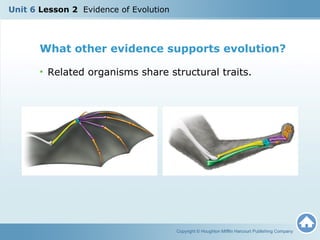
This document discusses different types of evidence that support the theory of evolution, including fossils, anatomical similarities, and DNA comparisons. Fossils provide evidence that organisms have changed over long periods of time as they are found in different rock layers. Similarities in anatomical structures and DNA between organisms indicate they share a common ancestor. Transitional fossils help fill in gaps in the fossil record and provide evidence of how organisms gradually evolved over generations.