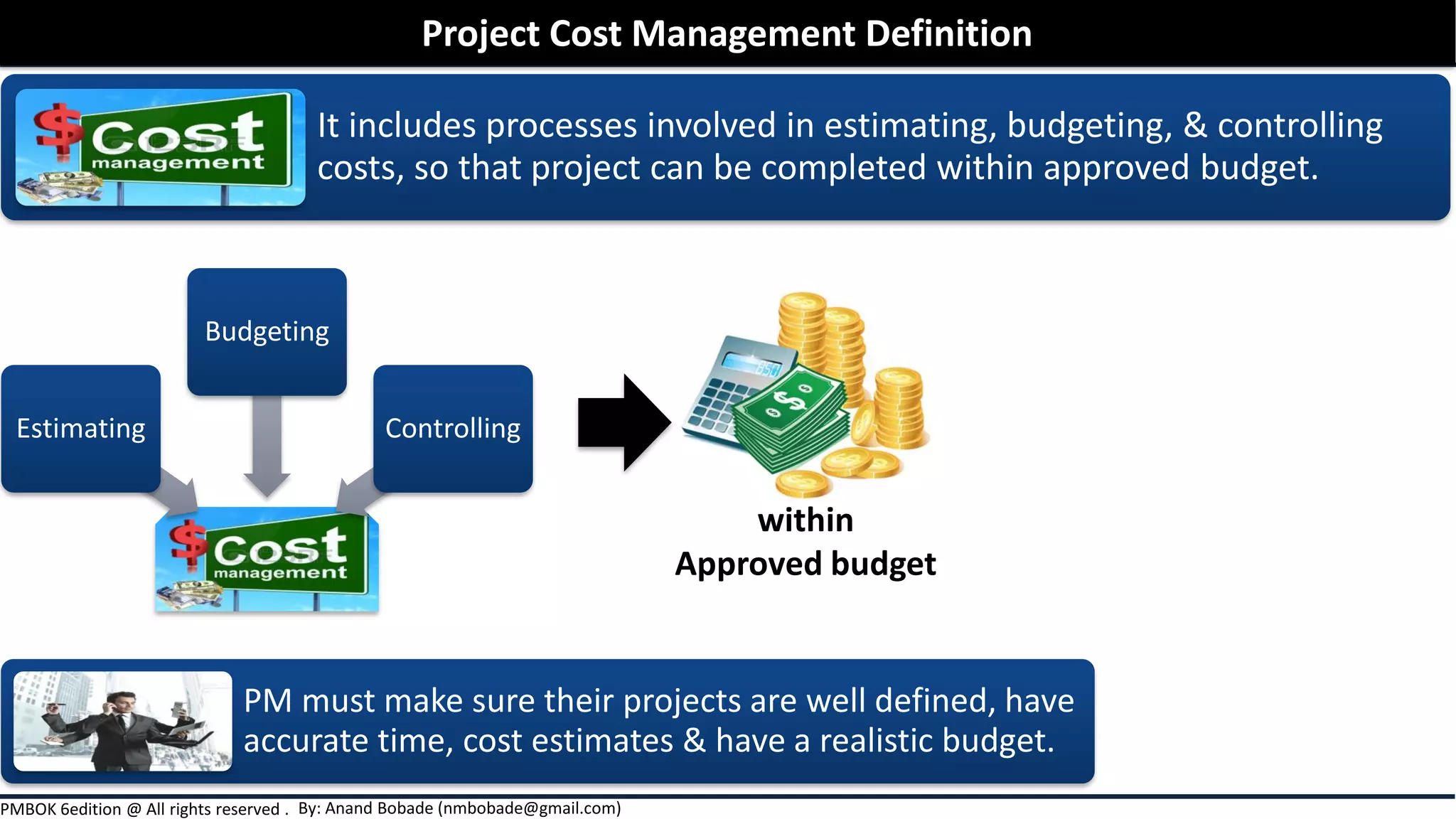
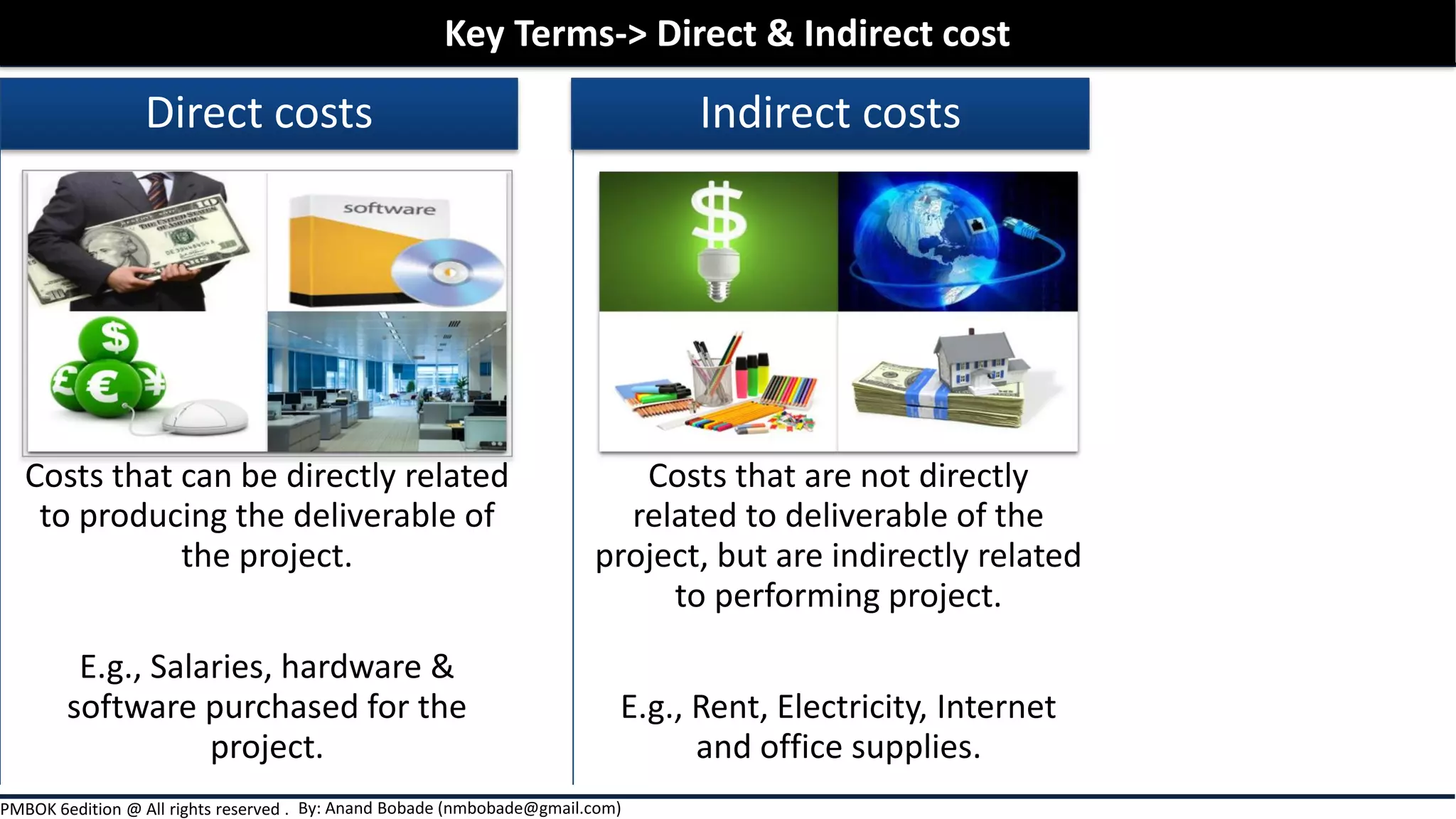
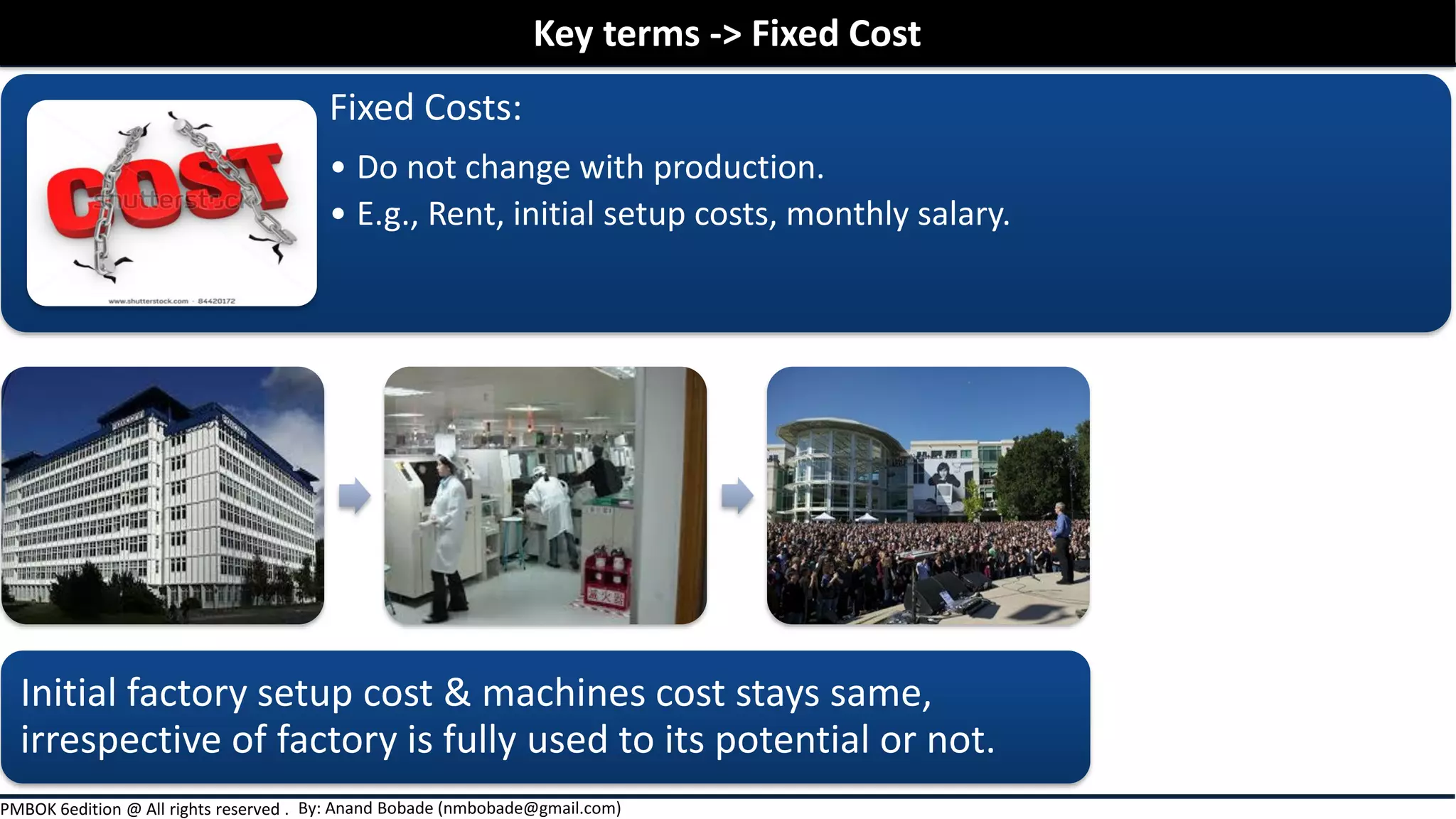
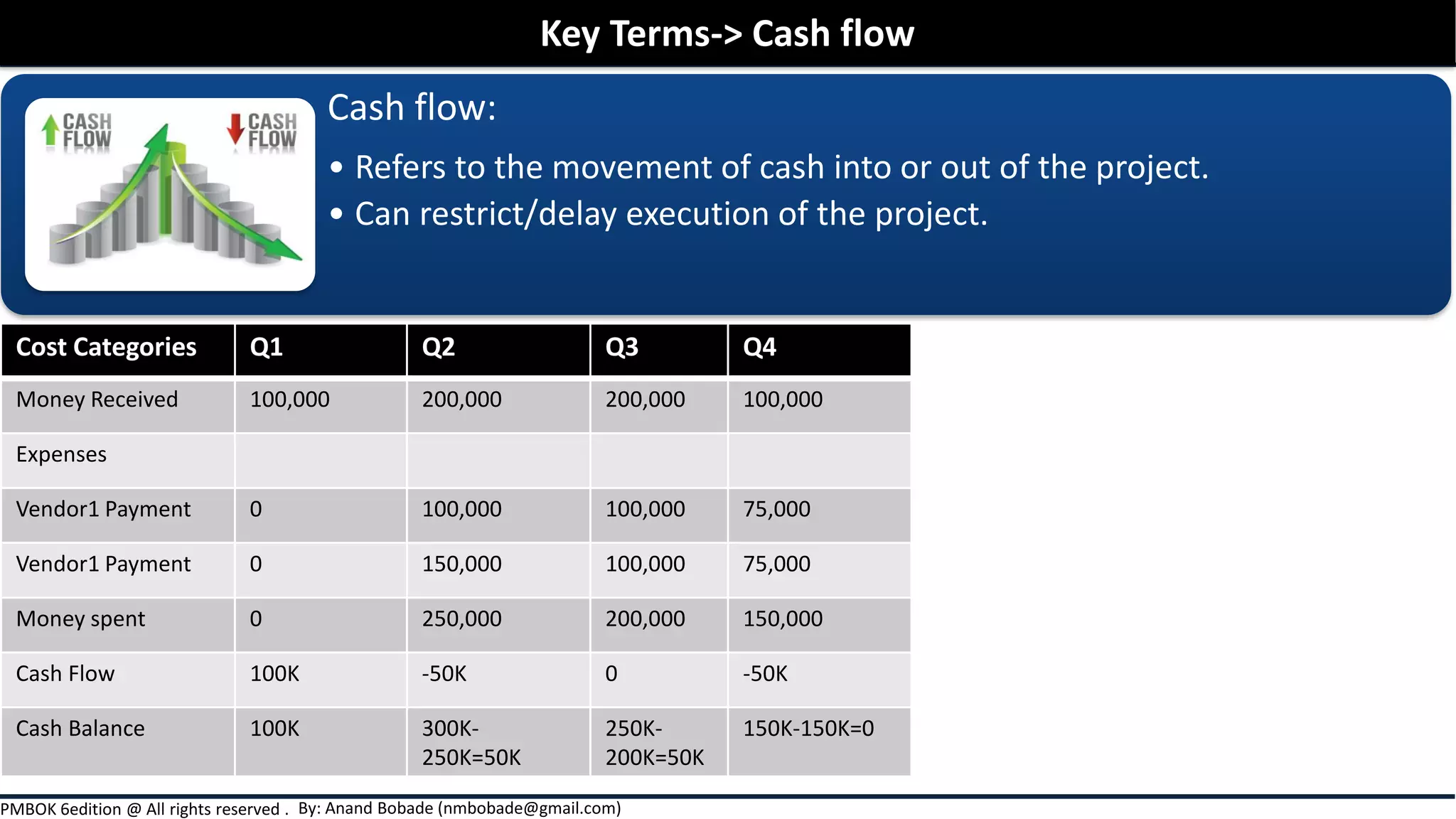
The document outlines project cost management processes, including planning, budgeting, and controlling costs to ensure projects remain within approved budgets. It discusses key concepts such as earned value management, direct and indirect costs, fixed and variable costs, and opportunity costs. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accurate estimates and financial management to successfully complete projects.