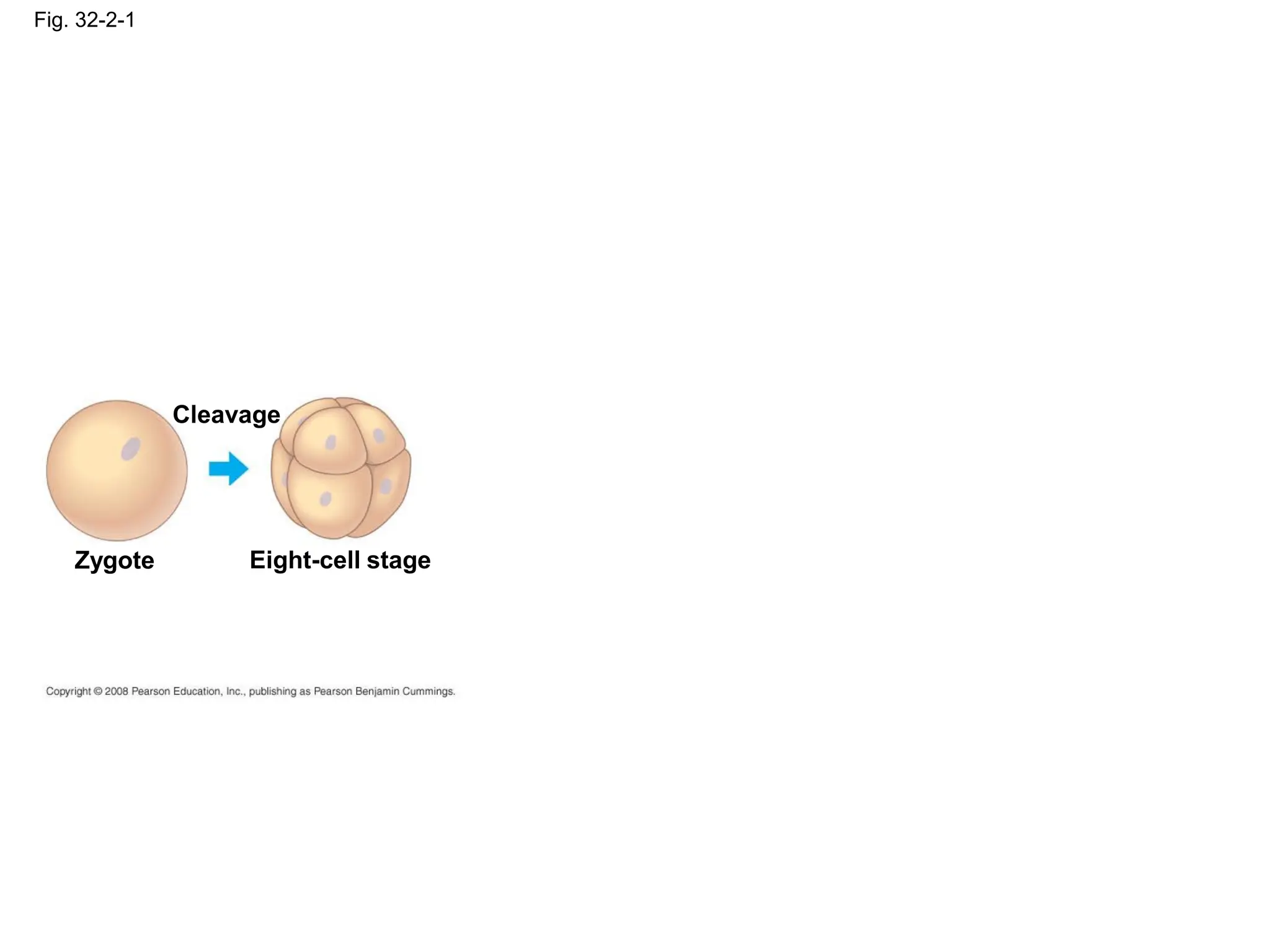
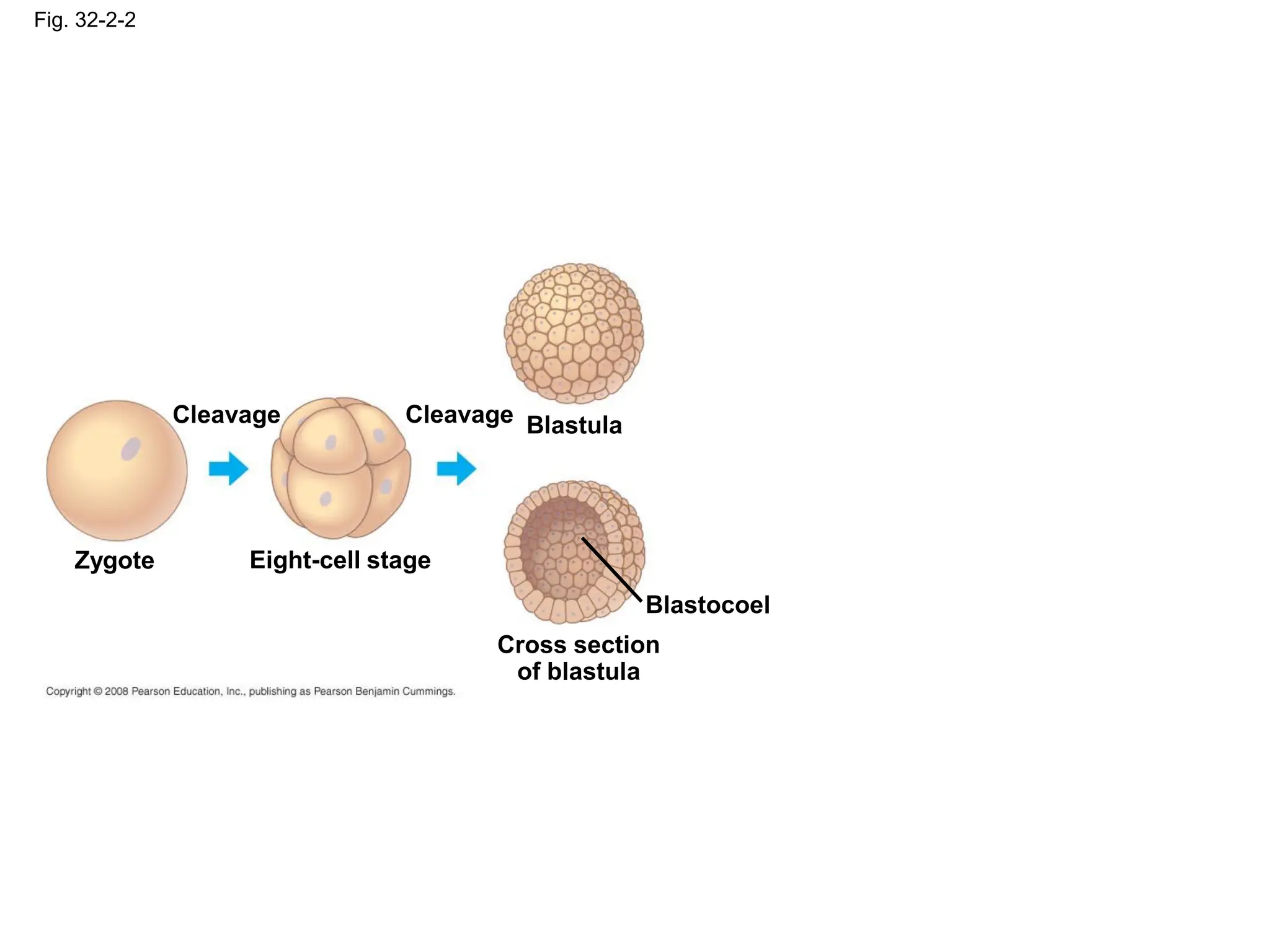
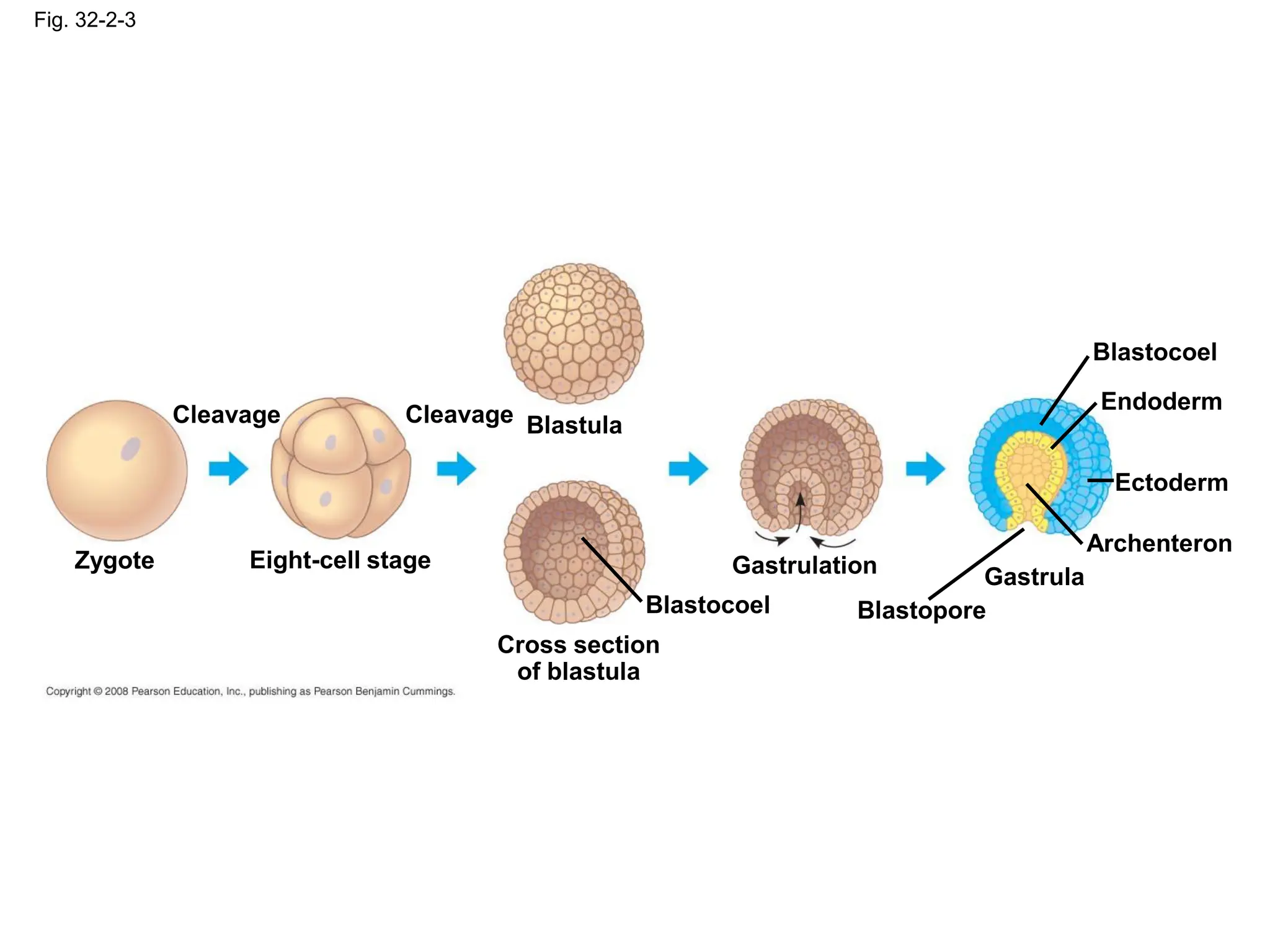
