Embed presentation
Download to read offline


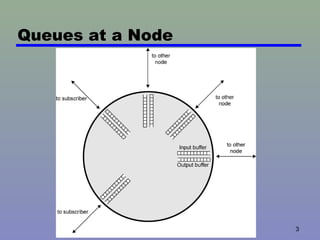
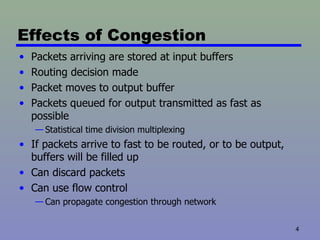

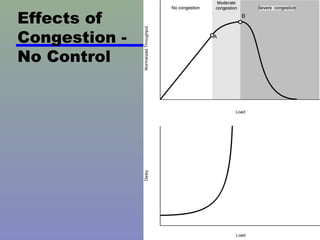


Congestion occurs when the number of packets being transmitted through a network approaches the packet handling capacity, which can cause performance to fall dramatically. Networks are composed of queues at nodes where packets are stored before being routed and transmitted. If packets arrive faster than they can be routed and transmitted, the buffers will fill up, which can cause packets to be discarded. Congestion control aims to keep the number of packets below this critical level through techniques like flow control and propagating congestion information through the network.






