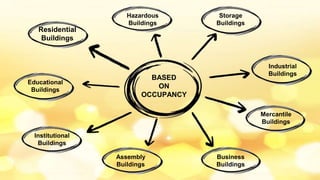
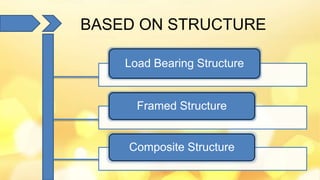
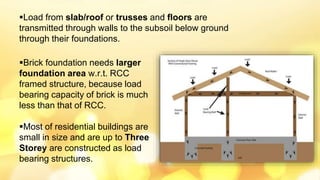
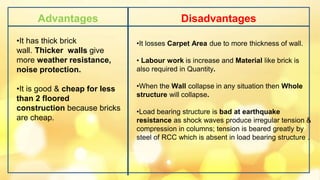
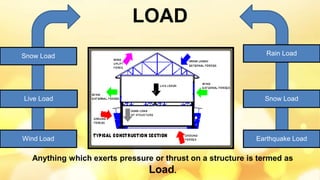
This document provides information about building construction components and their functions. It discusses the classification of buildings based on occupancy and structure, including residential, educational, and industrial buildings. It also describes the different types of building loads like dead, live, wind, and earthquake loads. The key building components are foundations and superstructure. Foundations can be shallow like spread footings or deep like pile foundations, and transfer load from the superstructure to the soil.