This document provides an overview of key topics related to introduction to computers including:
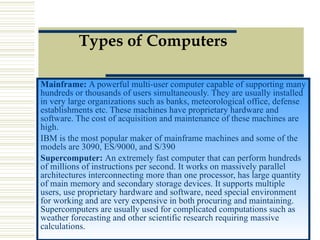
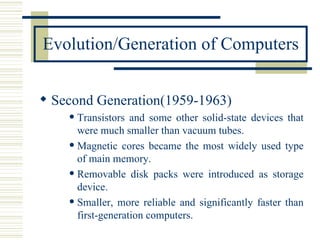
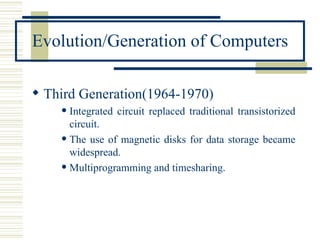
- Definitions of computer, types of computers categorized by size and power, and the evolution of computers through four generations.
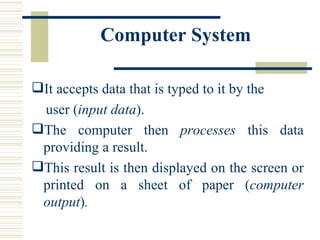
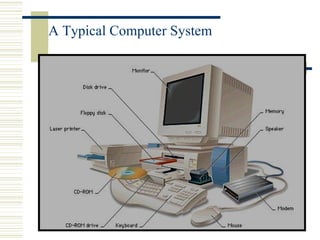
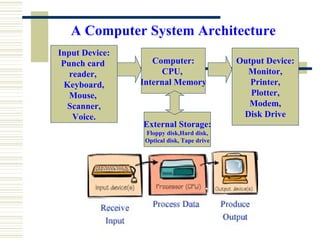
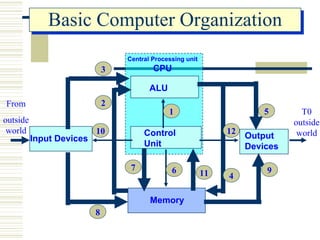
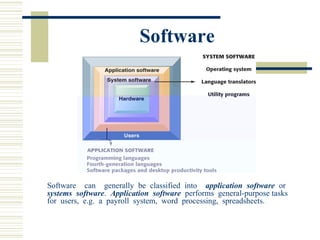
- The basic elements of a computer system including hardware, peripheral devices, and software. Hardware consists of components like the CPU and memory while software includes operating systems and application programs.
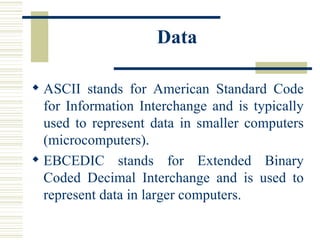
- How data is represented digitally using binary digits and coding schemes and how it is processed into meaningful information.
- Key roles in a computer system including users, professionals who design and operate systems, and end-users who utilize computers for tasks.