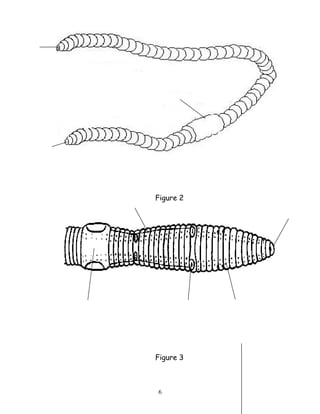
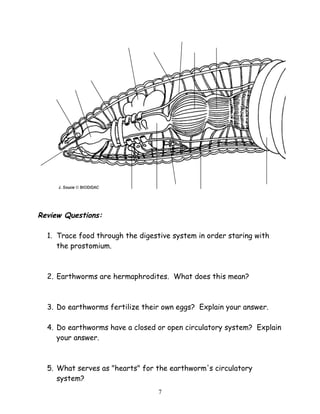
The document describes the anatomy and physiology of earthworms. It notes that earthworms are segmented invertebrates classified as annelids due to their ring-like segments. The mouth is located at the front and the anus at the rear. Earthworms have a prostomium lip to help dig, setae bristles to help move, and septa dividing walls between segments. Reproductive structures include seminal receptacles, vesicles, ovaries, and testes, and earthworms are hermaphrodites. The circulatory system has aortic arches and closed circulation within blood vessels. The digestive system includes a mouth, pharynx, esophagus, crop, gizzard,