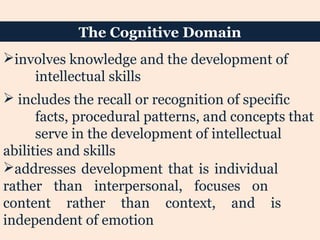
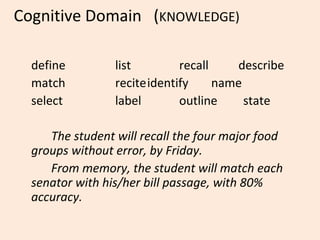
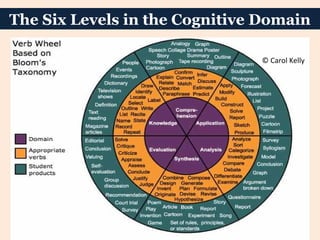
This document discusses cognitive learning targets and Bloom's Taxonomy of educational objectives. It explains that learning targets need to be clearly stated and observable. Bloom's Taxonomy outlines six levels of cognitive skills - knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation - moving from simpler to more complex thinking. Each level involves different cognitive processes and can be identified by specific verbs. The levels form a hierarchy where mastery of lower levels is required before advancing to higher levels. Examples are provided to illustrate questions and verbs associated with each cognitive skill level in Bloom's Taxonomy.