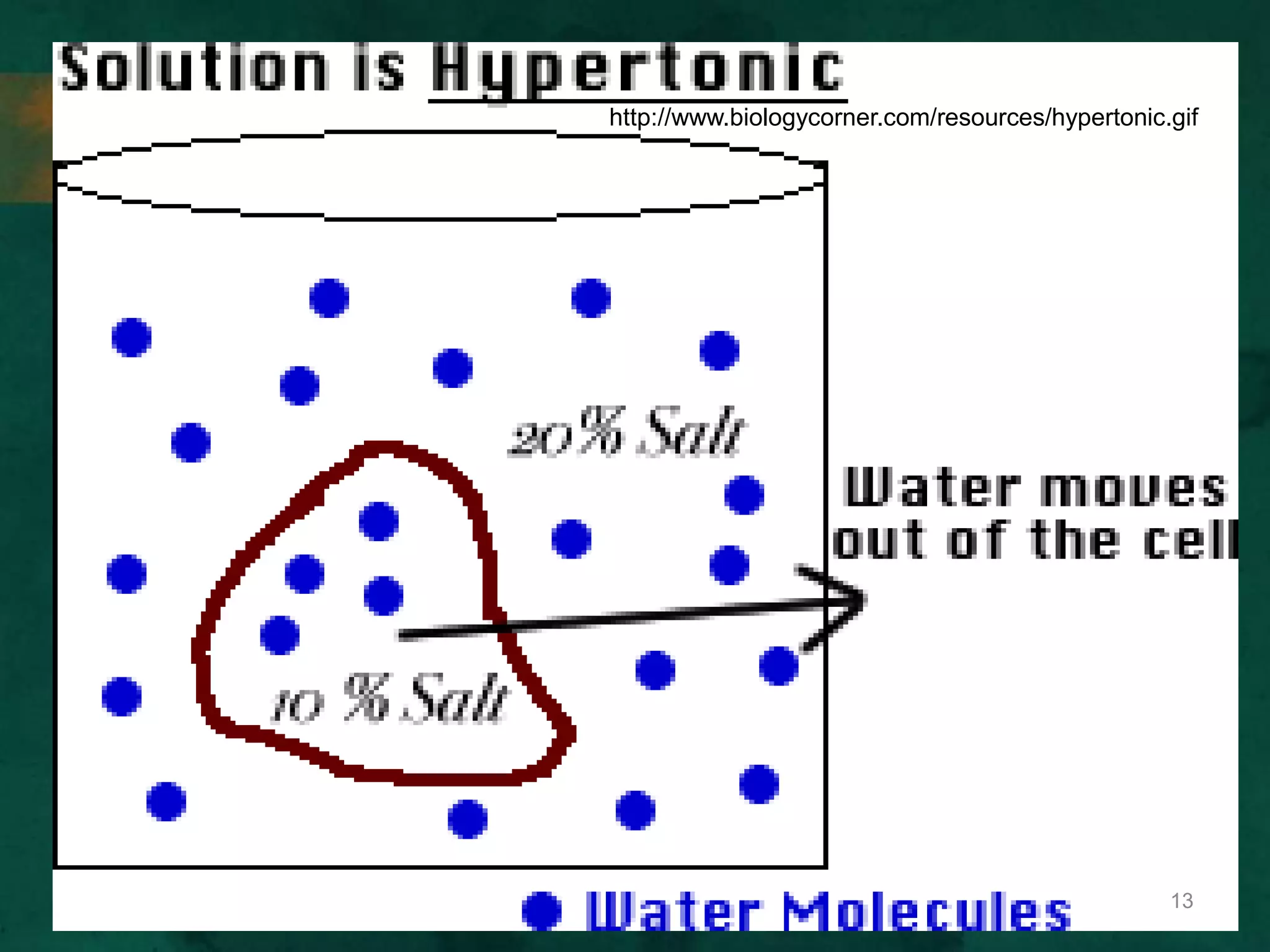
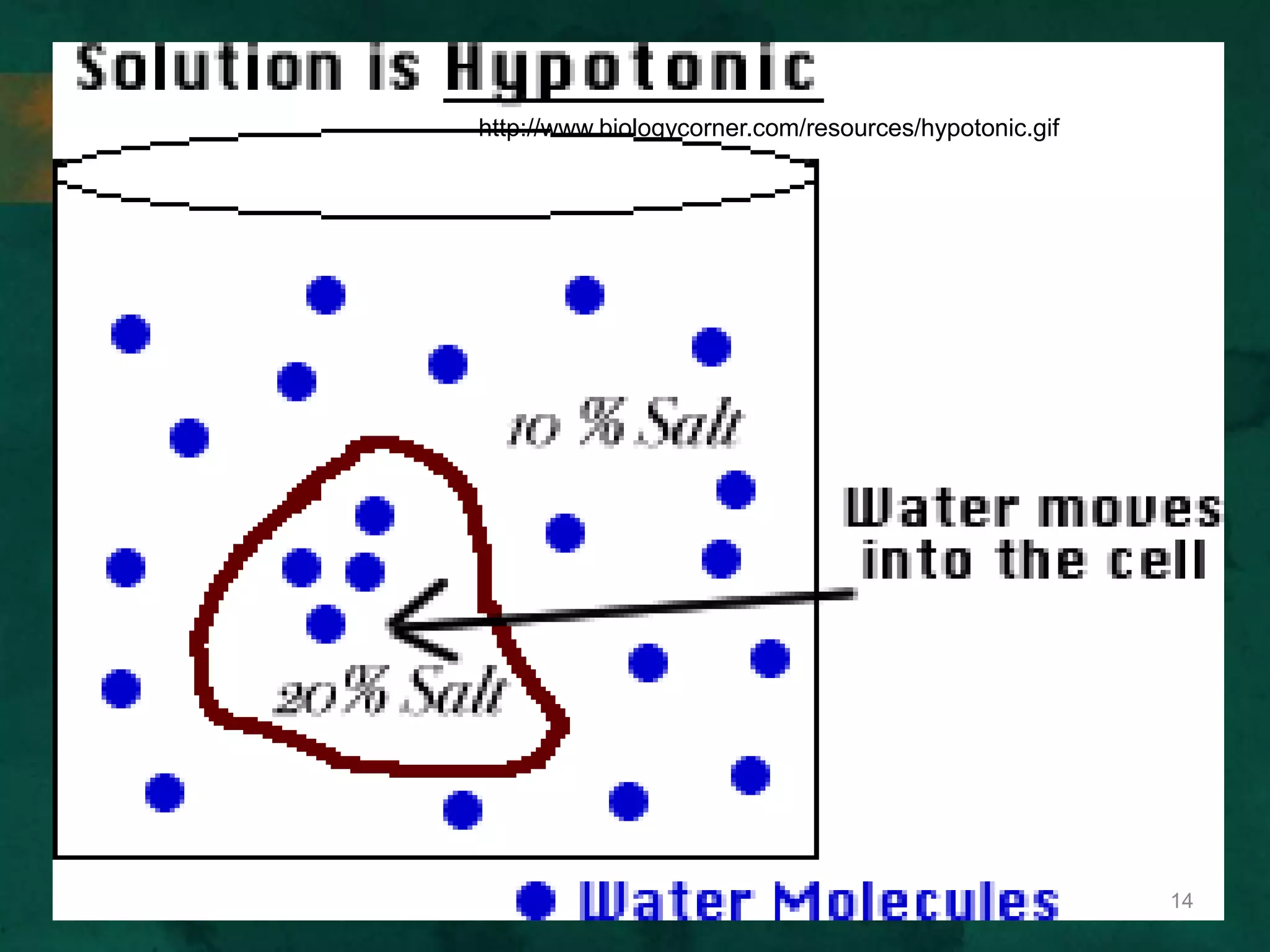
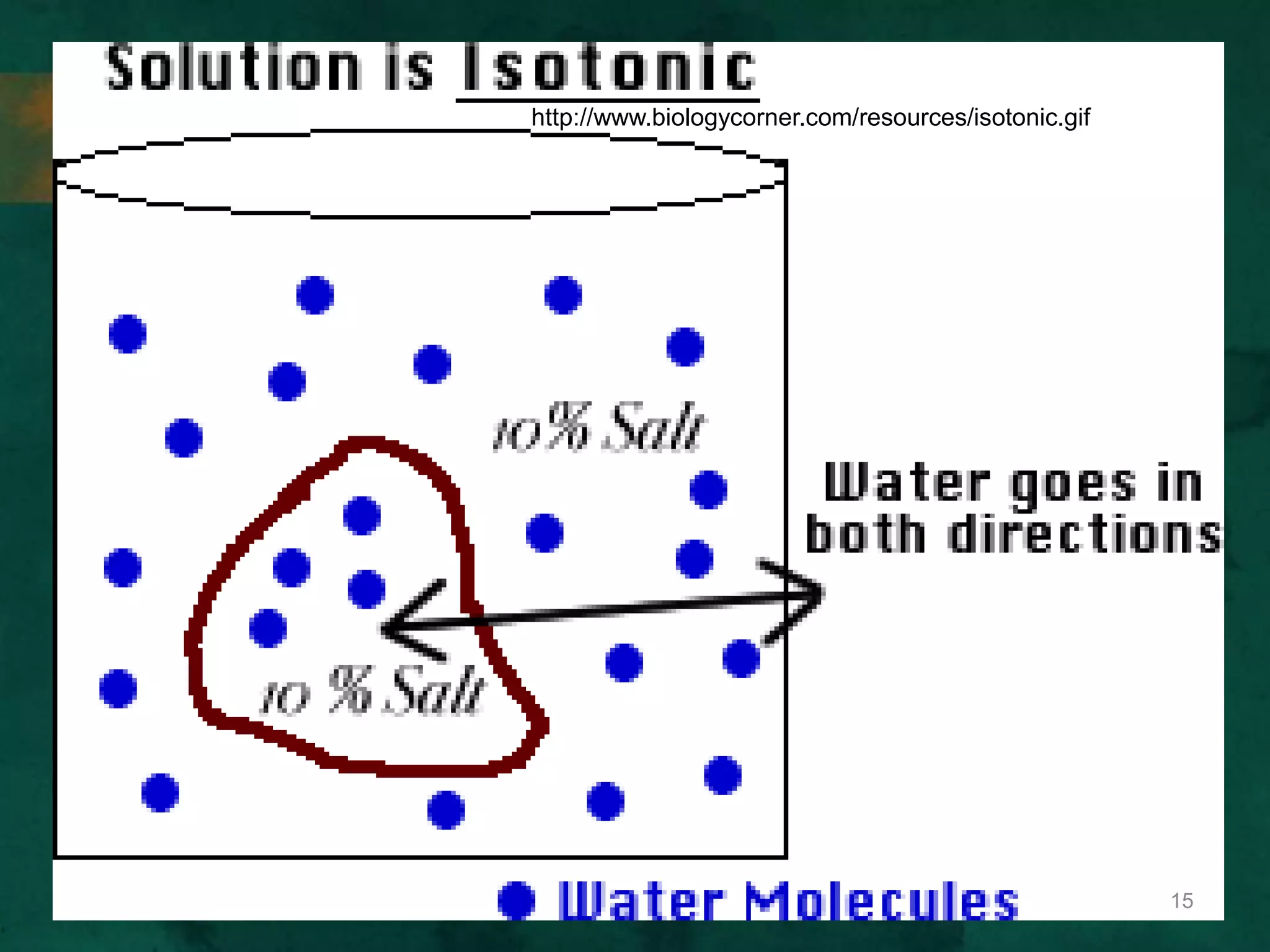
