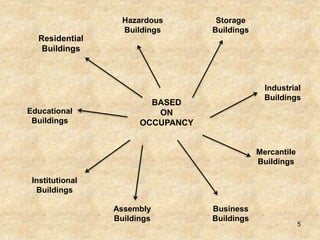
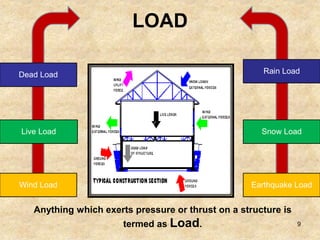
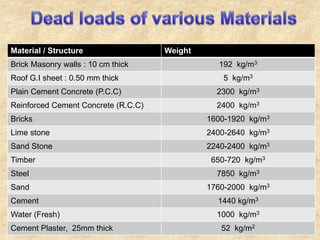
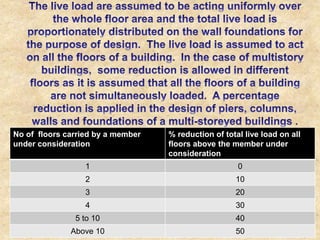
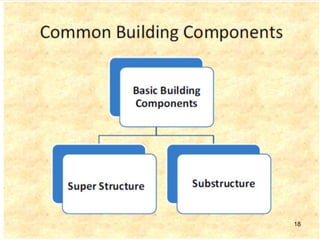
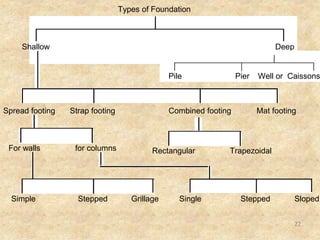
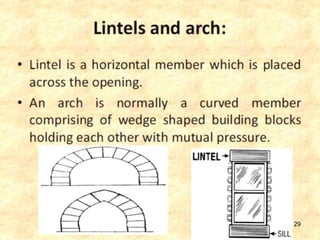
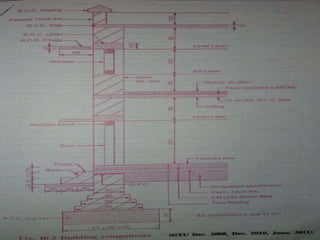
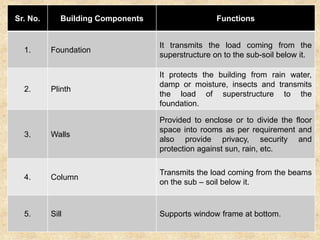
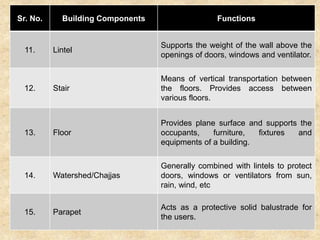
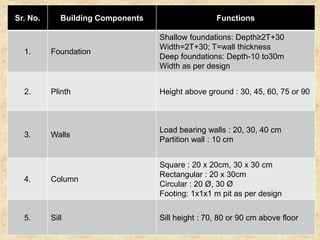
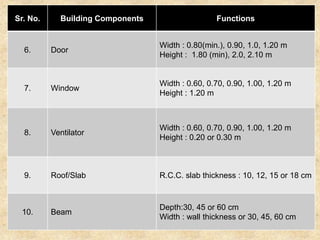
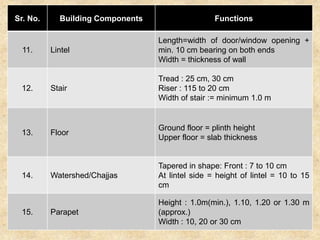
The document discusses the history and evolution of building construction from primitive human shelters like caves to modern buildings. It then categorizes buildings based on occupancy into residential, educational, institutional, assembly, business, mercantile, industrial and storage buildings. Various loads that act on buildings like dead load, live load, snow load, rain load, wind load and earthquake load are explained. Common building materials and their weights are listed. Foundations, doors, windows and other typical building components and their functions are described along with their standard dimensions.