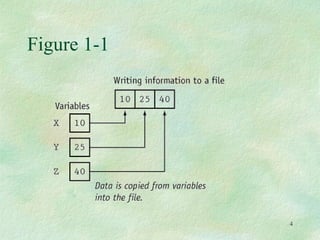
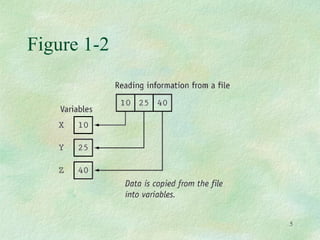
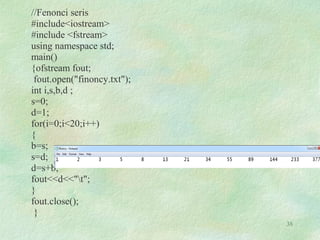
Basic file operations in C++ involve opening, reading from, and writing to files. The key classes for input/output with files are ofstream for writing, ifstream for reading, and fstream for both reading and writing. A file must first be opened before performing any operations on it. Common operations include writing data to files with put() or write(), reading data from files with get() or read(), and closing files after completion. Proper opening modes and error handling should be used to ensure successful file input/output.

























![#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ char FirstName[30], LastName[30];
int Age;
char FileName[20];
cout << "Enter First Name: ";
cin >> FirstName;
cout << "Enter Last Name: ";
cin >> LastName;
cout << "Enter Age: ";
cin >> Age;
cout << "nEnter the name of the file you want to create:. .txt ";
cin >> FileName;
ofstream Students(FileName, ios::out);
Students << FirstName << "n" << LastName << "n" << Age;
cout << "nn";
return 0;
}
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-29-320.jpg)










![Read from file
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ char array [80];
ifstream fin;
fin.open("firstExa.txt");
while(!fin.eof())
{fin.getline(array,80);
cout<<array<<endl;}
fin.close();
}
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-41-320.jpg)

![Binary form
#include<iostream.h>
#include <fstream.h>
main()
{ int Array[80],i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
cin>> Array[i];
ofstream fout;
fout.open("D:ahmed.bin",ios::binary);
fout .write((char *) & Array , sizeof(Array));
fout.close();
system("pause");
}
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-43-320.jpg)


![Using fout
Slide 6- 46
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main (int aaa,char *avg[])
{
ofstream fout ("my_out.txt");
fout<<" Assalamualikom Hope fine" << endl;
fout<<"Please tray good in second exam this frist file " << endl;
return 0;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-46-320.jpg)







![Basic file operations
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main (int argc, char *arvg[ ])
{
ofstream fout("XXX.txt");
fout << "**Writing this to a file.n";
fout << "****Writing this to a file.n";
fout << "*********Writing this to a file.n";
system("PAUSE");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-54-320.jpg)

![// reading a text file
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main () {
char buffer[256];
ifstream examplefile ("kk.txt");
if (! examplefile.is_open())
{ cout << "Error opening file"; exit (1); }
while (! examplefile.eof() )
{
examplefile.getline (buffer,100);
cout << buffer << endl;
}
return 0;
} 56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fileincpp2016-161108102642/85/File-in-cpp-2016-56-320.jpg)
