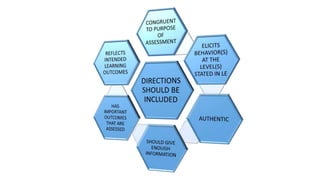
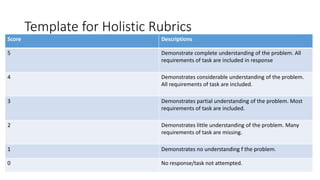
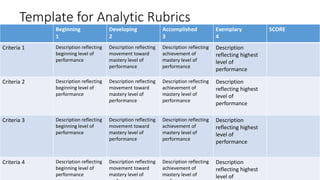
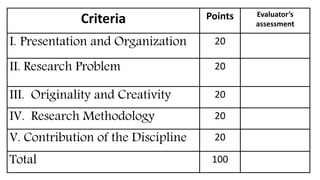
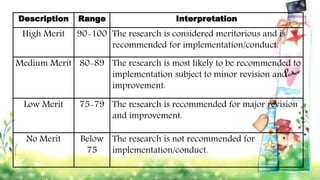
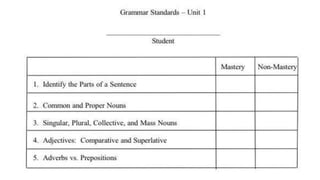
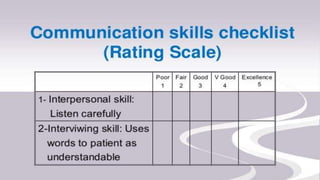
This document discusses performance-based assessment. It defines performance-based assessment as a direct and systematic observation of student performance based on predetermined criteria. This is presented as an alternative form of assessment to traditional paper-and-pencil tests. The document outlines key features of performance-based assessment, including greater realism and complexity of tasks, as well as greater time needed for assessment and use of judgment in scoring. It also discusses different types of performance-based assessment, developing rubrics to evaluate student performance, and the advantages and limitations of this assessment approach.