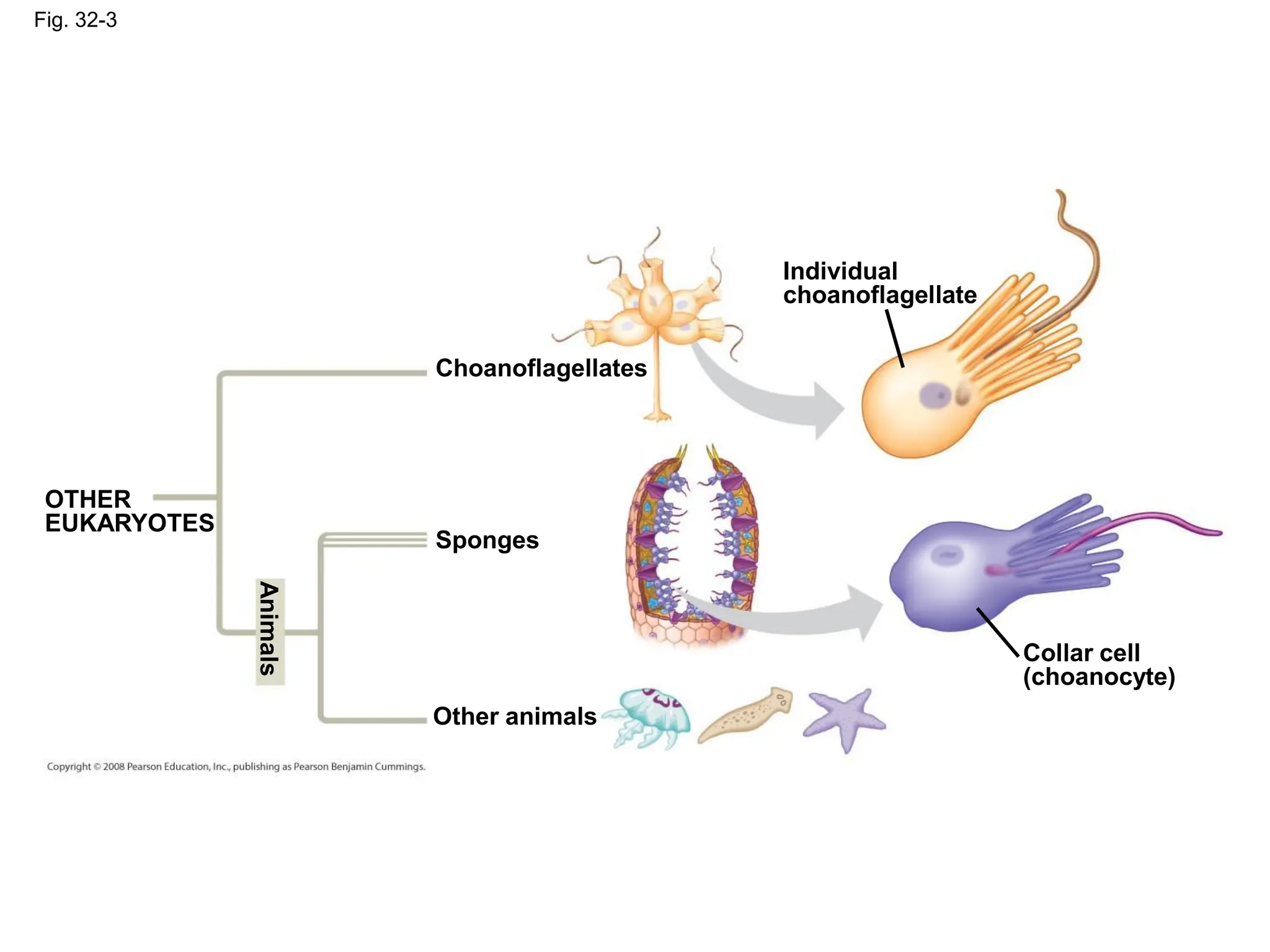
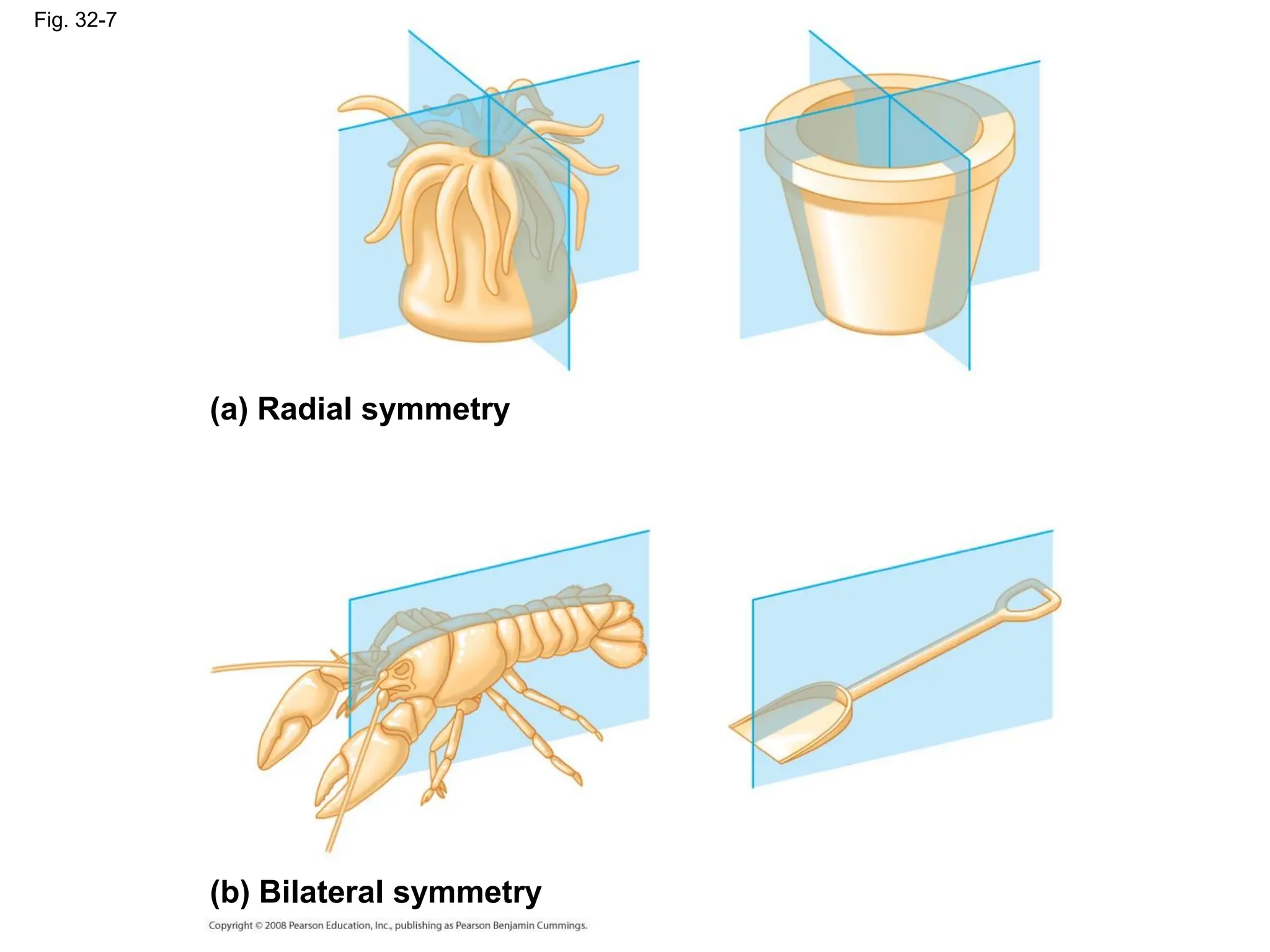
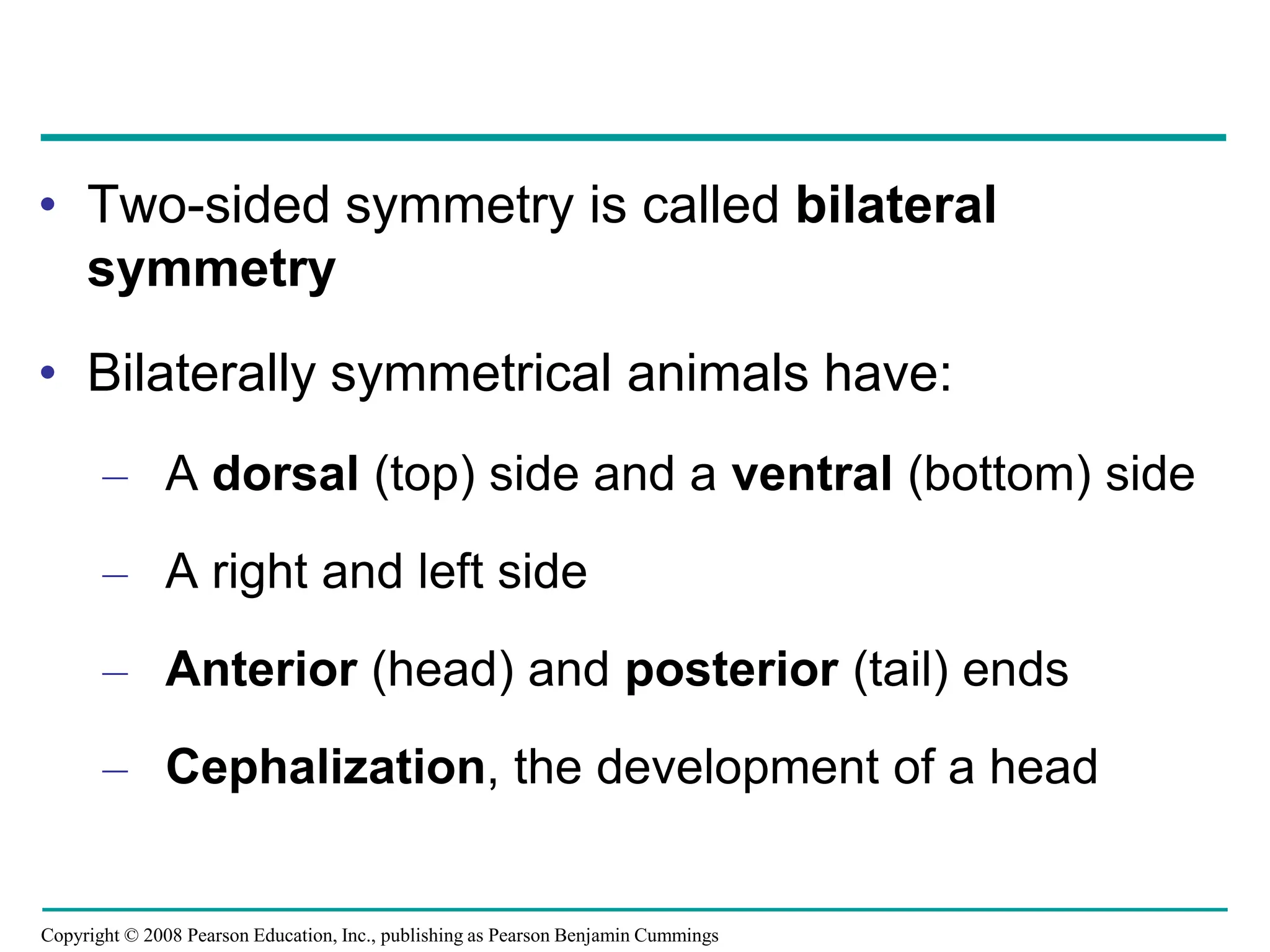
