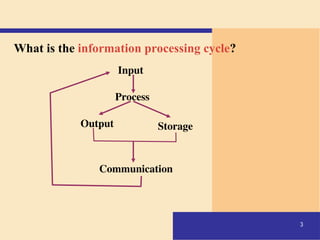
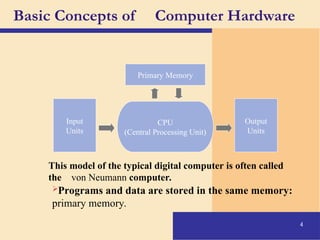
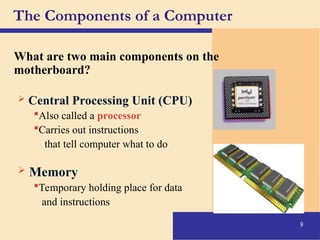
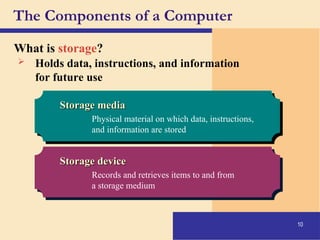
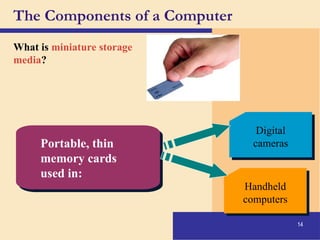
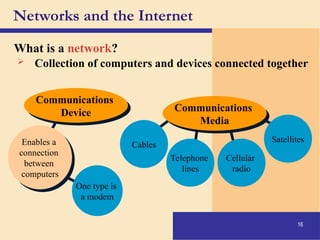
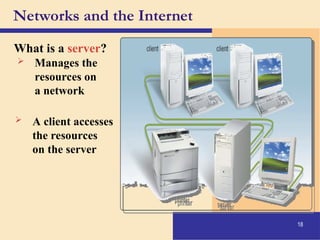
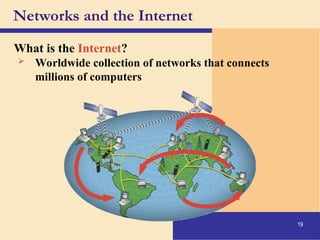
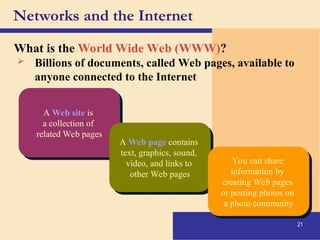
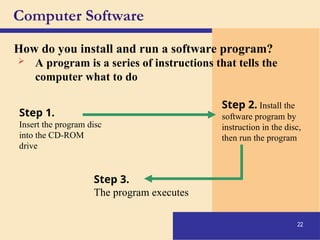
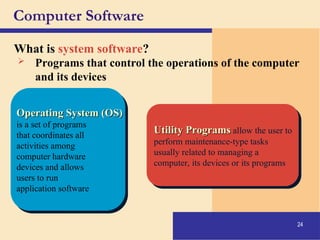
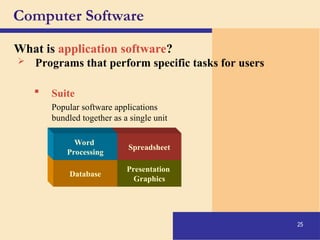
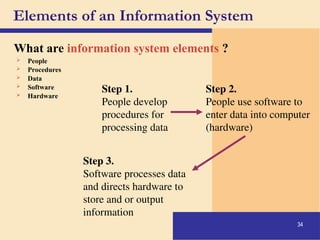
The document provides an introduction to computers, covering their definition, components, and the information processing cycle, which includes input, processing, output, storage, and communication. It details the hardware, software types, and categories of computers, along with their applications in various sectors such as education, healthcare, and finance. Networking and the internet are also discussed, emphasizing their role in resource sharing and communication.