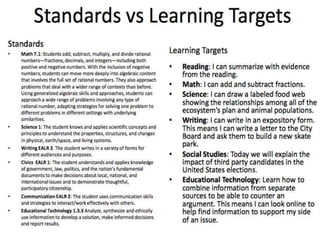
The document provides guidance on writing effective learning targets, outlining a process for teachers to 1) identify the intended learning for a lesson, 2) define the essential thinking processes, 3) design assessments of understanding, and 4) write the learning target as an "I can" statement along with what students need to understand and how they will show their understanding. Sample learning targets are provided and teachers are instructed to work with colleagues to write and provide feedback on each other's learning targets.