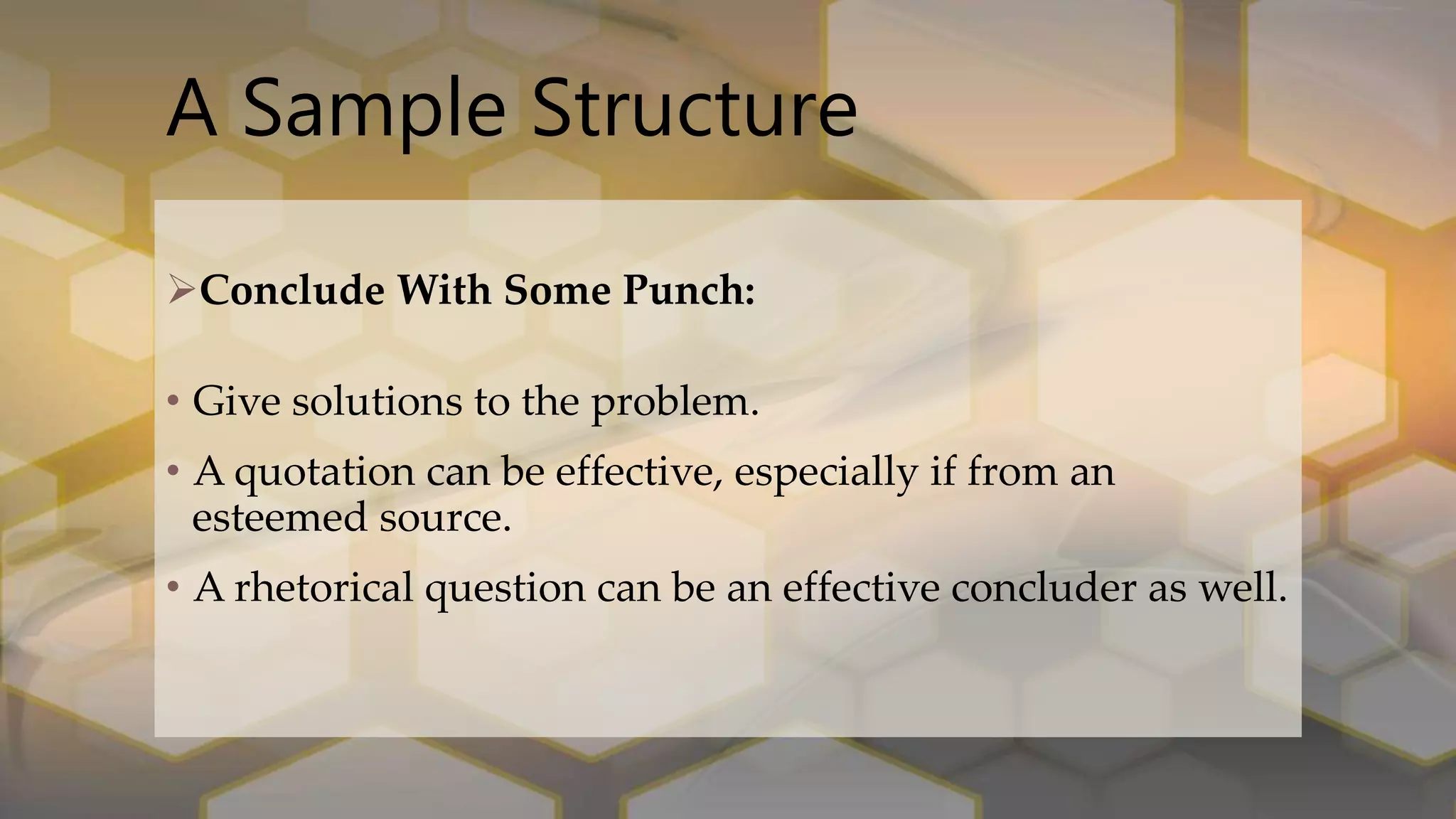
The document discusses the definition, structure, and types of editorials, emphasizing their role as analytical essays expressing editorial opinions on pertinent societal issues. It outlines a standard structure for writing editorials, which includes an introduction, opposing viewpoints, refutation, reasoning, and a strong conclusion. Additionally, it categorizes editorials into style and subject divisions, detailing various types such as serious, informative, persuasive, and those focused on political, social, or economic themes.