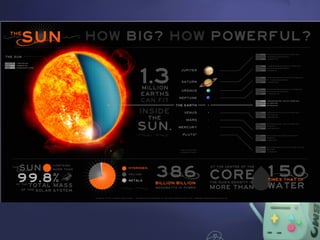
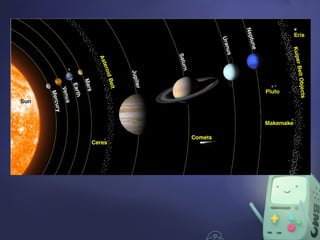
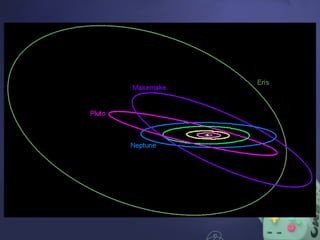
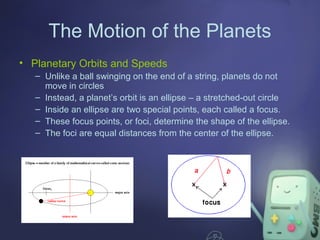
The document describes the structures of the solar system, including the sun, planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. It emphasizes the sun as the largest object, the classification of planets into inner and outer categories, and the definition of dwarf planets. It also covers concepts such as orbits, revolution, and the use of astronomical units for measuring distances in space.