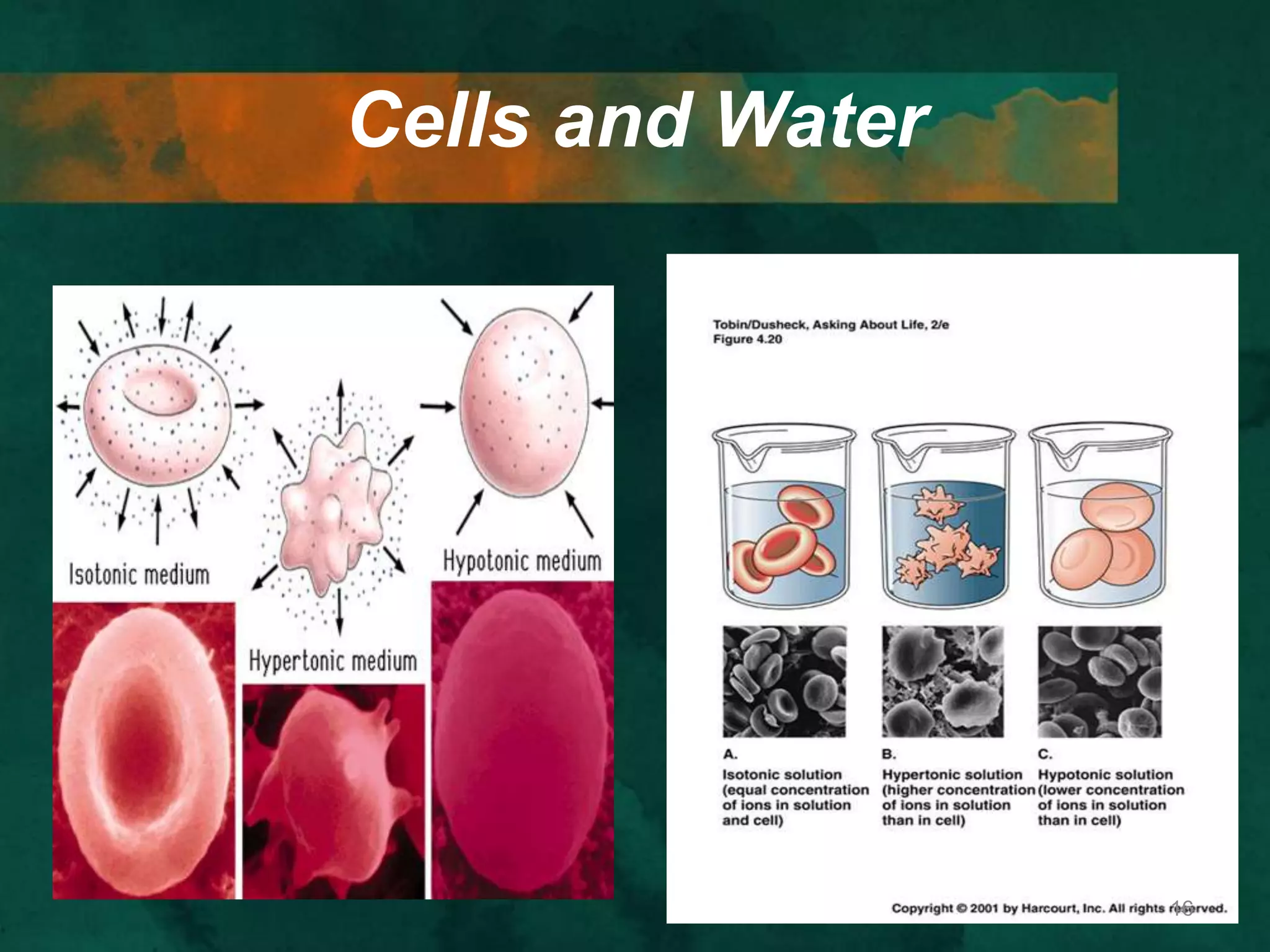
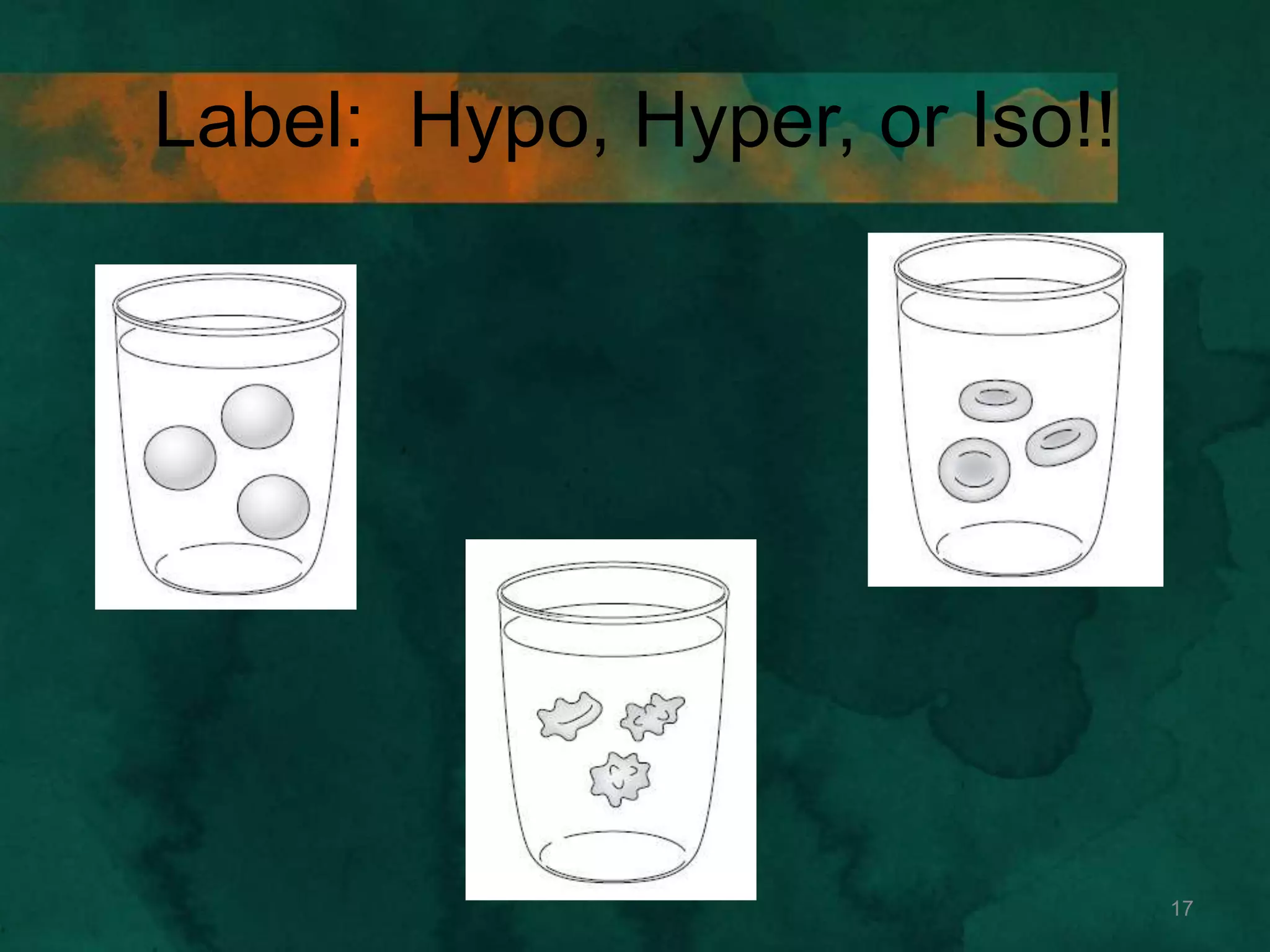
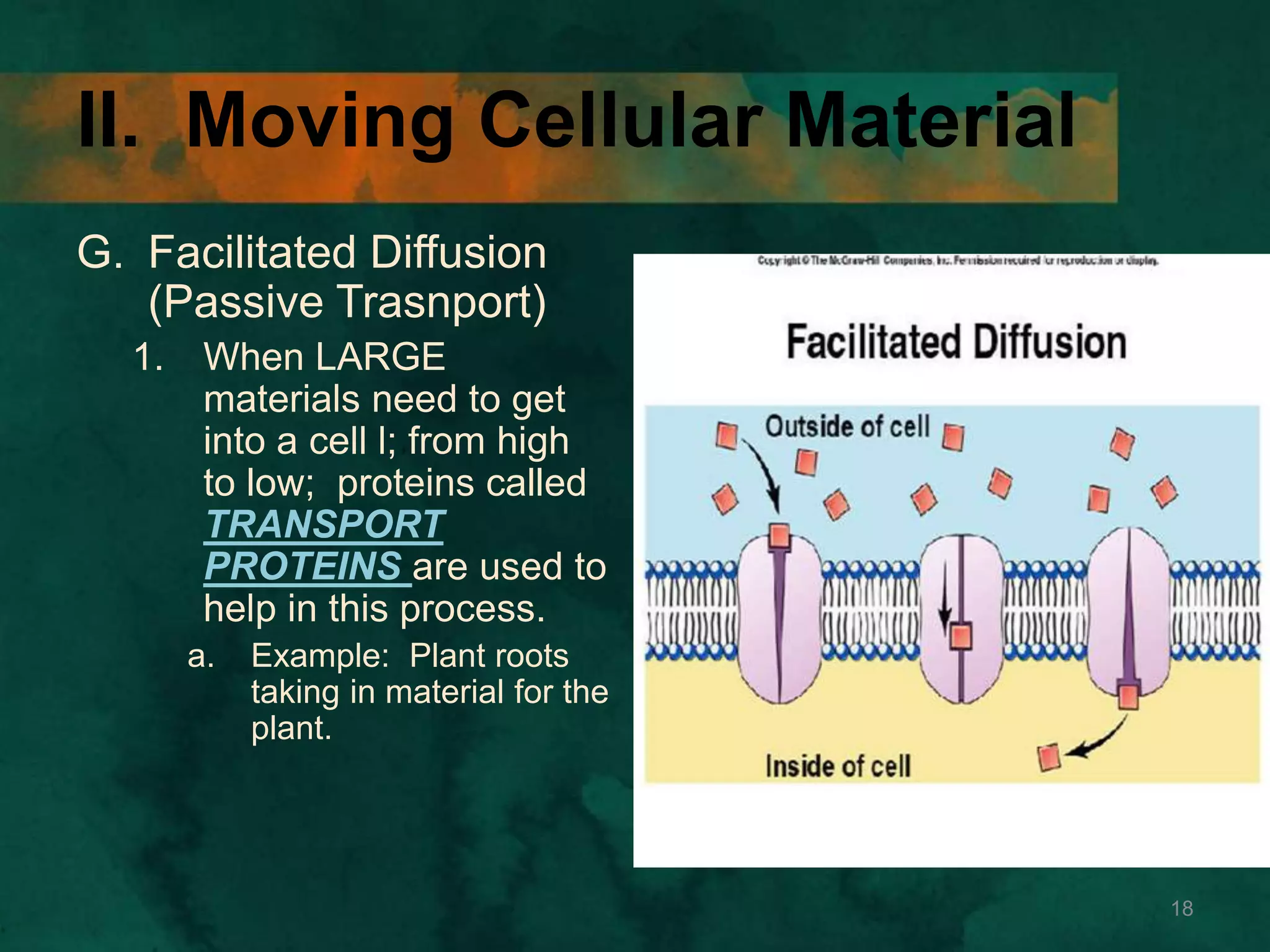
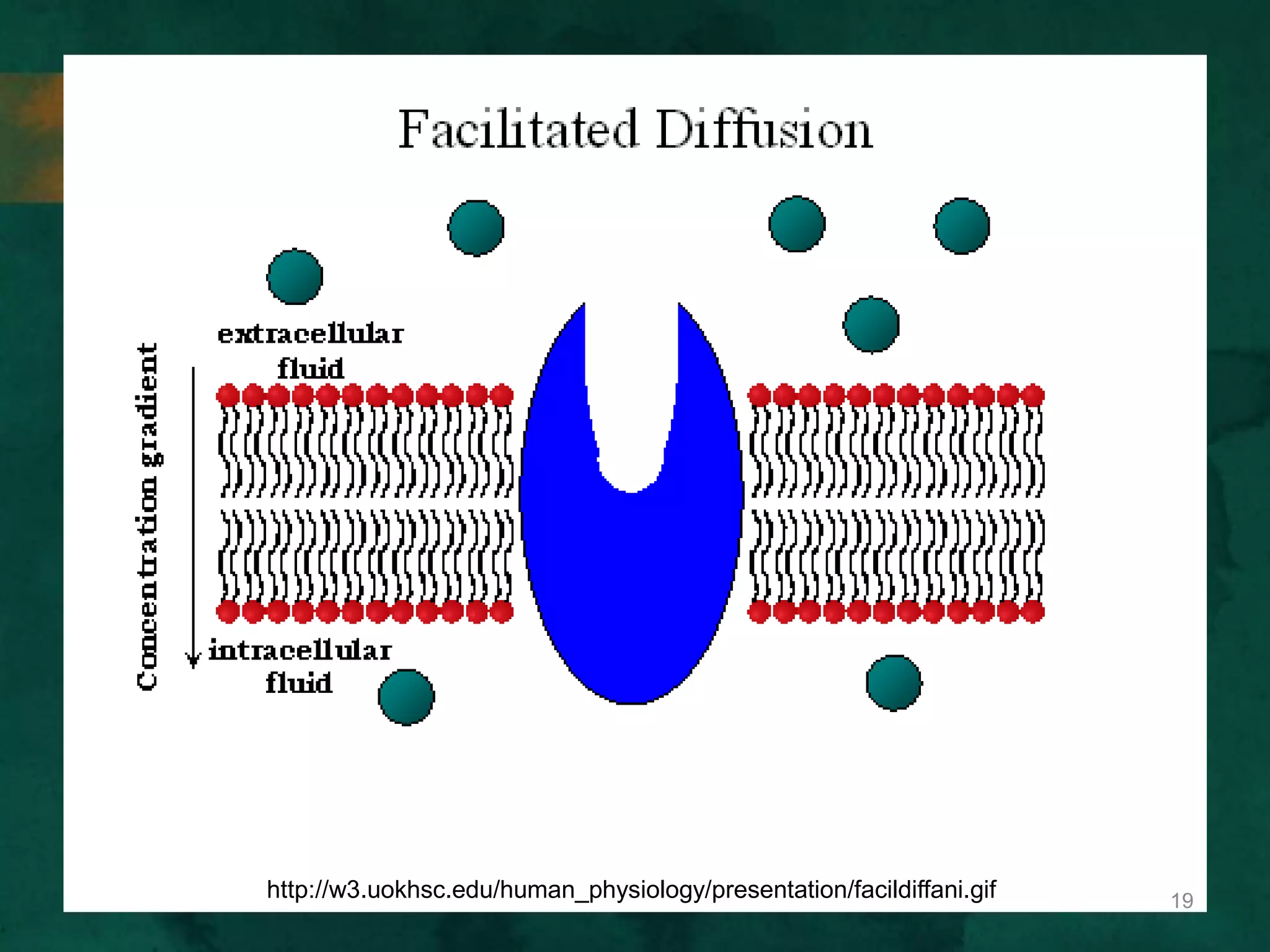
