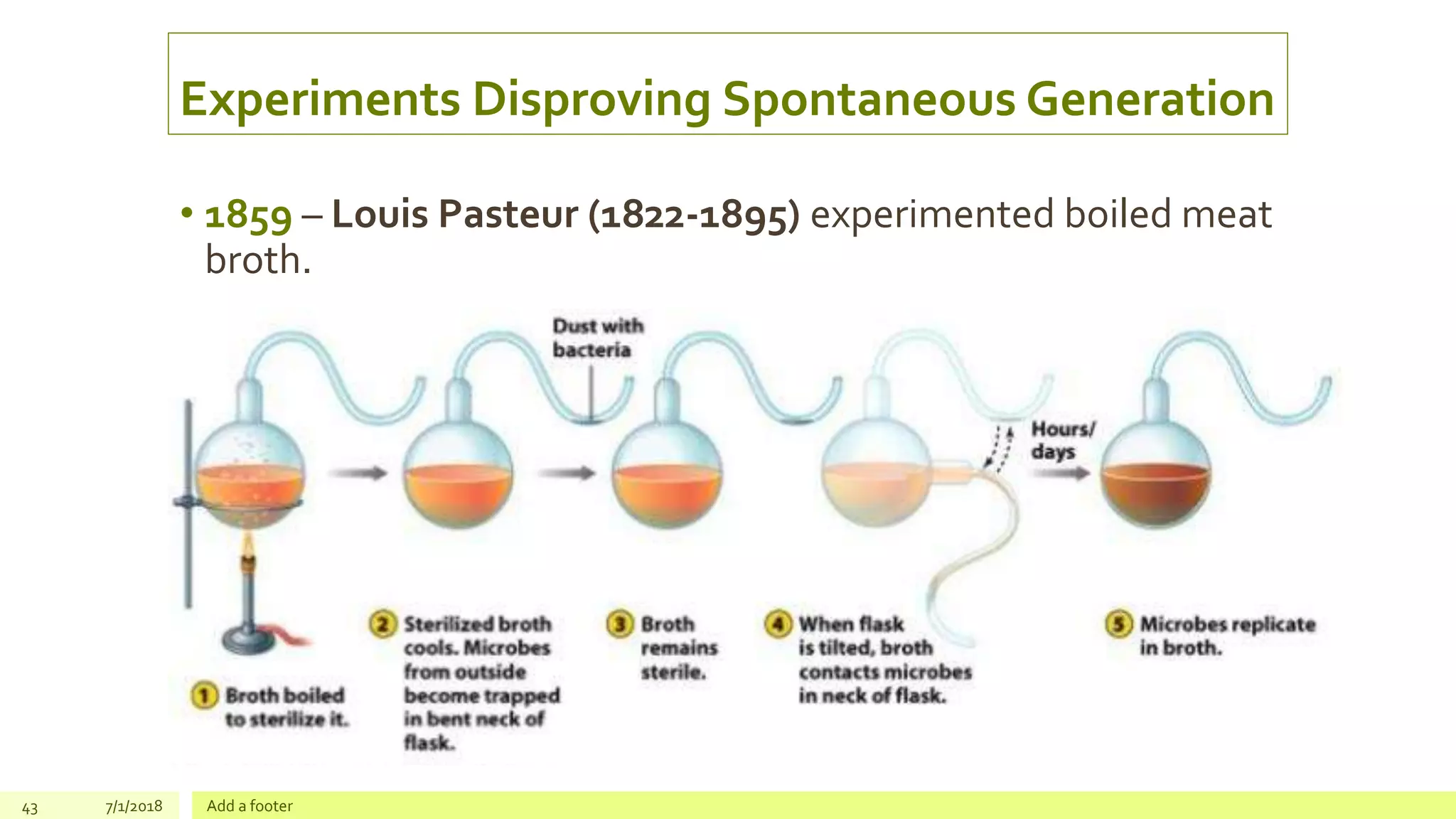
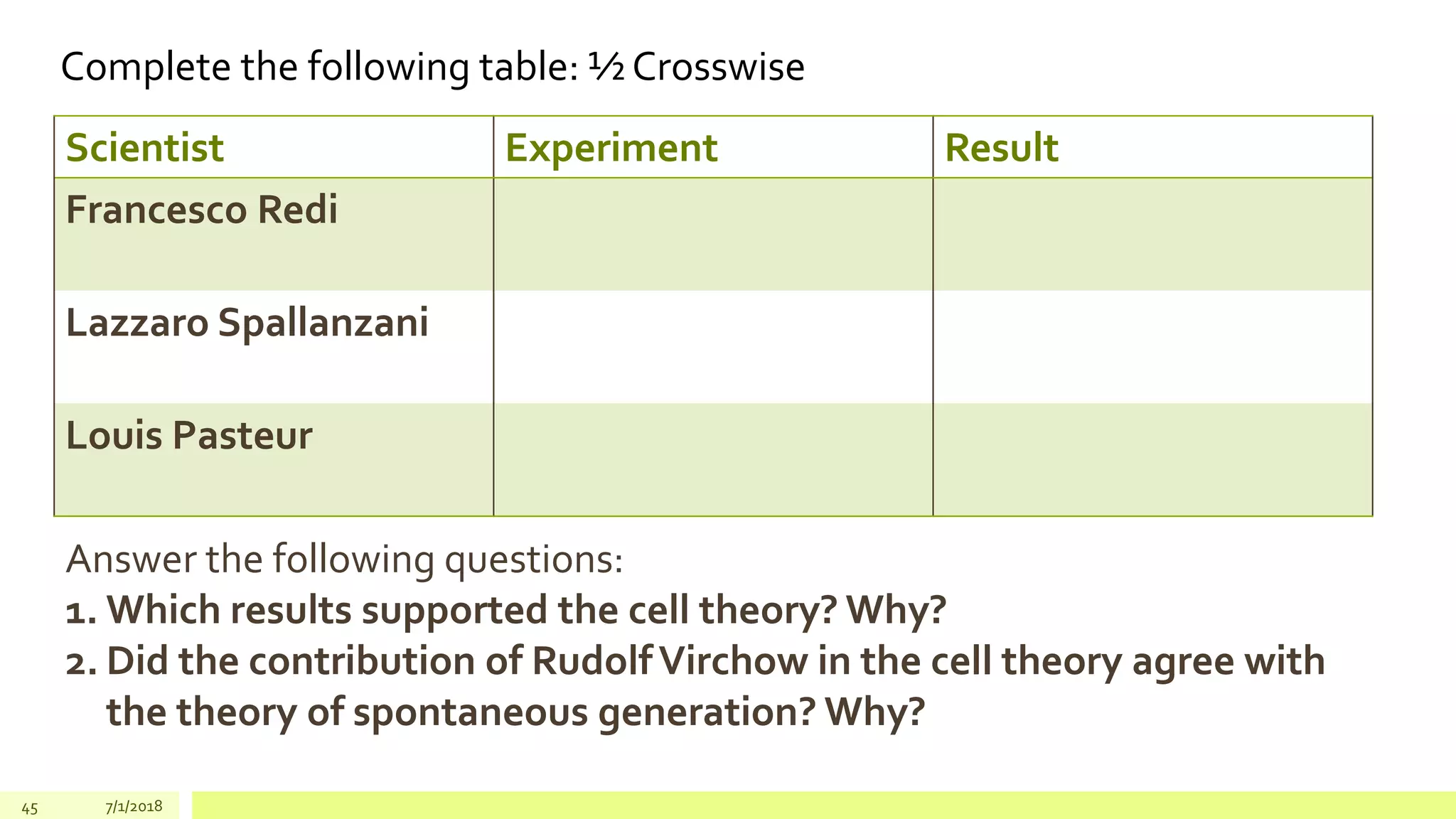
Here are the answers to your questions:
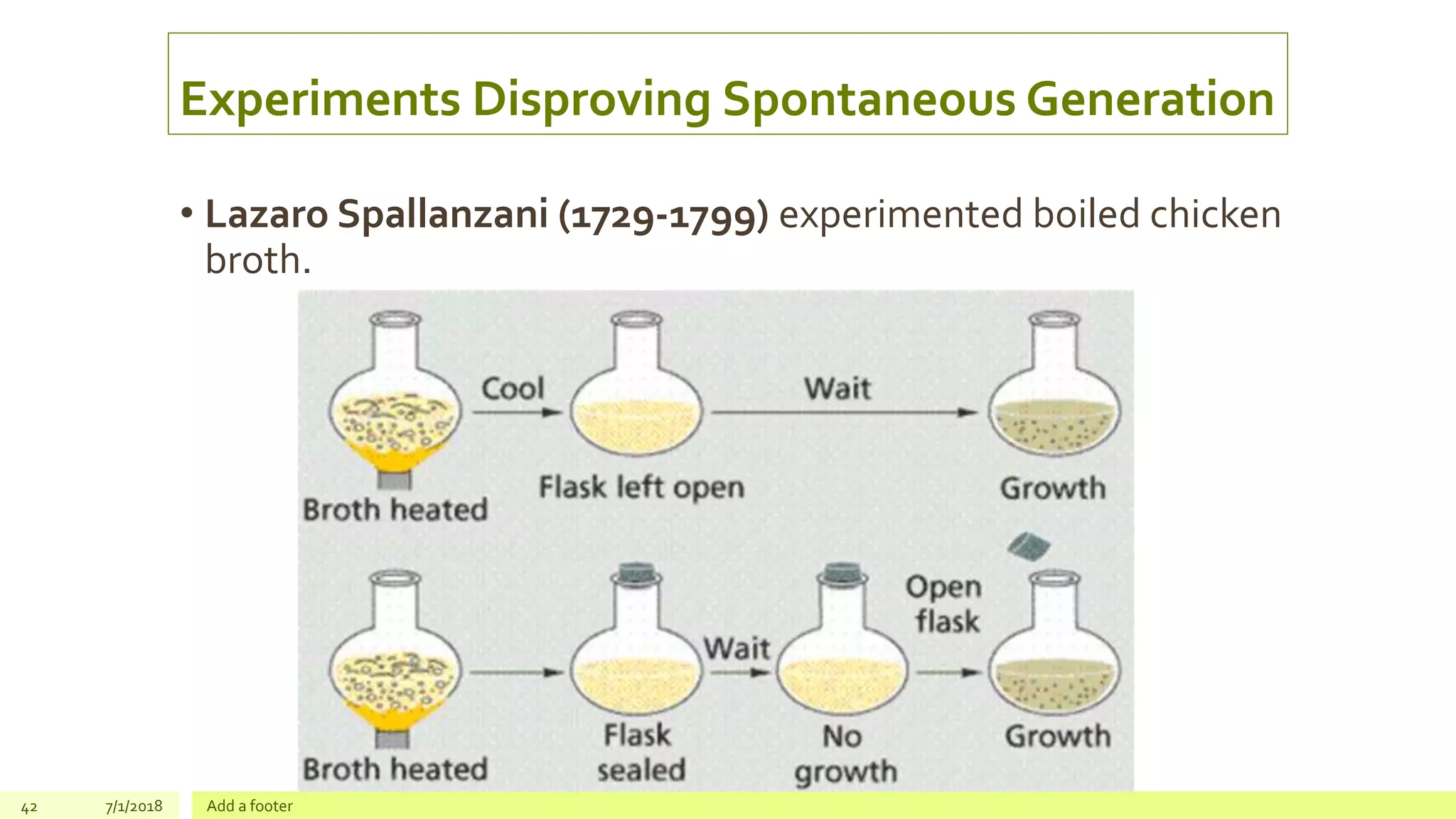
1. The results of experiments by Redi, Spallanzani and Pasteur supported the cell theory because they disproved the theory of spontaneous generation. Their experiments showed that living organisms arise only from pre-existing living organisms of the same kind, not from non-living matter. This observation agreed with the cell theory that all cells come from pre-existing cells.
