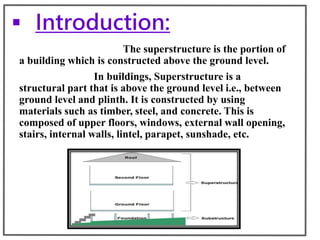
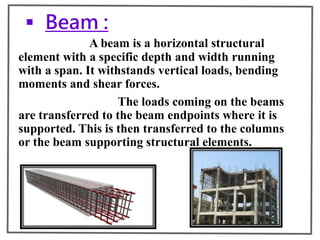
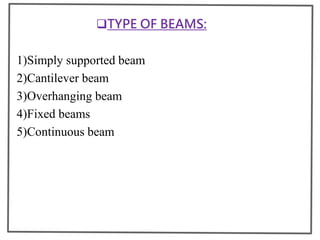
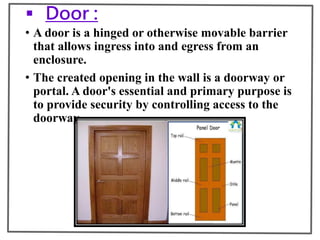
The superstructure is the part of a building above the ground level and includes floors, walls, beams, columns, slabs, stairs, doors, windows and other structural elements. It transfers loads from these elements to the foundation below. The document then describes the common components of a superstructure like slabs, beams, columns, walls, floors, stairs, doors and windows along with their types and functions.