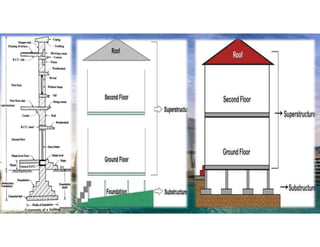
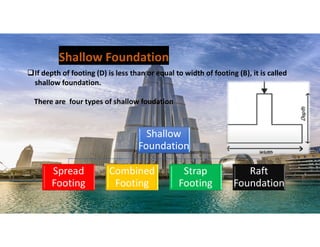
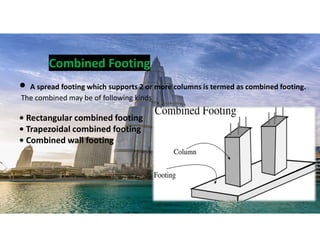
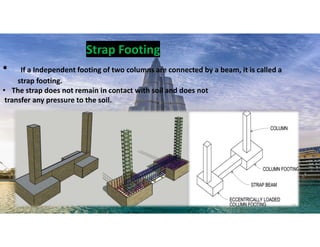
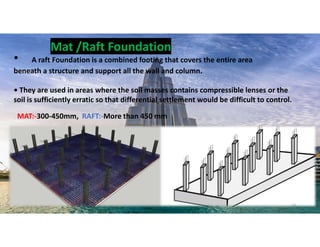
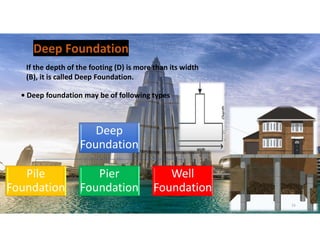
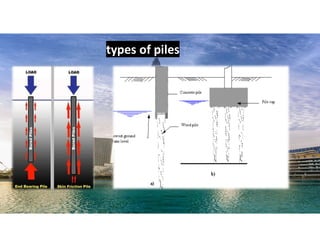
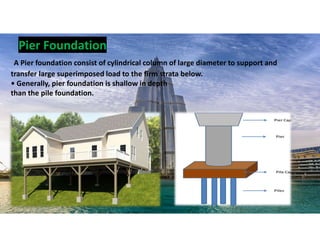
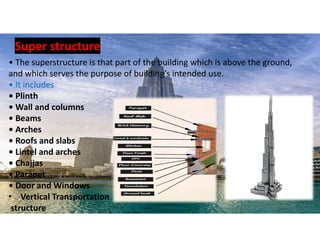
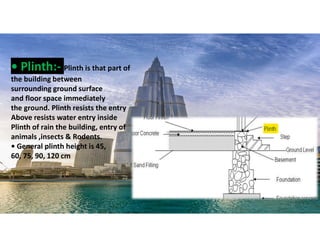
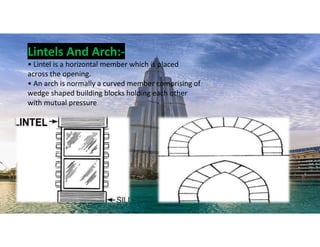
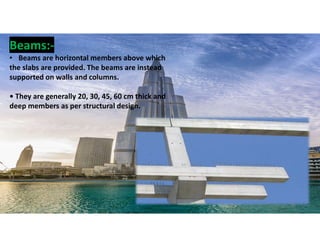
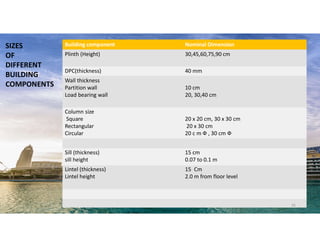
The document outlines the essential components and types of building structures according to the National Building Code 2016, including definitions and classifications of residential, educational, and industrial buildings. It describes the substructure and superstructure, detailing various types of foundations, walls, columns, and other structural elements. Additionally, it provides specific measurements for different building components and emphasizes the importance of building finishes.