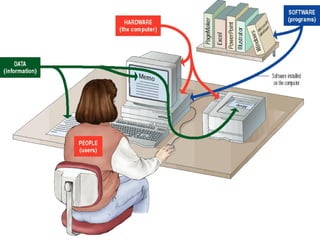
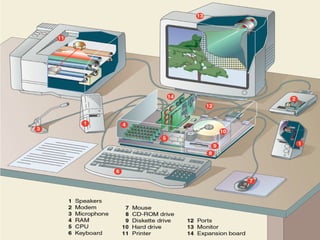
The document provides an overview of the key components of a computer system, including hardware, software, data, and users. It defines hardware as the physical parts of a computer like keyboards and monitors. Software consists of organized instructions that control the computer and enable it to perform tasks for users. Data refers to raw facts that are stored digitally and processed into useful information. Users are people who operate computers. It also describes different types of computers from supercomputers to microcomputers/personal computers.