This document discusses file handling functions in C including:
- fopen() to open a file
- fclose() to close a file
- The FILE data type which is a pointer to a structure containing file status information
- Mode strings used in fopen() to specify read/write access and text/binary format
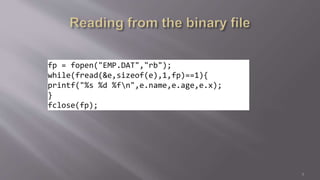
- Examples using fopen(), fwrite(), fread(), fclose() to write structured data to a binary file and read it back



![struct rna{
char name[20];
int age;
float x;
};
struct rna e;
fp = fopen("EMP.DAT","wb");
if(fp == NULL){
puts("Cannot open file");
}
printf("Enter name, age and basic salary");
scanf("%s%d%f",e.name,&e.age,&e.x);
fwrite(&e,sizeof(e),1,fp);
fclose(fp); 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileprocessingdetails-160827193940/85/File-in-C-programming-4-320.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
FILE *fp;
struct rna{
char name[40];
int age;
float x;
};
struct rna e;
fp = fopen("employ.dat","w");
if(fp == NULL){ //if file is not opened
puts("Cannot open file");
exit(1);
}
printf("nEnter name, age and basic salary: ");
scanf("%s %d %f", e.name, &e.age, &e.bs);
//writes name age and basic salary to the file
fprintf(fp, "%s %d %fn", e.name, e.age, e.x);
fclose(fp); //close the file
return 0;
} 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileprocessingdetails-160827193940/85/File-in-C-programming-6-320.jpg)