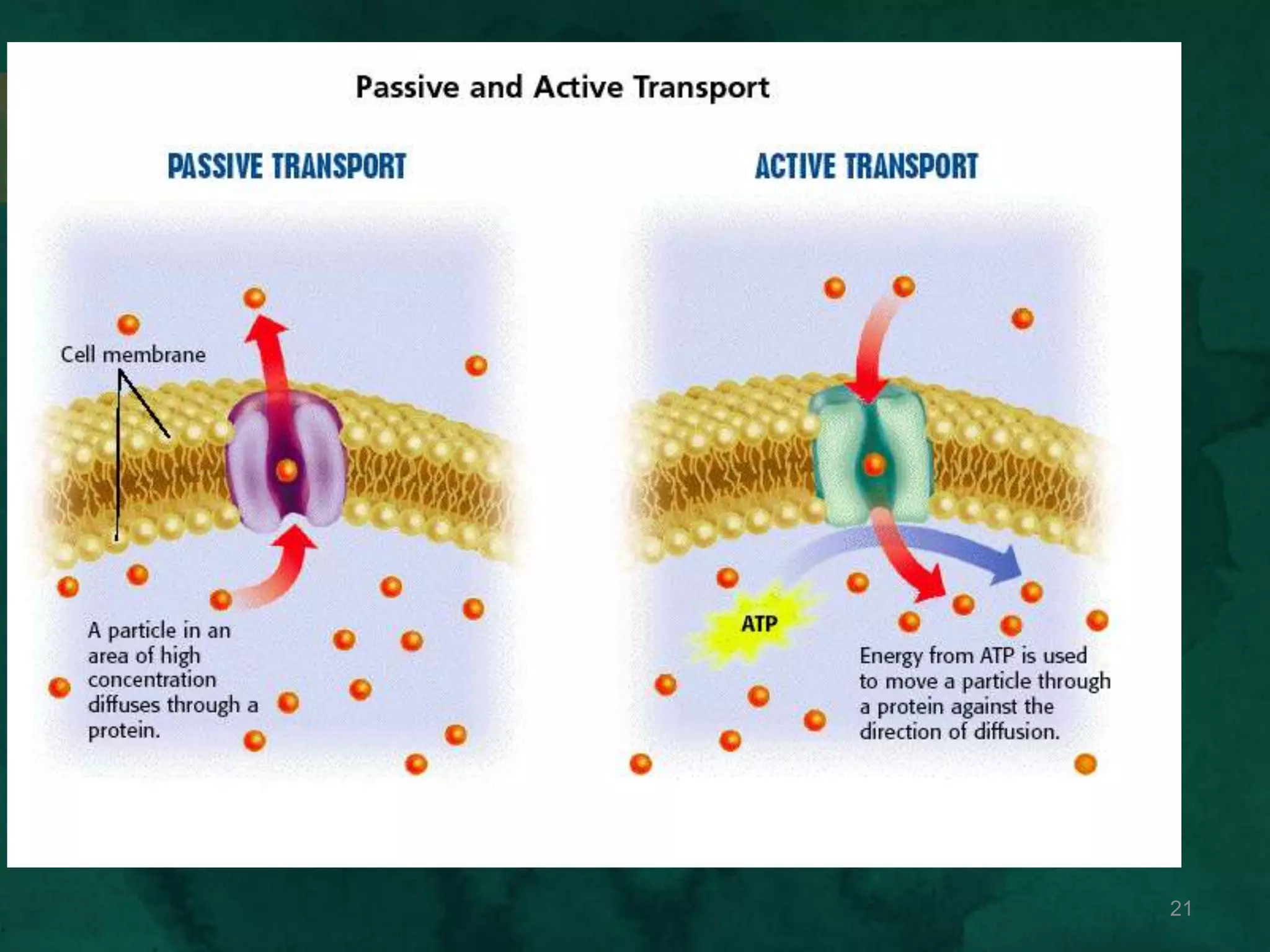
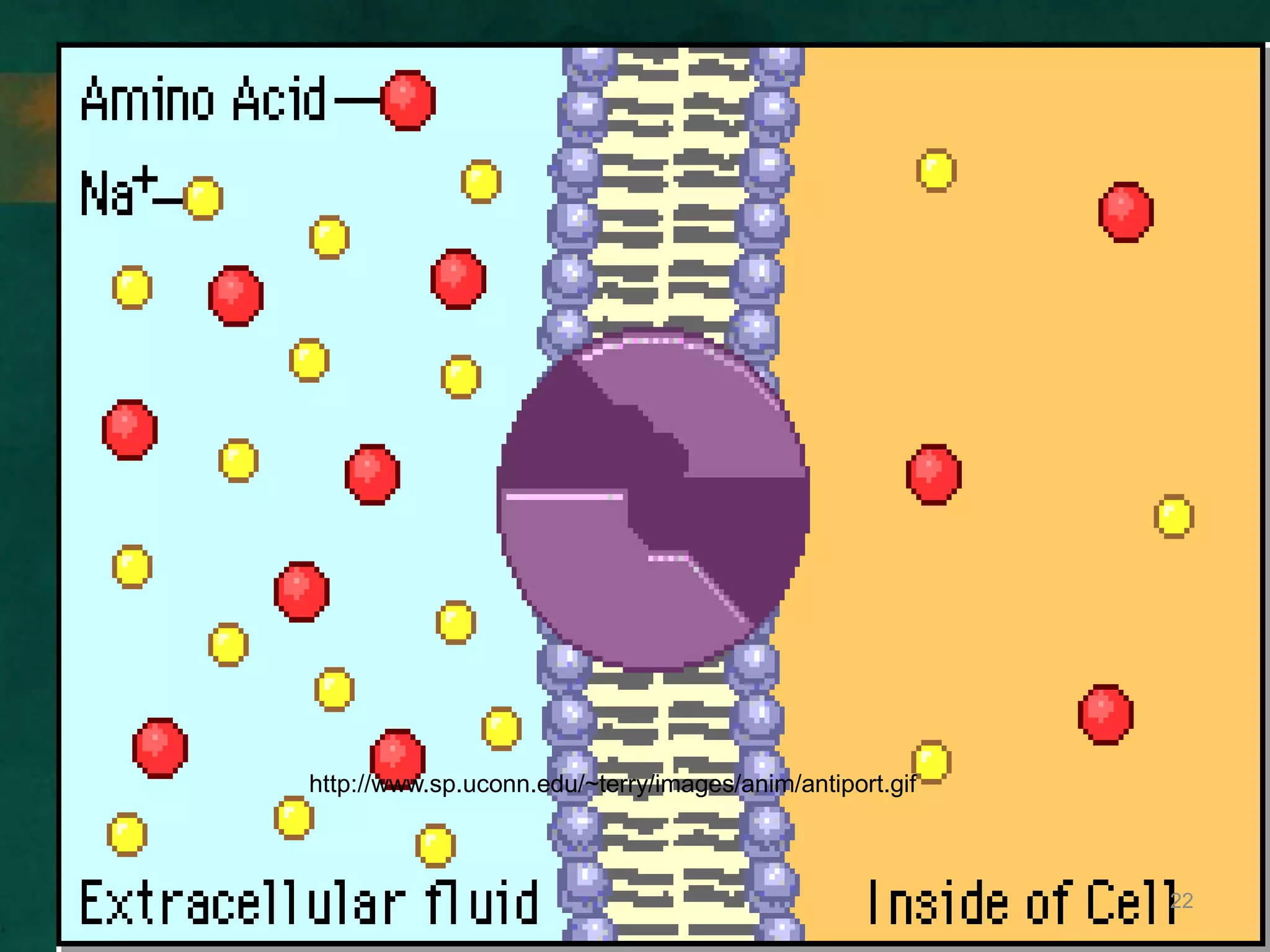
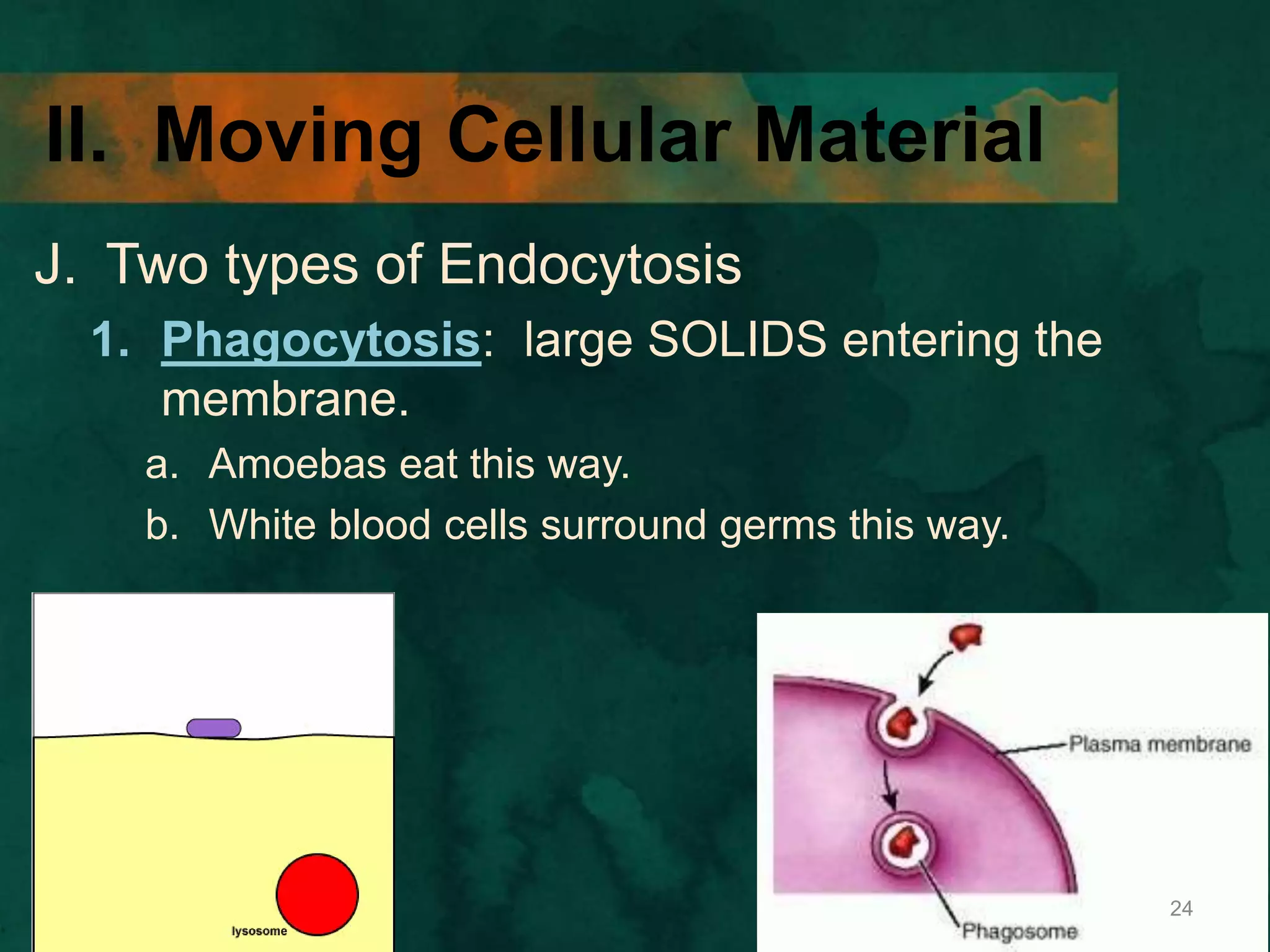
