Embed presentation
Download to read offline



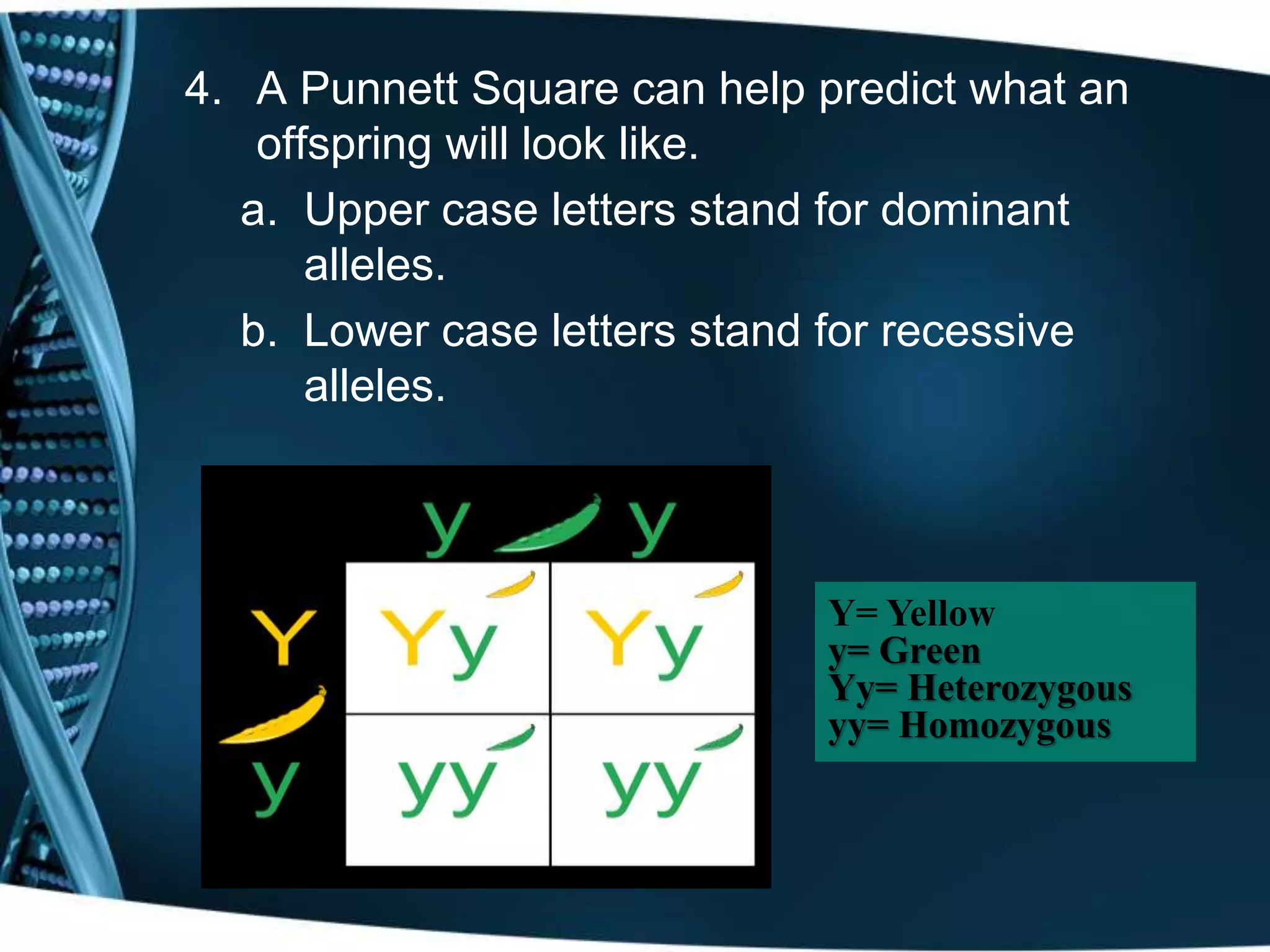


The document discusses heredity and genetics. It explains that genes on chromosomes control traits that are passed from parents to offspring. These genes have different forms called alleles. The study of how traits are inherited is genetics. The section then discusses Gregor Mendel's contributions as the father of genetics, including his use of mathematics and experiments with pea plants to understand dominant and recessive alleles and heredity over generations. It also defines key genetics terms like genotype, phenotype, homozygous, and heterozygous.