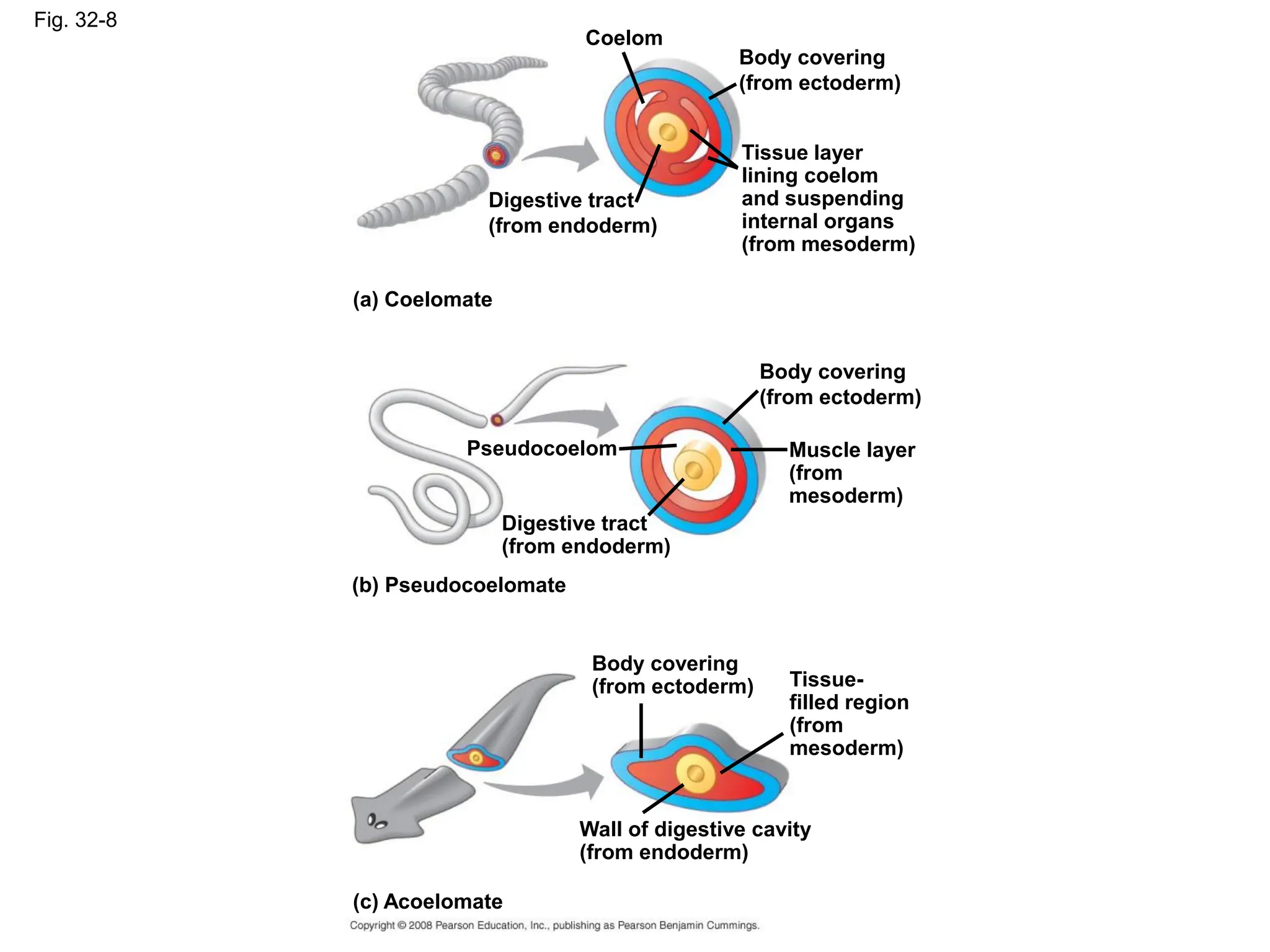
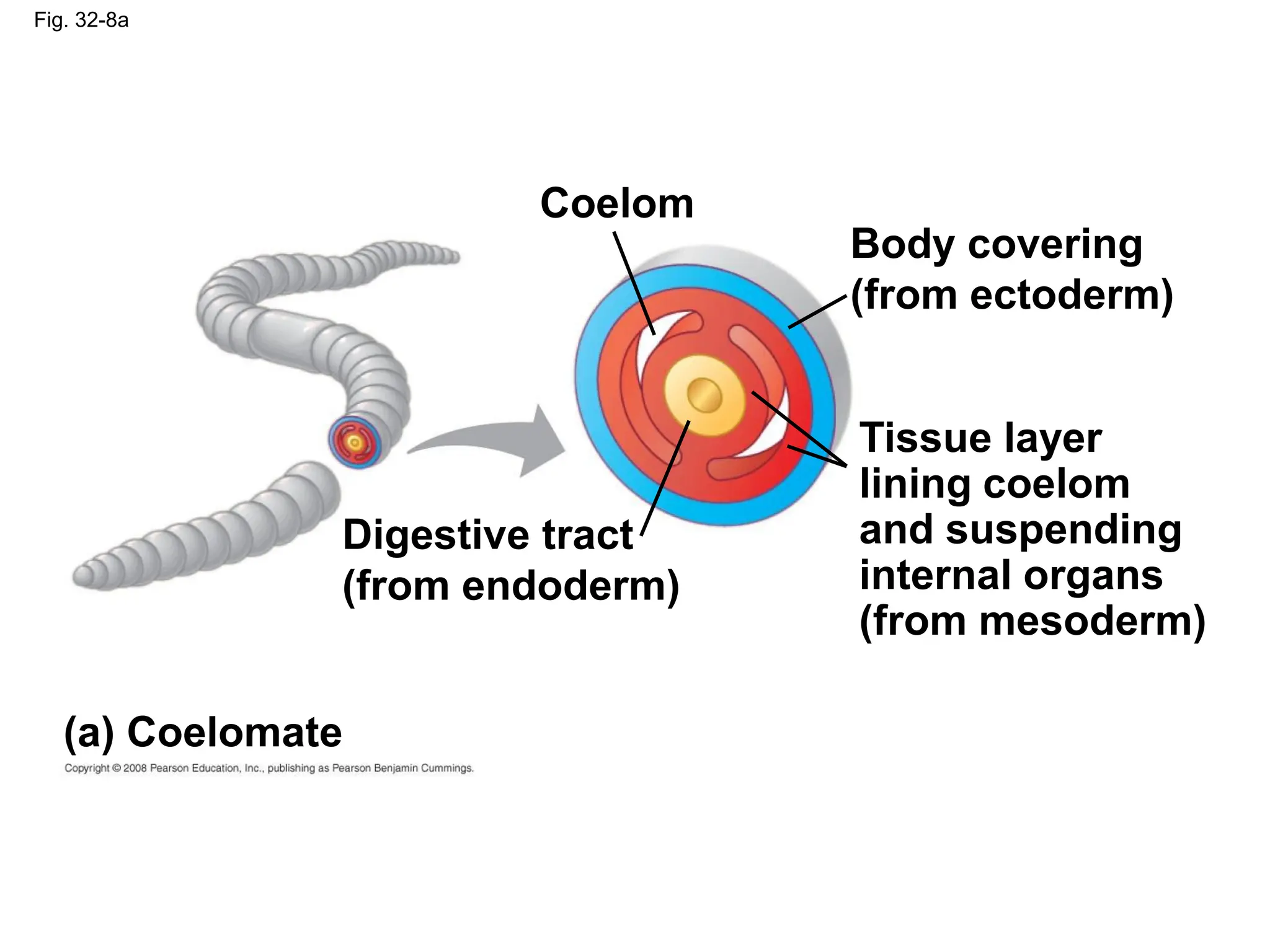
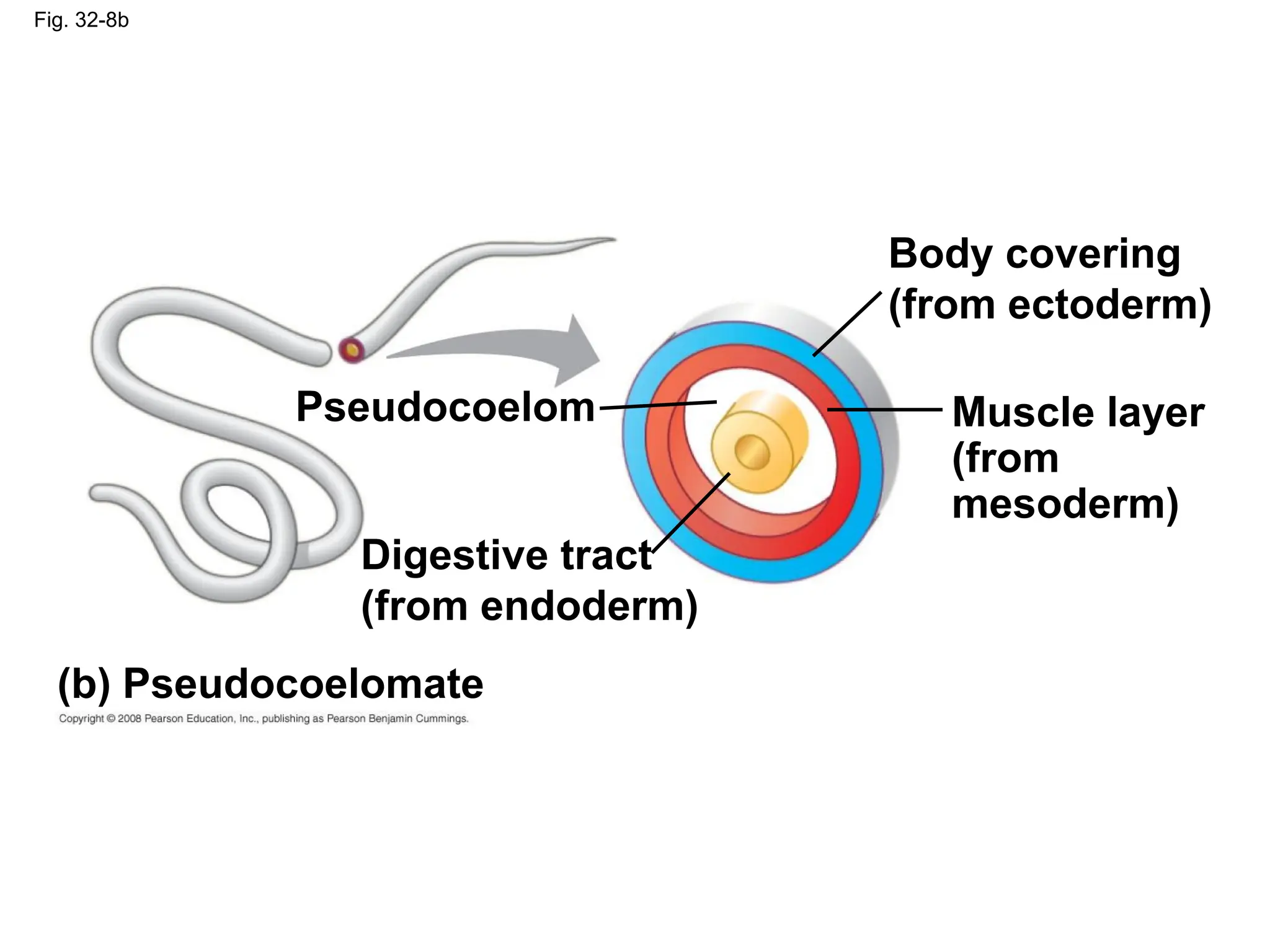