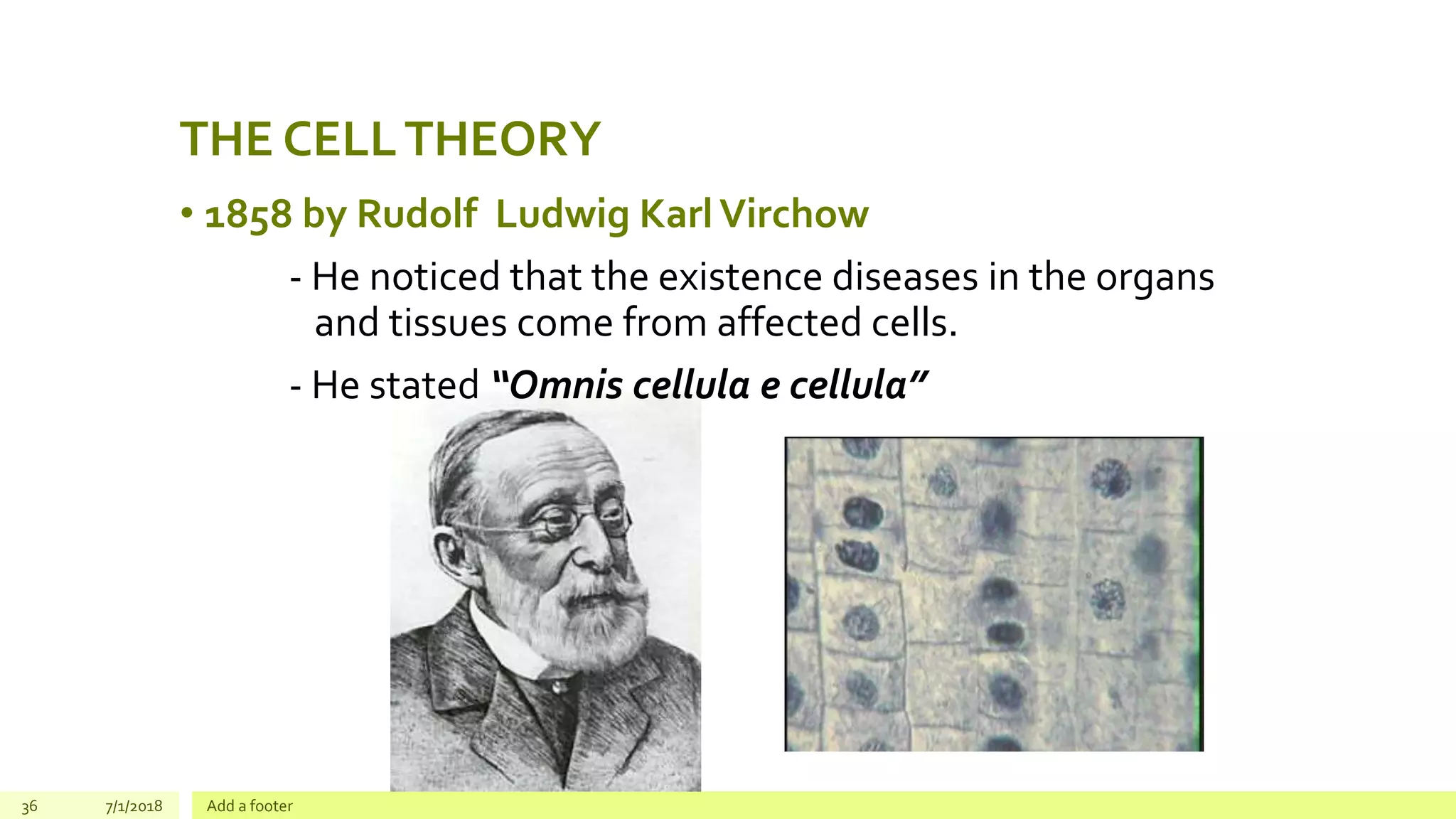
2. Rudolf Virchow's contribution to the cell theory, which stated that "all cells come from pre-existing cells", did not agree with the theory of spontaneous generation. The theory of spontaneous generation claimed that living organisms could arise from non-living matter, while Virchow's statement and the cell