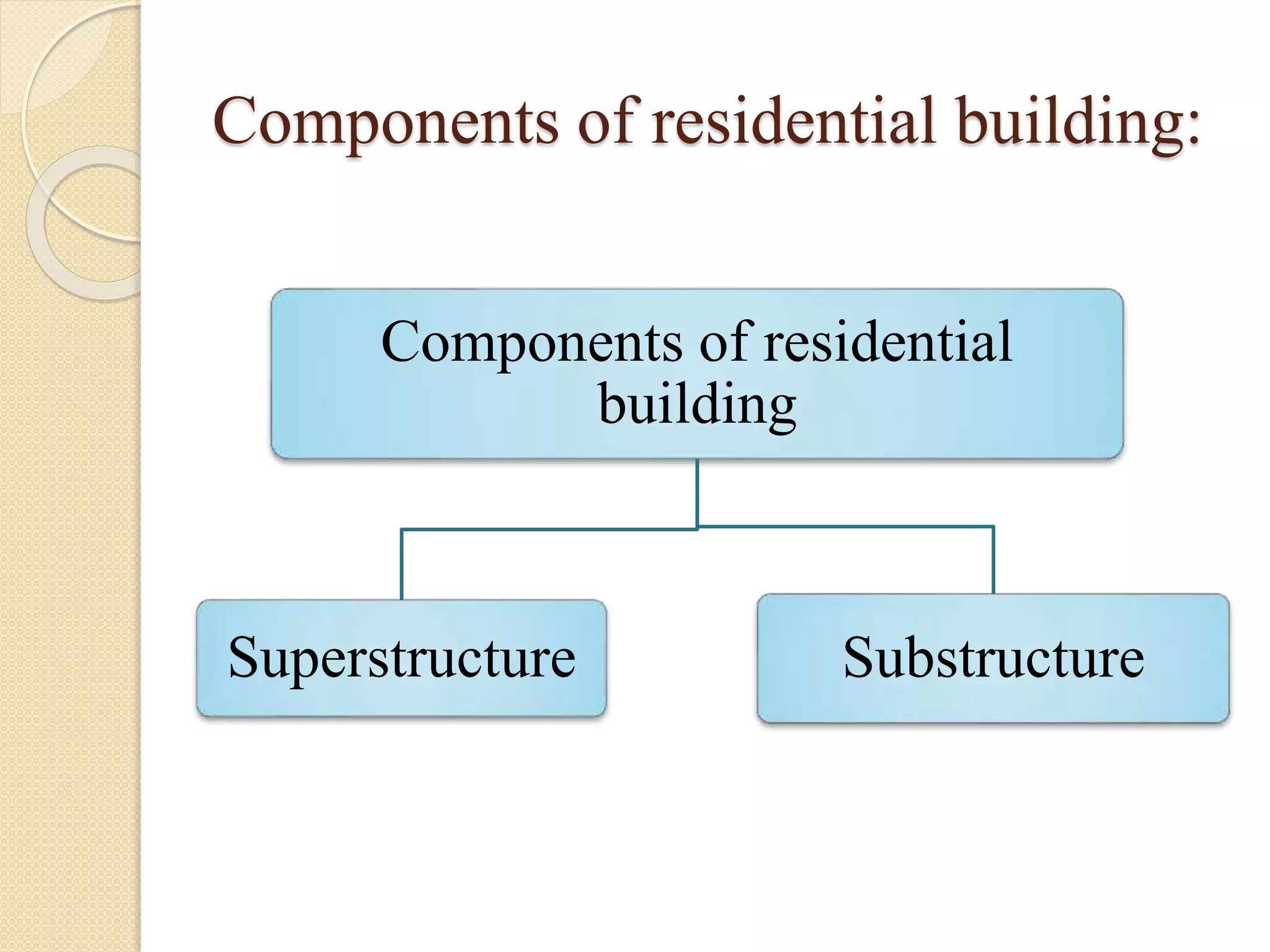
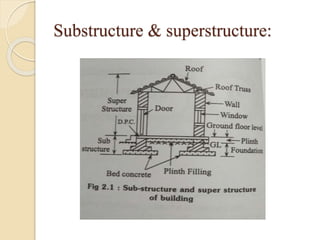
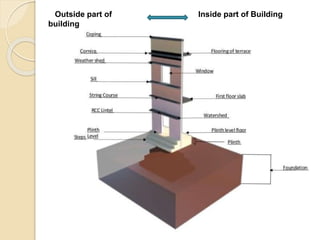
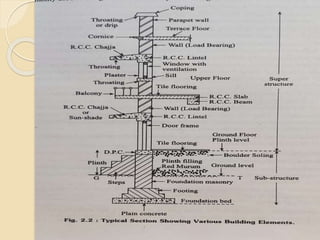
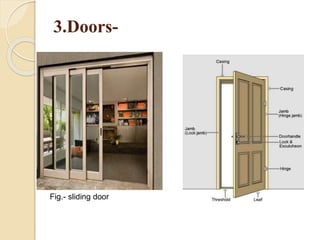
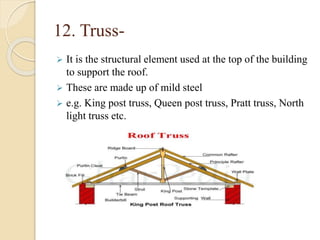
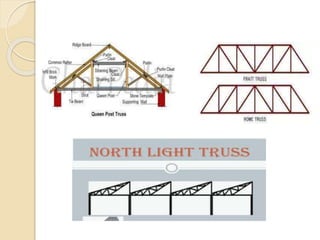
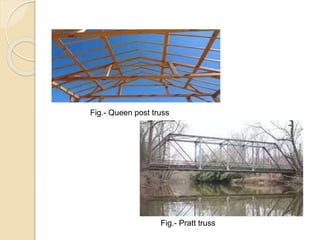
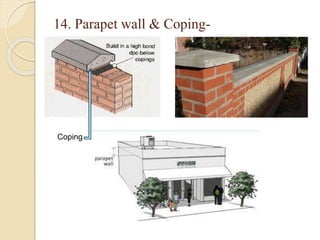
The document discusses the key components of residential buildings. It describes the substructure, which includes the foundation, plinth, and damp proof course below ground level. The superstructure above ground includes load-bearing and non-load bearing walls, pillars, doors, windows, floors, ceilings, beams, slabs, trusses, and roofs. Specific materials and functions are provided for each component.