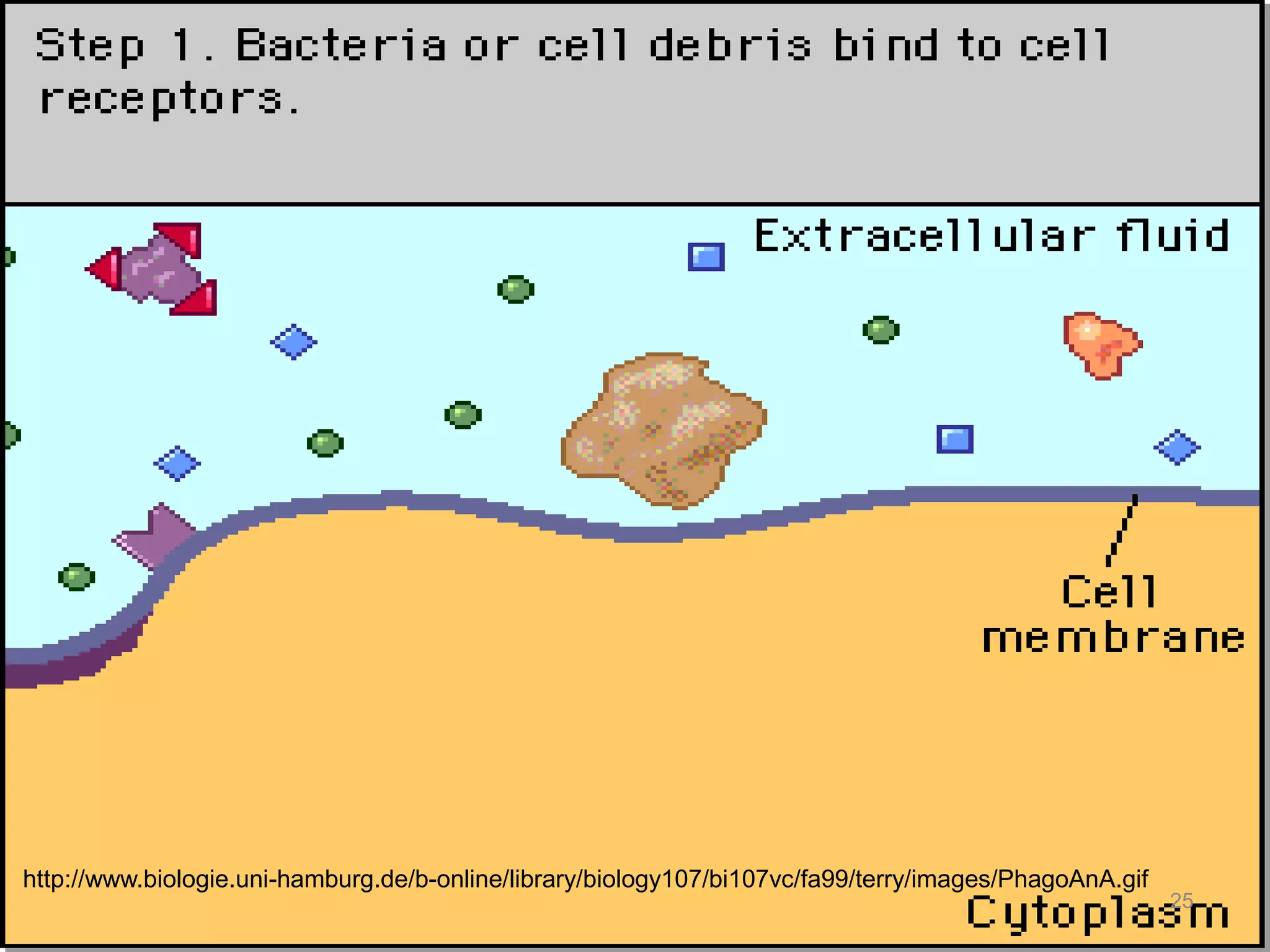
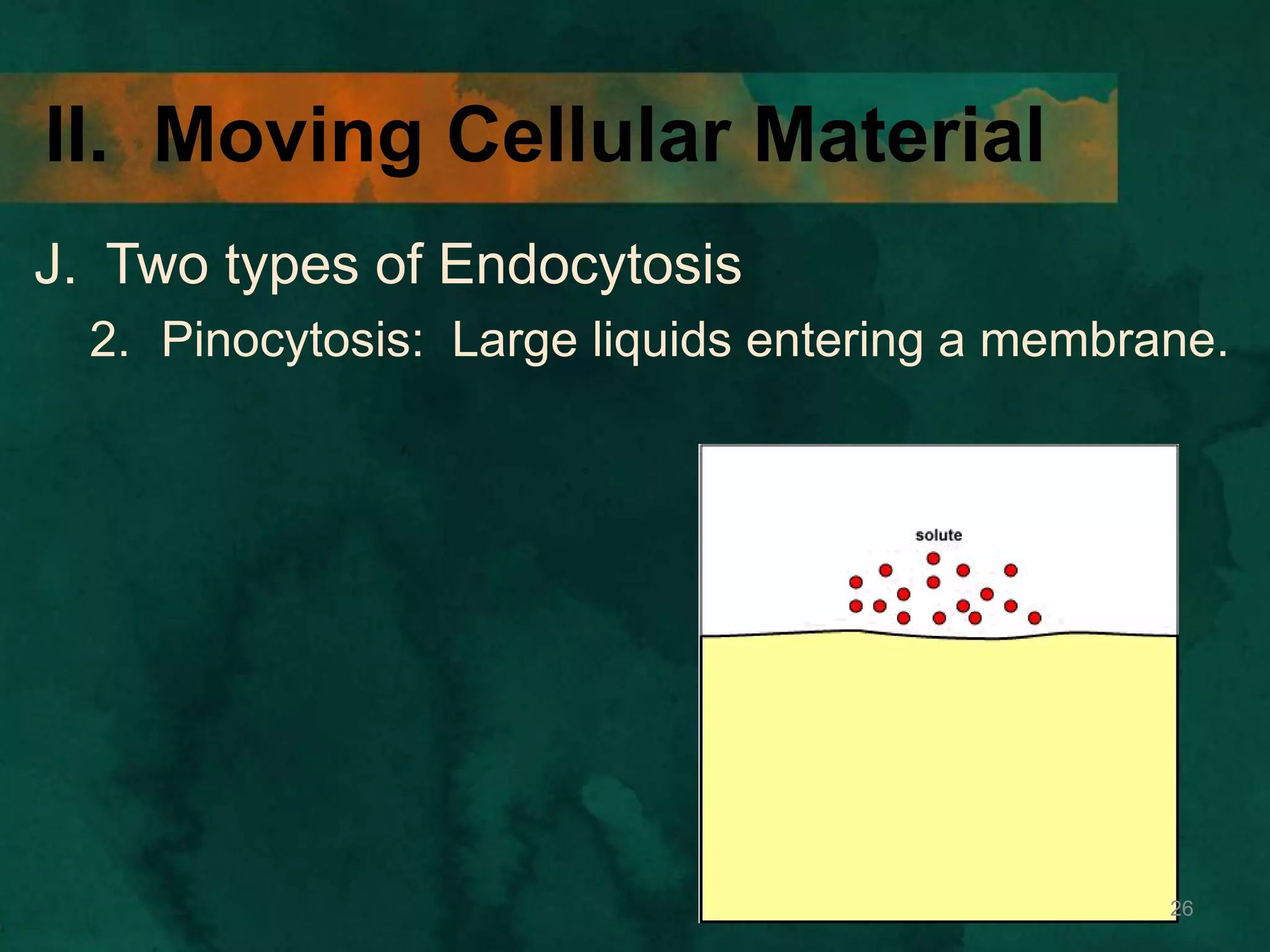
This document discusses how cells transport materials across their selectively permeable membranes. It describes three main types of transport: passive transport which includes diffusion and osmosis and moves substances down concentration gradients without energy; facilitated diffusion which uses transport proteins to move larger molecules; and active transport which moves substances against concentration gradients using energy from ATP with the help of transport proteins. Endocytosis and exocytosis are also covered as forms of active transport where large particles enter or leave cells through membrane invagination and budding.