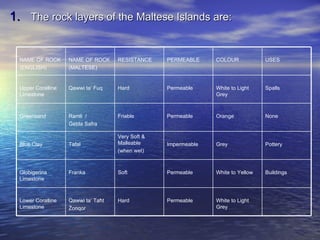
The document discusses the different types of rocks that make up the Maltese Islands, which are primarily marine sedimentary rocks. It describes how these rocks were formed over millions of years through the accumulation of sediment, silt, and remains of sea creatures on the seafloor. The rocks were later uplifted due to pressure from colliding tectonic plates under Africa and Europe. The document also gives examples of different types of weathering that can break down rocks, such as chemical weathering from acid rain, physical weathering from frost damage or expansion/contraction, and biological weathering caused by organisms.