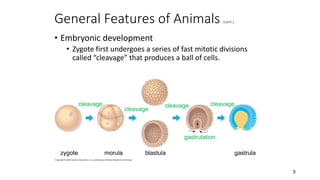
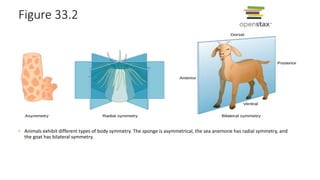
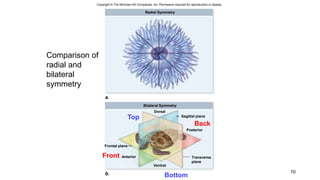
1. Animals exhibit different types of symmetry and levels of complexity, ranging from asymmetrical sponges to bilaterally symmetrical organisms like humans.
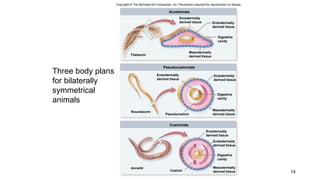
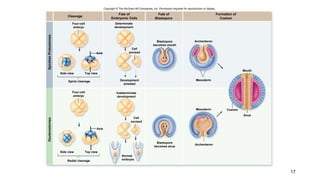
2. Key transitions in animal evolution include the development of tissues, body cavities, patterns of embryonic development, and segmentation.
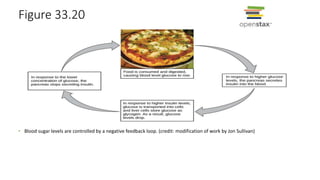
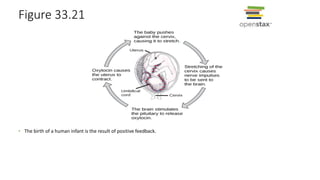
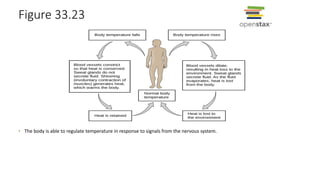
3. Animals use homeostasis, negative feedback loops, and positive feedback to maintain internal stability and regulate processes like glucose levels and childbirth.