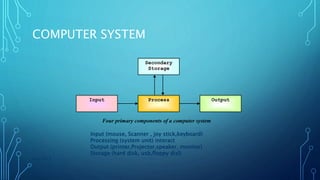
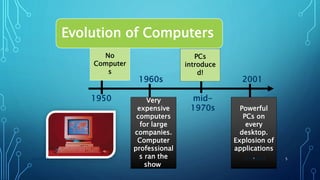
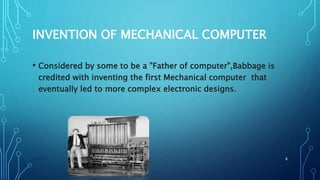
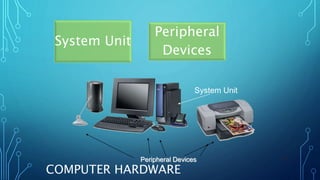
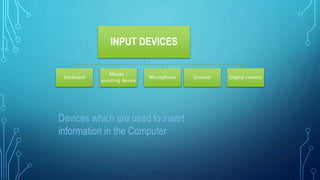
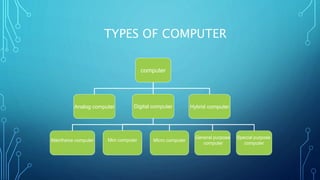
This document provides an outline for a mid-term exam course on computers. It covers the evolution of computers from the 1940s to present day, the generations of computers, computer hardware and software components, types of computers, and the importance of computers in various fields such as business, education, healthcare and more. Key topics include the invention of the earliest mechanical computers by Charles Babbage and ENIAC, the development of programming languages like BASIC, the introduction of transistors, integrated circuits and portable PCs, and the widespread use of computers in daily life today.