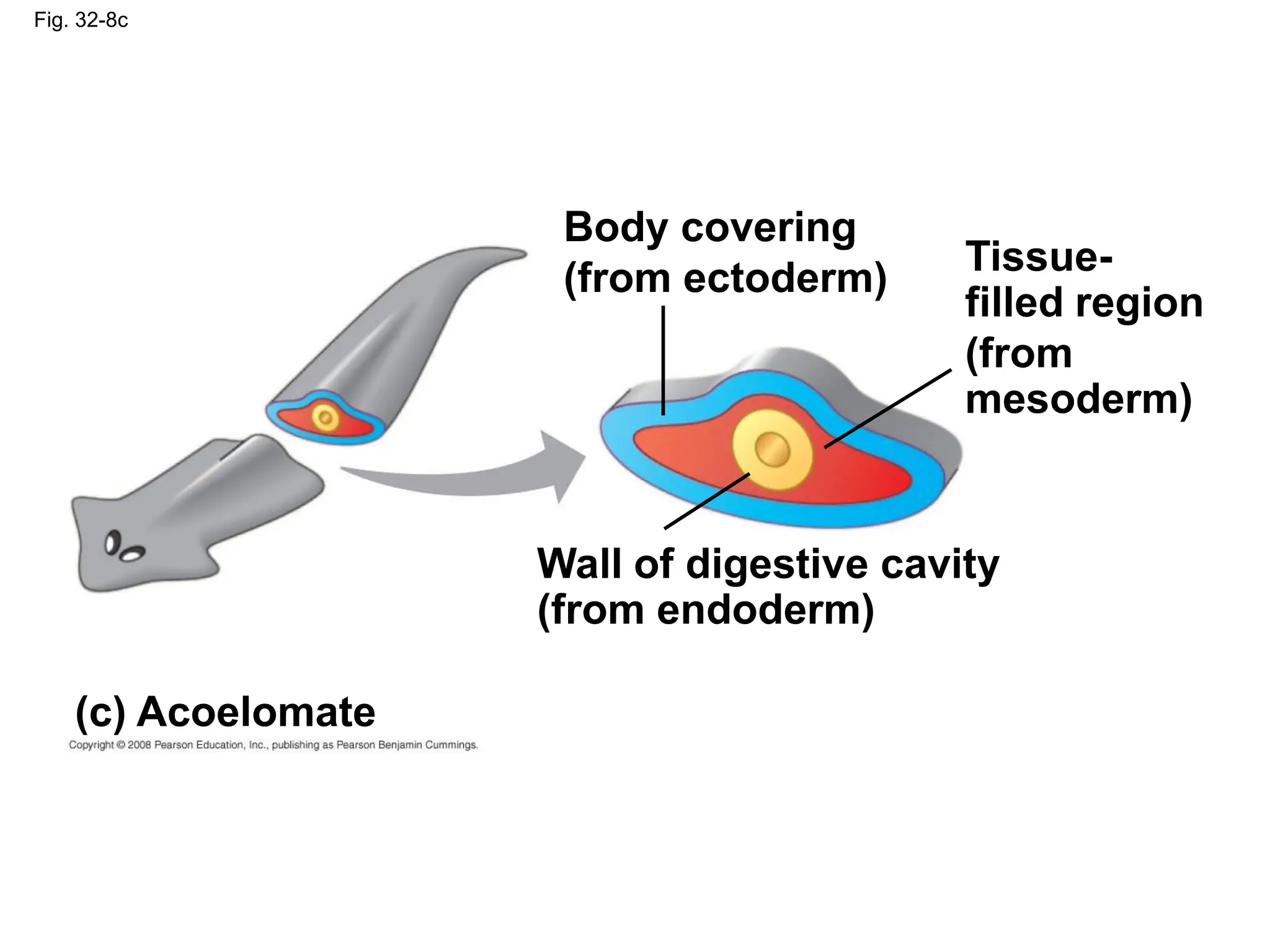
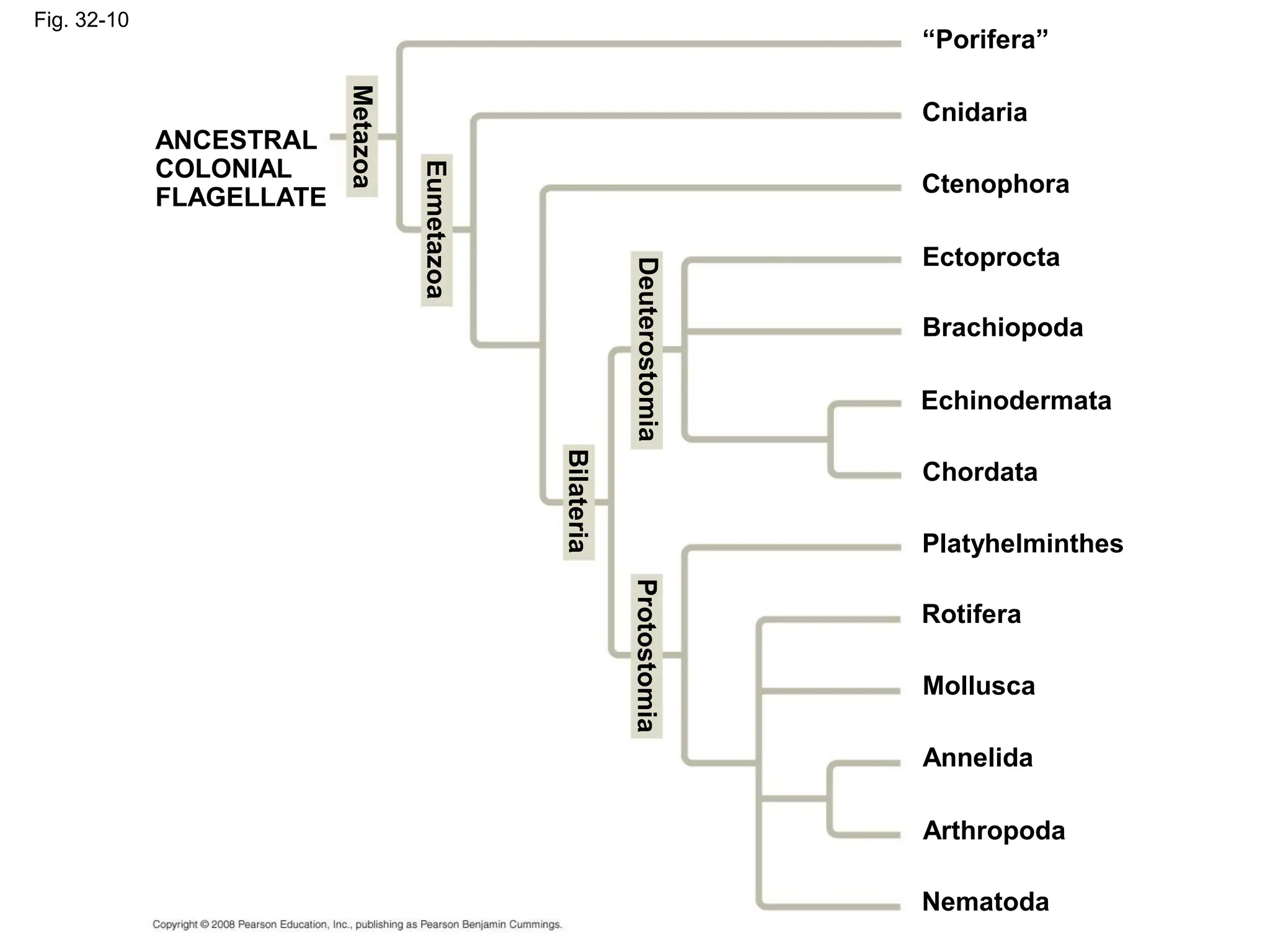
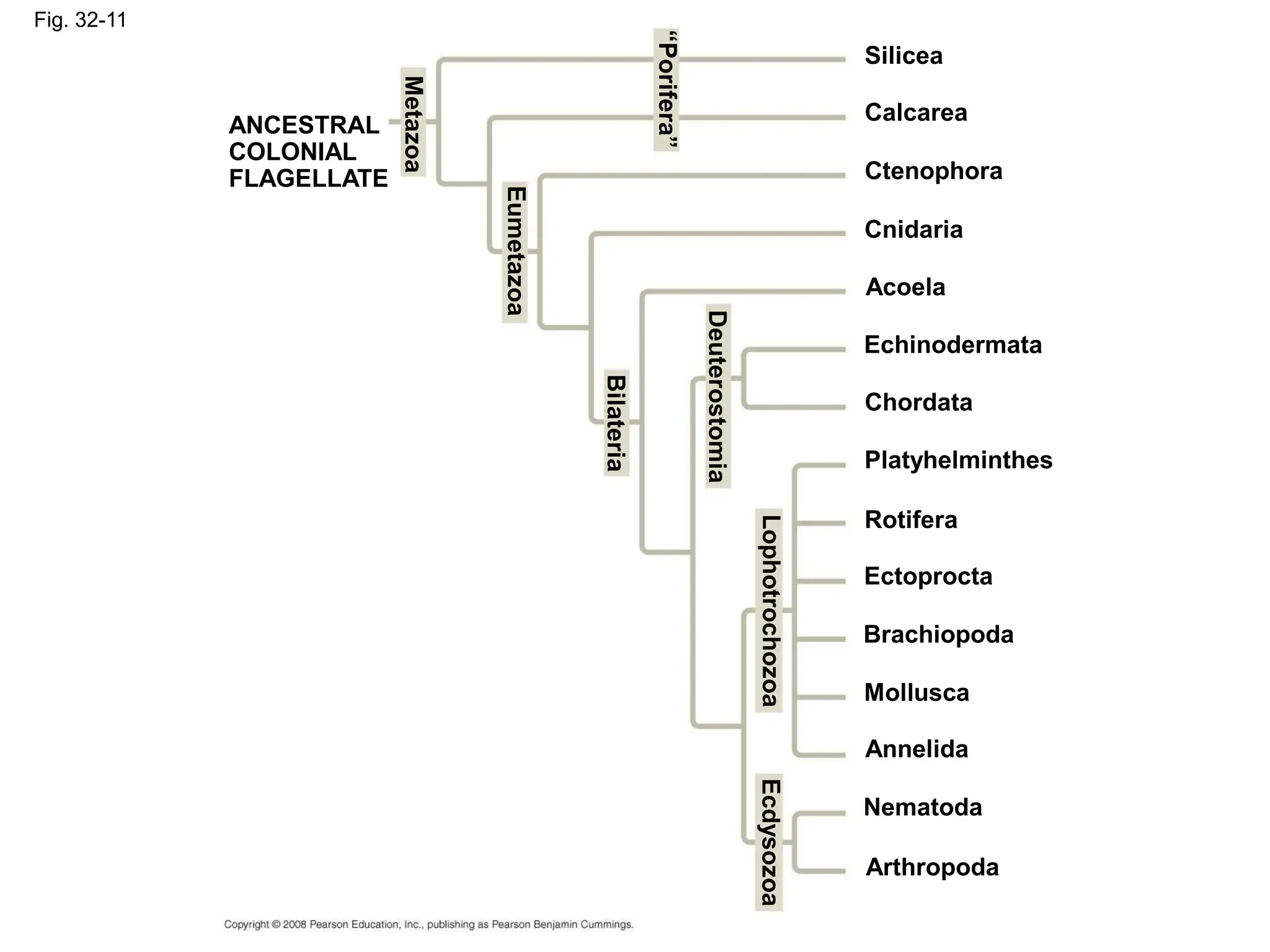
This document provides an overview of Chapter 32 from the textbook "Biology" by Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. It summarizes key concepts about the diversity of the animal kingdom, including that animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that develop from embryonic layers. It also discusses the evolutionary history of animals, major animal groups, and competing hypotheses for the phylogenetic relationships between animal phyla.